In the captivating world of avian companionship, lovebirds and budgies stand as popular choices, each bringing their distinct charm and qualities. Lovebirds enchant with their vivid colors and strong emotional bonds, while budgies captivate with their sociable nature and playful demeanor.
As potential pet owners navigate the decision between these two delightful species, understanding the nuances of their characteristics becomes paramount.
This exploration delves into the lesser-discussed differentiating factors between lovebirds and budgies, shedding light on their breeding behavior, grooming habits, playfulness, mating displays, and availability.
Through this knowledge, prospective bird enthusiasts can make an informed choice that aligns with their preferences and lifestyle.
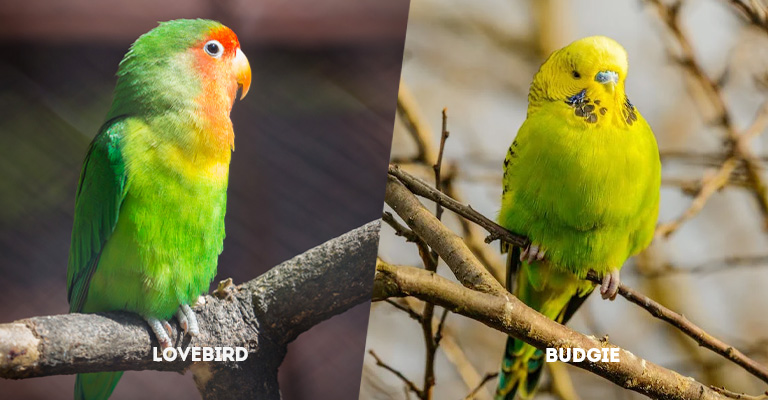

Key Differences Between Lovebirds and Budgies
Here are some key differences between the two:
Appearance
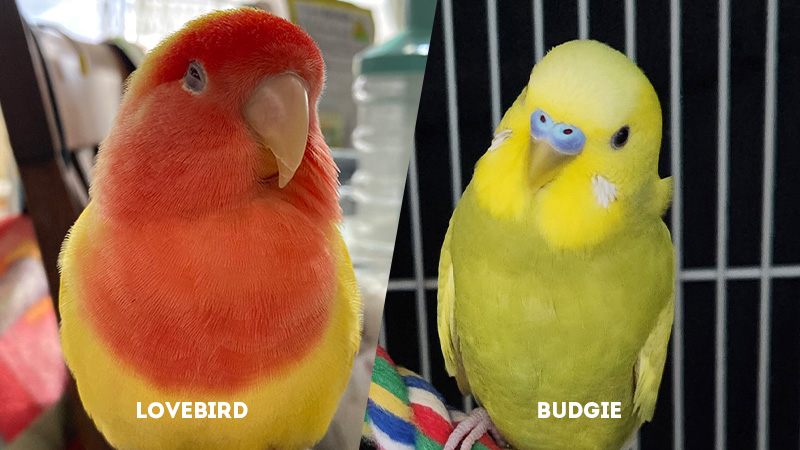
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds are renowned for their vibrant and captivating plumage. They exhibit a rich spectrum of colors, including reds, greens, yellows, and blues. Their stocky build is accentuated by a short tail, creating an adorable compact look.
Lovebirds’ captivating color variations and their expressive facial features make them visually striking and appealing to those who appreciate colorful companions. - Budgies: On the other hand, budgerigars, commonly referred to as budgies, present a more slender and elongated appearance. Their body shape and posture are elegant, and their overall size is slightly larger than lovebirds.
Budgies are equally diverse in color, boasting shades of blue, green, yellow, and even white. Their long, graceful tail adds to their aesthetic appeal.
Temperament
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds are known for their affectionate and social nature. They are birds that often form strong bonds with their human companions.
They can develop a deep attachment and exhibit signs of love and affection towards their owners. However, this strong bond can sometimes lead to territorial behavior, where they become possessive of their owners and their surroundings. - Budgies: Budgies are celebrated for their playful and adaptable temperament. They are generally more open to interactions with multiple people and can quickly adapt to new environments.
Budgies’ friendly and easygoing nature makes them ideal for households with varied family members, as they readily engage in interactions and can be socialized effectively.
Size
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds are relatively smaller birds, which contributes to their endearing charm. Their petite size makes them suitable for those with limited space or smaller living quarters. Despite their small stature, lovebirds can make a big impact on their owners’ lives through their affectionate behavior and lively personalities.
- Budgies: Budgies are slightly larger compared to lovebirds. Their elongated body and larger wingspan give them a graceful appearance. While still small enough to fit comfortably in most indoor environments, their slightly bigger size can make them more visible and easily noticeable within a room.
Interaction
- Lovebirds: The strong bond lovebirds form with their owners demands a higher level of interaction. They thrive on attention and appreciate spending quality time with their human companions. Lovebirds’ need for social interaction makes them a wonderful choice for individuals seeking a deeply connected avian friend.
- Budgies: Budgies’ adaptable and sociable nature means they enjoy interaction as well, but they are also comfortable with a broader range of social dynamics. They can bond with multiple people in the household and even form friendships with other budgies, allowing for a more flexible interaction style.
Vocalization
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds have a quieter and melodious vocalization compared to budgies. Their soft and sweet sounds can be pleasant background music in the home. While they may not be as chatty as budgies, their occasional chirps and whistles contribute to a peaceful and serene atmosphere.
- Budgies: Budgies are known for their energetic and talkative nature. They possess an exceptional ability to mimic sounds and voices, often surprising their owners with their repertoire of noises. Budgies’ vibrant and varied vocalizations can add liveliness to a household, though their talkative nature may require a tolerance for noise.
Lifespan
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds have an average lifespan of 10 to 15 years when kept in a well-maintained and nurturing environment. Proper diet, exercise, and veterinary care can contribute to their longevity. Their lifespan can be influenced by genetics, diet, and overall care.
- Budgies: Budgies share a similar lifespan range of 5 to 10 years when provided with appropriate care. Their lifespan can vary based on genetics, diet, housing conditions, and access to regular veterinary check-ups.
Social Behavior
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds are known for their intense social bonds. They form strong attachments with their owners and can become quite dependent on human interaction. This social behavior can result in deep emotional connections but may also lead to stress or behavioral issues if not properly managed.
- Budgies: Budgies exhibit social behavior as well, but their approach is often more adaptable. They can form close relationships with their owners, yet they also have the ability to interact harmoniously with other birds and family members. This makes them suitable for households with varying degrees of human interaction.
Aggression
- Lovebirds: Due to their strong attachment to their owners, lovebirds might display territorial behavior and aggression towards perceived threats or intruders, including other birds or even household members. This aggression can vary among individual birds and is often more pronounced during breeding periods.
- Budgies: Budgies generally have a milder temperament when it comes to aggression. They are less likely to exhibit territorial behavior and are more tolerant of interactions with other birds, making them more suitable for multi-bird households.
Diet

- Lovebirds: Lovebirds’ diet mainly consists of seeds, grains, fruits, and vegetables. Providing a balanced and varied diet is crucial to their overall health and well-being. Pelleted diets formulated for lovebirds can help ensure they receive the necessary nutrients.
- Budgies: Budgies share a similar dietary requirement, including seeds, grains, fruits, and vegetables. Additionally, budgies can benefit from pelleted diets that provide a balanced nutritional profile. Proper diet maintenance is essential for their vibrant colors, energy levels, and overall health.
Cage Space
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds can thrive in slightly smaller cages compared to budgies due to their smaller size. However, it’s important to provide enough space for them to exercise and move around comfortably. A spacious cage with opportunities for climbing and exploring is beneficial for their physical and mental health.
- Budgies: Budgies require slightly larger cages due to their longer wingspan and active nature. A larger cage allows them to spread their wings and fly short distances within the enclosure. Providing perches, toys, and opportunities for exercise is essential to keep them engaged and healthy.
Training
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds have the potential to be trained for various tricks and behaviors, but their level of receptiveness can vary based on individual personality. They can learn to step onto a hand, perch on command, and even perform simple tricks with positive reinforcement training.
- Budgies: Budgies are highly trainable and are often considered one of the more trainable parrot species. They have a natural curiosity and intelligence that makes them responsive to training. Budgies can be taught tricks, mimicry of sounds and words, and even basic agility exercises.
Care Complexity
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds require consistent care and attention due to their social nature. They thrive on interaction and may become stressed or exhibit behavioral issues if left alone for extended periods. Their emotional needs and potential territorial behavior demand vigilant care.
- Budgies: Budgies are relatively easier to care for due to their adaptable and sociable nature. While they also benefit from social interaction, they are more flexible in their interactions and can adjust to various schedules and family dynamics.
Feather Plucking

- Lovebirds: Lovebirds, especially those that lack social interaction or are stressed, can develop a habit of feather plucking. This behavior can lead to bald patches and skin irritation. Addressing the underlying causes, such as boredom or loneliness, is essential to prevent and manage feather plucking.
- Budgies: Budgies are less prone to feather plucking compared to some other parrot species. However, they can engage in feather preening to maintain their plumage. Providing mental and physical stimulation through toys and interaction can help prevent unwanted feather-related behaviors.
Noise Level
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds have a quieter and more melodious vocalization compared to some other parrot species. While they do make sounds, their volume is generally manageable and may not disrupt a peaceful household.
- Budgies: Budgies are known for their chattering, singing, and mimicry abilities, which can result in a higher noise level. Their vocalizations can be energetic and varied, which some individuals find charming, while others may need to adjust to the increased auditory stimulation.
Habitat Requirements
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds are native to various regions in Africa and nearby islands. They prefer tropical environments and are suited to warmer temperatures. Providing a well-ventilated and appropriately heated living space is important for their comfort.
- Budgies: Budgies are native to the arid regions of Australia. They are adapted to a drier climate and are more tolerant of fluctuations in temperature. Proper ventilation and temperature control are still essential, but they can adapt to a wider range of environmental conditions.
Breeding Behavior
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds are known for their strong pair bonds and often form monogamous relationships with a single mate. They exhibit affectionate behaviors such as preening each other and regurgitating food as a sign of bonding. Lovebirds are dedicated parents and actively participate in nesting and raising their offspring.
- Budgies: Budgies are also social and may form pair bonds, but they are not as intense as those of lovebirds. They can breed in colonies in the wild and exhibit less intense pair-bonding behaviors.
Budgies are generally good parents and can raise their chicks effectively, although they may need more supervision during the breeding process.
Grooming
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds are meticulous groomers and often engage in preening not only themselves but also their bonded mate. This behavior reinforces their social bonds and helps maintain their plumage in good condition.
- Budgies: Budgies are also diligent groomers, spending time preening their feathers to keep them clean and well-maintained. They groom themselves individually rather than engaging in mutual preening to the same extent as lovebirds.
Playfulness
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds have a playful side and can enjoy interacting with toys and their owners. They may engage in playful behaviors such as swinging on perches, exploring their environment, and even playing with small objects.
- Budgies: Budgies are known for their energetic and curious nature, which translates into playful behaviors. They enjoy exploring their surroundings, interacting with toys, and even engaging in activities like shredding paper or climbing on objects.
Mating Displays
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds engage in elaborate mating displays as part of their courtship rituals. These displays involve fluffing feathers, regurgitating food, and engaging in synchronized movements to attract a mate.
- Budgies: Budgies also perform mating displays, which can include showing off their plumage, hopping, and singing to attract a potential mate. However, these displays may not be as elaborate or intense as those of lovebirds.
Availability
- Lovebirds: Lovebirds are widely available in the pet trade, and their diverse color mutations make them a popular choice among bird enthusiasts. They come in a variety of colors and patterns, allowing potential owners to choose a bird that matches their preferences.
- Budgies: Budgies are among the most popular and commonly kept pet birds globally. They are readily available in various colors and are often an affordable option for those looking to bring a feathered friend into their home.
Lovebird Vs Budgie: Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lovebirds | Budgies |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Vibrant colors, stocky build, short tail | Varied colors, slim build, longer tail |
| Temperament | Affectionate, strong bonds, territorial | Sociable, playful, adaptable |
| Size | Smaller | Slightly larger |
| Interaction | Requires close attention, bonding | Tolerant of multiple interactions |
| Vocalization | Melodious, less vocal | Chatty, mimicry abilities |
| Lifespan | 10-15 years | 5-10 years |
| Social Behavior | Strong bonds with owners | Friendly with owners and other birds |
| Aggression | Can display aggression | Generally more easygoing |
| Diet | Similar, seeds and fruits | Similar, seeds and vegetables |
| Cage Space | Smaller cages may suffice | Larger cages preferred |
| Training | Can be trained for tricks | Can be trained to mimic and perform |
| Care Complexity | Requires consistent attention | Relatively easier care |
| Feather Plucking | Prone to feather plucking | Less prone to feather plucking |
| Noise Level | Quieter, melodious sounds | More vocal, chattering, and singing |
| Habitat Requirements | Tropical regions | Native to Australia |
| Breeding Behavior | Form strong pair bonds | Nest in cavities, social breeders |
| Grooming | Prune feathers, preen each other | Preen and groom themselves |
| Playfulness | Play with toys, explore surroundings | Curious and playful |
| Mating Displays | Display courtship behavior | Engage in courtship rituals |
| Availability | Widely available | Common and readily available |
Frequently Asked Questions
Budgies are generally more adaptable and open to forming bonds with multiple family members. Their sociable nature allows them to interact harmoniously with different individuals, making them a suitable choice for households with varying schedules and family dynamics.
While it’s possible to house lovebirds and budgies together, it’s generally not recommended due to differences in size, temperament, and potential aggression. Lovebirds can be territorial and might bully budgies, leading to stress and potential conflicts. It’s safer to provide separate living spaces for each species.
While both lovebirds and budgies enjoy interacting with toys, their play preferences can differ. Lovebirds might prefer toys they can manipulate with their beaks, such as hanging toys with movable parts. Budgies often enjoy toys they can chew, shred, and climb on, like swings, mirrors, and hanging bells.
Providing a stimulating environment is key. For lovebirds, focus on social interaction, mental enrichment, and providing a companion if keeping just one. For budgies, offer a variety of toys, rotate them regularly, and ensure they have plenty of opportunities for exercise. Addressing boredom and stress can help prevent feather plucking.
Both species are susceptible to respiratory issues, especially if exposed to drafts or poor air quality. Budgies can be prone to obesity if their diet lacks variety and is high in fatty seeds. Lovebirds may exhibit feather plucking due to stress or health issues. Regular veterinary check-ups, a balanced diet, and a clean environment are essential for their well-being.
To Recap
In the dynamic tapestry of avian companionship, the distinctions between lovebirds and budgies unveil a world of possibilities. The choice between these charming species is a reflection of one’s aspirations, lifestyle, and commitment.
Whether captivated by lovebirds’ intense bonds or enticed by budgies’ adaptability, both species offer rewarding companionship.
By comprehending their diverse behaviors, care requirements, and unique traits, potential owners can forge a lasting connection that brings color, joy, and vitality into their lives.
Ultimately, whether it’s the enchanting allure of lovebirds or the spirited playfulness of budgies, the journey of avian companionship is a remarkable and enriching adventure.