The Blue-throated Mountain Gem (Lampornis clemenciae) is a captivating hummingbird species gracing the montane landscapes of Central America.
Renowned for its breathtaking iridescent plumage, this avian jewel belongs to the Trochilidae family and the Lampornis genus.
Males boast a vivid, electric blue throat that extends down to their chest, creating a striking contrast with metallic green upperparts. Females, while equally elegant, exhibit more subdued throat colors.
Adapted to high-altitude habitats, these hummingbirds navigate montane forests and cloud-covered regions, showcasing remarkable agility in flight.
With a wingspan of around 4 to 4.5 inches, the Blue-throated Mountain Gem hovers gracefully while feeding on nectar from a variety of blooming flowers.
As an essential pollinator, it plays a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance of its habitat.
Beyond its aesthetic allure, the Blue-throated Mountain Gem’s life history, nesting behaviors, and conservation challenges unveil a captivating narrative of resilience and significance in Central America’s diverse ecosystems. Stay focused.
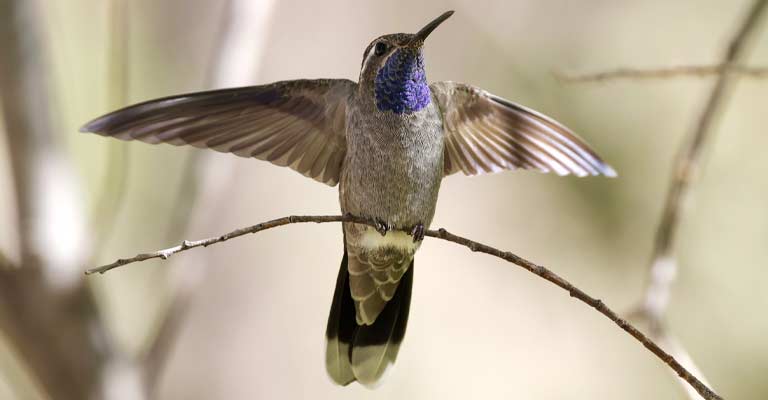

Identifying Characteristics of Blue-throated Mountain-Gem
The Blue-throated mountain gem (Lampornis clemenciae) is a dazzling and distinctive hummingbird species found primarily in the mountainous regions of Central America, spanning from southern Mexico to western Panama.
Identifying this remarkable bird involves paying attention to various key characteristics, which contribute to its unique appearance and behavior.
Physical Appearance
The Blue-throated Mountain Gem boasts a striking combination of iridescent colors that make it stand out among other hummingbird species.
As the name suggests, its most notable feature is the vibrant blue throat patch that extends down to its chest.
This contrasting blue coloration is a defining characteristic and is particularly vivid in males, serving as a key identifier. Females, on the other hand, exhibit a more muted throat color, often leaning towards greenish or grayish tones.
In addition to the prominent blue throat, both male and female Blue-throated Mountain Gems display metallic green upperparts, which shimmer in the sunlight.
Their underparts are generally lighter in color, featuring a mix of white and gray feathers. The tail is long and deeply forked, contributing to the bird’s overall graceful and agile flight.
Size and Shape
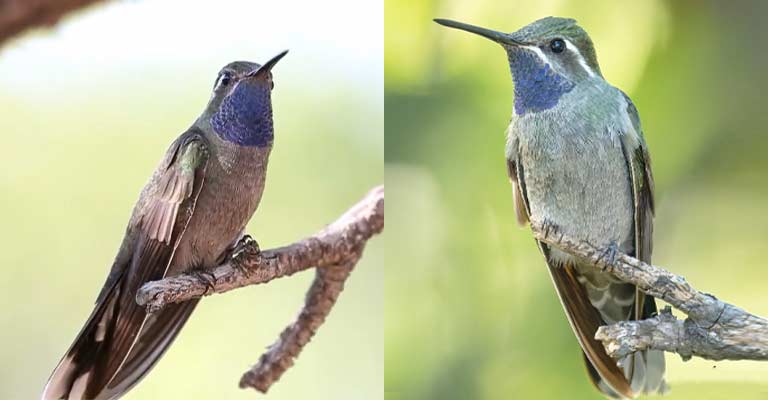

The Blue-throated Mountain Gem falls within the medium-sized range for hummingbirds, measuring approximately 4 to 4.5 inches (10-11 cm) in length.
Its slender body and elongated bill are well-adapted for feeding on nectar from flowers, a primary component of its diet.
The slightly curved bill facilitates the efficient extraction of nectar from tubular flowers.
Habitat and Range
Understanding the bird’s habitat and geographical range is crucial for identification.
Blue-throated mountain gems inhabit montane forests, cloud forests, and pine-oak woodlands at elevations ranging from 1,000 to 3,000 meters.
Their distribution spans various countries in Central America, including Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
Behavioral Traits
Observing the behavior of the Blue-throated Mountain-Gem can also aid in identification. Like many hummingbirds, they are highly agile fliers, capable of rapid and precise movements.
Their feeding habits involve hovering in front of flowers and using their specialized bills to extract nectar.
Additionally, these hummingbirds are known for their vocalizations, emitting sharp chirps and trills during flight or when perched.
Identifying the Blue-throated Mountain Gem involves recognizing its distinctive physical characteristics, such as the vibrant blue throat, metallic green plumage, and forked tail.
Understanding its size, habitat preferences, and behavior further enhances the ability to distinguish this species from other hummingbirds in its range.
Taxonomy of Blue-throated Mountain-Gem

Here’s a table summarizing the taxonomy details of the Blue-throated Mountain Gem:
| Taxonomic Level | Classification |
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Clade | Strisores |
| Order | Apodiformes |
| Family | Trochilidae |
| Genus | Lampornis |
| Species | L. clemenciae |
This table outlines the hierarchical classification of the Blue-throated mountain gem according to the Linnaean taxonomy system.
From the broad categories such as Domain and Kingdom to the more specific classifications like Order and Species, this taxonomy provides a systematic framework for understanding the bird’s evolutionary relationships within the animal kingdom.
The Blue-throated mountain gem (Lampornis clemenciae) is a hummingbird species that has undergone taxonomic changes since the mid-1900s and is currently classified within the genus Lampornis.
Within this species, there are three recognized subspecies, each exhibiting subtle variations in characteristics and distribution:
- L. c. clemenciae (Nominate Subspecies): This is the nominate subspecies, representing the standard or typical form of the Blue-throated Mountain-Gem. It is characterized by the distinctive iridescent blue throat and metallic green upperparts that define the species. Found in specific geographic regions within the broader range of the species.
- L. c. phasmorus: This subspecies showcases variations in certain morphological features and may have distinct geographic distributions. The specific characteristics that differentiate L. c. phasmorus may include variations in size, coloration, or other subtle traits. Typically found in specific habitats within the overall range of the Blue-throated Mountain-Gem.
- L. c. bessophilus: The third subspecies, L. c. bessophilus, represents another morphologically distinct group within the Blue-throated Mountain-Gem species. Like the other subspecies, it may have unique characteristics that distinguish it from the nominate form. It occupies specific habitats or regions within the overall distribution of the species.
These subspecies demonstrate the evolutionary diversity and adaptations that can occur within a species over different geographic regions.
Studying these variations helps ornithologists and researchers gain a more nuanced understanding of the Blue-throated mountain gem’s ecology, behavior, and genetic makeup.
Blue-throated Mountain-Gem Life History
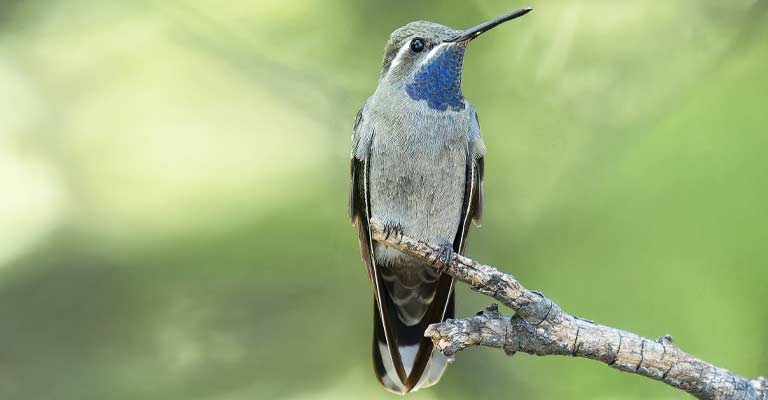

The Blue-throated mountain gem (Lampornis clemenciae) is not only a stunning presence in the montane landscapes of Central America but also a fascinating subject when exploring its life history.
From its dietary habits to nesting behavior, breeding patterns, and conservation status, each aspect of the Blue-throated Mountain Gem’s life provides insights into the intricate web of its existence.
Food
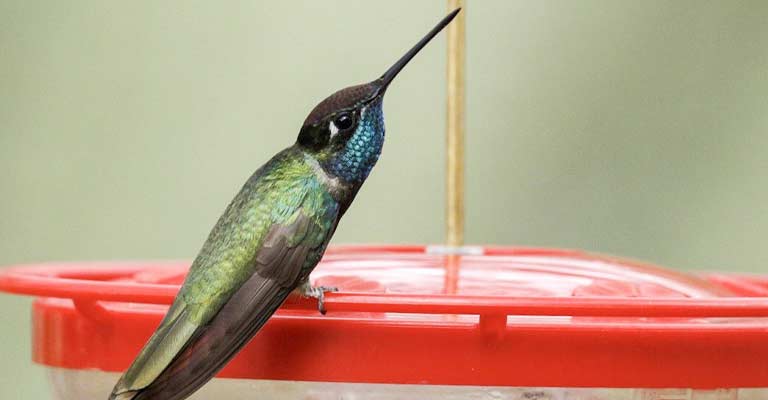

The primary component of the Blue-throated Mountain Gem’s diet is nectar from various flowering plants.
Possessing specialized bills adapted for extracting nectar, they play a crucial role in pollination as they move from flower to flower.
In addition to nectar, they supplement their diet with small insects and spiders, providing essential proteins and nutrients.
Habitat
These striking hummingbirds are inhabitants of montane forests, cloud forests, and pine-oak woodlands.
Found at elevations ranging from 1,000 to 3,000 meters, they thrive in the cool, misty environments characteristic of these habitats.
Their adaptability to diverse ecosystems is reflected in their ability to navigate through dense vegetation and access a variety of flowering plants for nectar.
Range Map
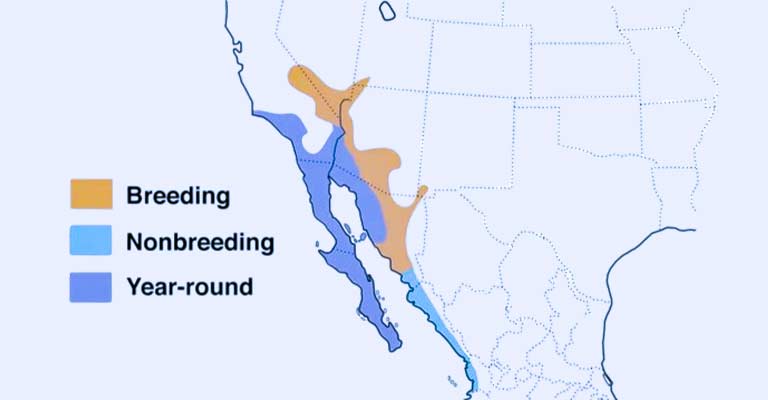
The Blue-throated Mountain-Gem’s range spans across Central America, including southern Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
Detailed range maps aid ornithologists and conservationists in understanding the distribution patterns of this species, providing valuable information for targeted conservation efforts.
Nesting
The female Blue-throated mountain gem is responsible for constructing the nest, typically situated on a horizontal branch.
The nest is composed of plant fibers, moss, and lichen, camouflaging it amidst the surrounding vegetation.
Their nesting sites are carefully chosen to ensure protection from predators and adverse weather conditions.
Here’s a table summarizing the nesting details of the Blue-throated mountain gem:
| Nesting Details | Blue-throated Mountain-Gem Facts |
| Clutch Size | Typically 2 eggs per clutch |
| Number of Broods | Usually raises a single brood per breeding season |
| Egg Length | Approximately 1.0 to 1.2 centimeters |
| Egg Width | Around 0.6 to 0.7 centimeters |
| Incubation Period | Approximately 15 to 19 days |
| Nestling Period | Fledglings spend several weeks in the nest before fledging |
| Egg Description | Small, elliptical-shaped eggs with a smooth surface |
| Nest Construction | Constructed by the female using plant fibers, moss, and lichen |
| Nest Placement | Positioned on a horizontal branch, often well-camouflaged in vegetation |
These details provide a snapshot of the Blue-throated Mountain Gem’s reproductive behavior, shedding light on aspects such as the number of eggs per clutch, the incubation period, and the characteristics of the eggs and nest.
This information is valuable for researchers and bird enthusiasts interested in the life cycle and breeding biology of this remarkable hummingbird species.
Breeding
Breeding seasons vary across the Blue-throated Mountain Gem’s range, often aligning with the availability of blooming flowers.
Males engage in elaborate courtship displays, showcasing their vibrant plumage and agility in flight. After successful mating, females lay two eggs, which they incubate for about 15-19 days.
The fledglings then spend several weeks in the nest before venturing out on their own.
Diseases and Treatment
Hummingbirds, including the Blue-throated Mountain Gem, may face health challenges such as avian diseases and parasites. Common issues include bacterial infections and external parasites.
Vigilance in monitoring the bird’s behavior, appearance, and feeding patterns can help in early detection.
Treatment may involve specialized veterinary care, including antibiotics or antiparasitic medications, and maintaining a clean environment around feeding stations.
Conservation
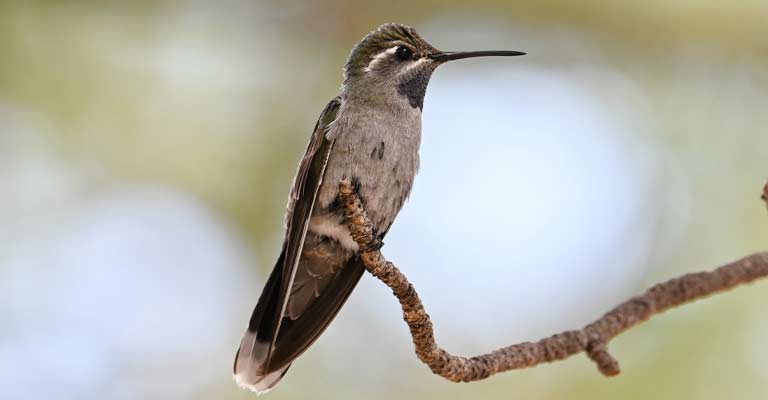

Despite their enchanting presence, the Blue-throated mountain gem faces threats such as habitat loss, climate change, and potential competition with other hummingbird species.
Conservation efforts involve protecting their natural habitats, promoting sustainable land use practices, and raising awareness about the importance of preserving these ecosystems.
Additionally, citizen science initiatives contribute valuable data to monitor population trends and inform conservation strategies.
The life history of the Blue-throated Mountain Gem reveals a delicate balance between ecological interactions, reproductive strategies, and the challenges posed by a changing environment.
Understanding and appreciating these facets are crucial for the ongoing conservation of this captivating hummingbird species.
10 Fun Facts About Blue-throated Mountain-Gem
The Blue-throated mountain gem is a fascinating and distinctive hummingbird species with several intriguing aspects to its behavior and characteristics. Here are some fun facts about this remarkable bird:
- Iridescent Elegance: The male Blue-throated Mountain Gem showcases a brilliant blue throat, which is a key feature in its courtship displays. The vibrant coloration is a result of the microscopic structure of the feathers rather than pigments, creating an iridescent effect.
- Altitudinal Adventurer: This hummingbird species is well-adapted to high-altitude habitats, often found in montane forests and cloud forests at elevations ranging from 1,000 to 3,000 meters. Its ability to thrive in such environments adds to its unique ecological niche.
- Forked Tail Flourish: The Blue-throated Mountain Gem is distinguished by its deeply forked tail, a feature that contributes to its agile and acrobatic flight. The forked tail aids in precise maneuvering as the bird hovers and darts between flowers.
- Floral Fantasia: Like many hummingbirds, the Blue-throated Mountain Gem plays a crucial role in pollination. As it feeds on nectar from flowers, its head comes into contact with the reproductive organs of the plants, facilitating the transfer of pollen and contributing to the plant’s reproduction.
- Mysterious Migrations: While some hummingbird species are known for long-distance migrations, the Blue-throated Mountain Gem’s migratory patterns are not well-documented. Some populations may undertake seasonal movements, but more research is needed to fully understand their migration behaviors.
- Nesting Niche: The female Blue-throated Mountain Gem takes charge of nest construction, carefully selecting a horizontal branch for placement. The nests are often well-camouflaged, blending with the surrounding vegetation to reduce the risk of predation.
- Diverse Diet: In addition to feeding on nectar, Blue-throated Mountain Gems supplement their diet with small insects and spiders. This eclectic feeding strategy provides essential proteins and nutrients to support their energetic lifestyle.
- Distinctive Vocalizations: While not known for elaborate songs, Blue-throated Mountain Gems produce sharp chirps and trills, especially during flight or when defending territories. These vocalizations contribute to their communication with conspecifics.
- Human Interaction: These hummingbirds are known to visit feeders, providing birdwatchers with an opportunity to observe them up close. Creating hummingbird-friendly gardens with a variety of blooming flowers can attract Blue-throated Mountain Gems, enhancing the backyard birdwatching experience.
- Conservation Concerns: Despite their stunning appearance, the Blue-throated Mountain-Gem faces threats from habitat loss, climate change, and potential competition with other hummingbird species. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the survival of this species and the preservation of its unique habitats.
These fun facts offer a glimpse into the captivating world of the Blue-throated mountain gem, highlighting its adaptability, ecological significance, and the marvels of its behavior and appearance.
Wrapping Up
The Blue-throated mountain gem emerges not only as a symbol of natural elegance but as a resilient and vital species in the complex ecosystems of Central American highlands.
From its iridescent blue throat to its acrobatic flight and unique nesting behaviors, this hummingbird encapsulates the wonders of avian life.
Understanding its life history, nesting intricacies, and conservation challenges allows us to appreciate and contribute to the preservation of this charismatic species.
As the Blue-throated Mountain Gem hovers amidst the cloud forests, its story becomes a testament to the delicate balance between nature’s beauty and the urgent need for conservation efforts in our ever-changing world. Best wishes.