The Black-browed Albatross (Thalassarche melanophris) is a majestic seabird renowned for its impressive wingspan and striking appearance.
Found primarily in the Southern Ocean, these birds exhibit fascinating behaviors and adaptations that have captured the interest of scientists and bird enthusiasts worldwide.
With their distinctive black eyebrows contrasting against white plumage, Black-browed Albatrosses are easily recognizable as they soar gracefully over the open seas.
Their complex social structures, monogamous breeding pairs, and elaborate courtship displays add to the intrigue surrounding this species.
As vital members of marine ecosystems, Black-browed Albatrosses play a significant role in nutrient cycling and maintaining ecological balance.
Understanding their biology and ecology is crucial for their conservation and preserving their oceanic habitats. Stay focused.
How to Identify Black-browed Albatross?
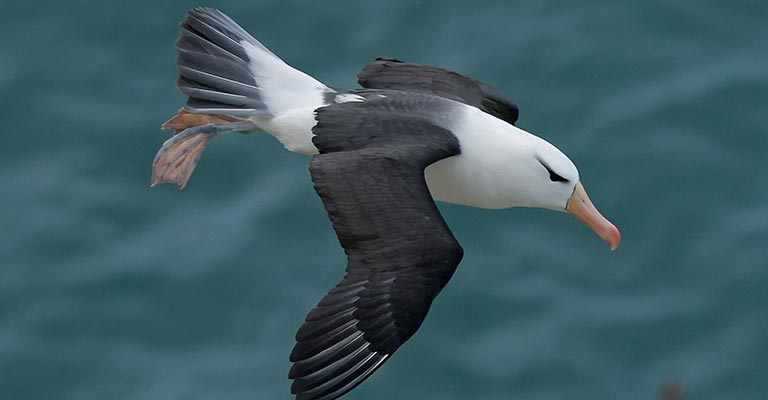

The Black-browed Albatross (Thalassarche melanophris) is a majestic seabird known for its striking appearance and impressive wingspan.
Identifying these birds can be an exciting challenge for birdwatchers and enthusiasts. Here are some of the key points to help you recognize this species:
Distinctive Facial Markings
One of the most prominent features of the Black-browed Albatross is its bold facial markings.
As the name suggests, these birds have distinct black eyebrows extending from the bill’s base to above the eye. This characteristic sets them apart from other albatross species.
White Head and Neck
Contrasting with the black eyebrows, the head and neck of the Black-browed Albatross are primarily white. This creates a striking color contrast and makes them easily identifiable, especially from a distance.
Grayish Back and Upper Wings
When in flight, the Black-browed Albatross displays a distinctive grayish coloration on its back and upper wings.
This coloration can vary slightly depending on lighting conditions, but it typically appears as a uniform gray or gray-brown hue.
Dark Underwing Markings
While flying, observers can spot the dark underwing markings characteristic of a Black-browed Albatross.
These markings consist of dark patches or bands along the trailing edge of the wings, creating a distinct pattern against the lighter underside of the wings.
Large Wingspan
Black-browed Albatrosses have an impressive wingspan, reaching up to 7 feet (over 2 meters) in length.
This expansive wingspan allows them to soar effortlessly over vast stretches of open ocean, making them highly adapted for long-distance flight.
Graceful Flight
When flying, Black-browed Albatrosses exhibit a graceful and effortless gliding motion. They often use dynamic soaring techniques, taking advantage of wind patterns and air currents to travel long distances with minimal effort.
This distinctive flight behavior can help observers distinguish them from other seabirds.
Habitat and Range
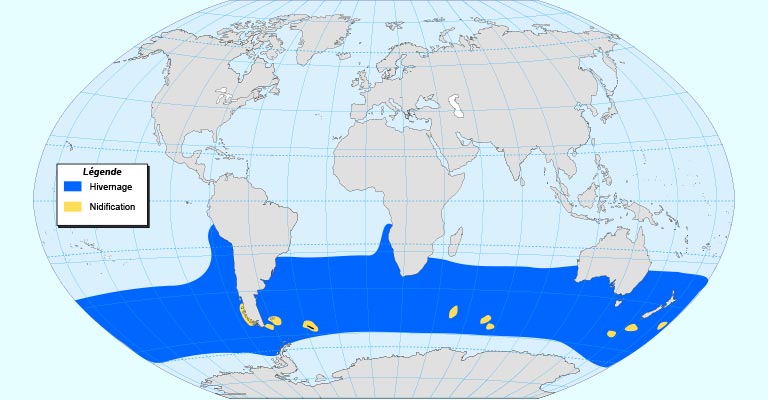
Black-browed Albatrosses are primarily found in the Southern Ocean, where they inhabit subantarctic and temperate waters.
They breed on remote islands such as the Falkland Islands, South Georgia, and islands in the southern Indian Ocean.
During the non-breeding season, they disperse over a broader range but remain predominantly in the Southern Hemisphere.
Social Behavior
These birds are often observed in large colonies during breeding, where they gather on steep coastal cliffs or tussock-covered slopes.
They may form loose flocks or solitary individuals at sea outside the breeding season. Their social behavior and tendency to congregate in specific habitats can aid their identification and observation.
The Black-browed Albatross can be identified by its distinctive facial markings, white head and neck, grayish back and upper wings, dark underwing markings, large wingspan, graceful flight, habitat preferences, and social behavior.
By familiarizing yourself with these key characteristics, you can confidently recognize and appreciate this remarkable seabird in its natural environment.
Taxonomy of Black-browed Albatross

Check out the table detailing the taxonomy of the Black-browed Albatross below:
| Taxonomic Rank | Classification |
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Order | Phaethontiformes |
| Family | Diomedeidae |
| Genus | Thalassarche |
| Species | T. melanophris |
The Black-browed Albatross (Thalassarche melanophris) belongs to the family Diomedeidae, which encompasses all species of albatrosses.
Within this family, it is classified under the genus Thalassarche, which includes several other albatross species.
The specific epithet melanophris refers to its characteristic black eyebrows. Due to their unique nasal passages, albatrosses are part of Procellariiformes, commonly known as tubenoses.
These birds are further classified into the suborder Procellariidae, which includes various species of petrels and shearwaters. Albatrosses are renowned for their impressive wingspans, efficient gliding flights, and long lifespans.
They are predominantly found in the Southern Hemisphere, where they inhabit open ocean environments and remote islands, playing essential roles in marine ecosystems.
Common Food of Black-browed Albatross

The Black-browed Albatross primarily feeds on various marine organisms found in its oceanic habitat. Everyday food items for these birds include:
- Squid: Black-browed Albatrosses often prey on squid, abundant in their oceanic range. They have specialized beaks and digestive systems adapted for consuming squid.
- Fish: Various species of fish make up a significant portion of the albatross’s diet. They may feed on small schooling fish such as lanternfish or larger species like mackerel and herring.
- Crustaceans: Crustaceans such as krill and shrimp are also important food sources for Black-browed Albatrosses. These tiny organisms are rich in nutrients and provide essential sustenance for the birds.
- Cephalopods: Besides squid, albatrosses may consume other cephalopods, such as octopus and cuttlefish.
- Offal and Carrion: Black-browed Albatrosses are opportunistic feeders and may scavenge on offal or carrion encountered at sea.
- Floating Debris: Unfortunately, these birds may also mistakenly consume floating debris, such as plastics, which can pose significant threats to their health.
Black-browed Albatross Life History
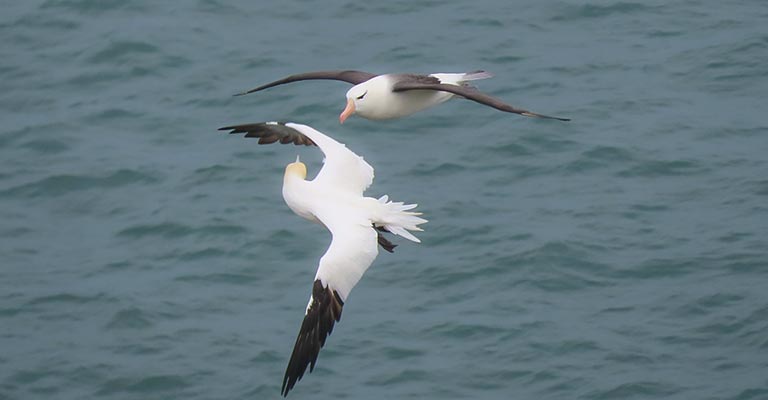

The Black-browed Albatross (Thalassarche melanophris) is a magnificent seabird known for its impressive wingspan and graceful flight.
This species has a fascinating life history, marked by its hunting habits, habitat preferences, nesting behaviors, breeding biology, disease susceptibility, conservation status, and ongoing conservation efforts.
Hunting Habit
Black-browed Albatrosses are skilled hunters who feed on squid, fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods and occasionally scavenge carrion or floating debris.
With their keen eyesight and mighty wings, they soar over vast expanses of ocean, effortlessly scanning the surface for prey.
Habitat and Range Map
These albatrosses inhabit subantarctic and temperate waters of the Southern Ocean, often frequenting remote islands and coastal regions.
Their range extends from South America to the Indian Ocean and parts of the Southern Hemisphere, as depicted on range maps indicating breeding colonies and foraging areas.
Nesting
Black-browed Albatrosses typically nest in large colonies on remote islands’ steep coastal cliffs or tussock-covered slopes.
They construct their nests from grass, soil, and other available materials, forming breeding colonies where they return annually to raise their young.
A table detailing nesting details of the Black-browed Albatross is given below:
| Nesting Details | Facts |
| Clutch Size | Typically, one brood per season |
| Number of Broods | Typically one brood per season |
| Egg Length | Approximately 11.5 to 12.5 cm |
| Egg Width | Approximately 7.0 to 7.5 cm |
| Incubation Period | Around 70 to 75 days |
| Nestling Period | About 120 to 140 days |
| Egg Description | Pale greenish or bluish-white with irregular brown spots or blotches |
| Nest Construction | Constructed from grass, soil, and other available materials, forming shallow scrapes or mounds |
| Parental Care | Both parents share incubation and chick-rearing duties, taking turns to forage and feed the chick |
This table provides a concise overview of the nesting habits and characteristics of the Black-browed Albatross, offering insights into their reproductive biology and parental care behaviors.
Breeding
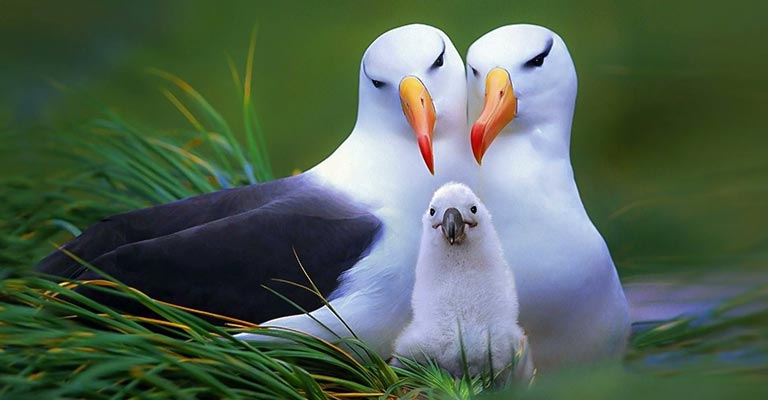

Breeding season for Black-browed Albatrosses begins in late spring or early summer. Males and females engage in elaborate courtship displays before forming monogamous pairs for the breeding season.
They lay a single egg per clutch, which both parents take turns incubating and caring for until hatching.
Diseases and Treatment
Despite their resilience, Black-browed Albatrosses are susceptible to diseases, including avian cholera, avian pox, and aspergillosis.
Conservation organizations and wildlife veterinarians work to monitor and treat affected populations, implementing measures to reduce disease transmission and improve overall health.
Conservation
Black-browed Albatrosses face various threats, including habitat loss, bycatch in fisheries, pollution, and climate change.
Conservation efforts focus on protecting breeding colonies, reducing bycatch through bird-scaring and tori lines, and advocating for marine protected areas to safeguard critical foraging habitats.
The life history of the Black-browed Albatross is a testament to its resilience and adaptability in the challenging marine environment.
Conservationists strive to ensure these magnificent birds’ continued survival and well-being for generations by understanding and addressing the threats.
10 Fun Facts About Black-browed Albatross
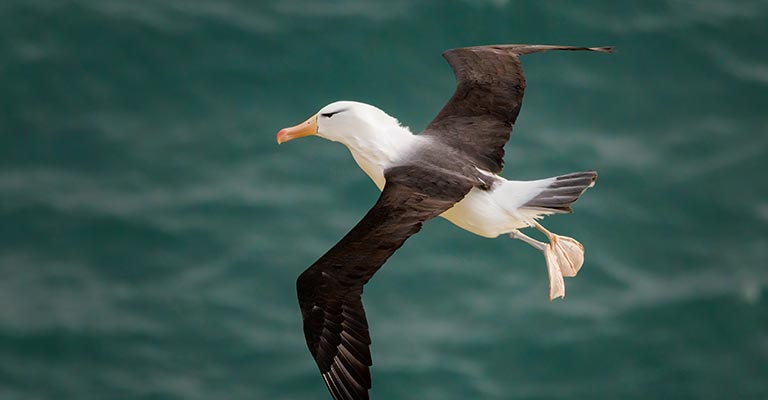

The Black-browed Albatross (Thalassarche melanophris) is a captivating seabird with remarkable characteristics and behaviors.
From its impressive wingspan to its fascinating social dynamics, here are 10 fun facts about this majestic bird:
- Longest Wingspan: Black-browed Albatrosses boast one of the longest bird wingspans, measuring up to 7 feet (over 2 meters) from tip to tip. This expansive wingspan allows them to effortlessly glide over vast stretches of open ocean for extended periods.
- Mature Late: These albatrosses typically don’t reach breeding maturity until they are around 6 to 10 years old, and they may not breed every year, making their reproductive cycle quite different from many other birds.
- Social Birds: Black-browed Albatrosses are highly social birds, often seen gathering in large colonies during the breeding season. These colonies can consist of thousands of individuals, creating a spectacular sight on remote island cliffs.
- Monogamous Pairs: During the breeding season, Black-browed Albatrosses form monogamous pairs that often remain together for life. They engage in elaborate courtship displays, including bill fencing and sky-pointing, to strengthen their bond.
- Dynamic Soaring: When in flight, Black-browed Albatrosses exhibit dynamic soaring techniques, utilizing wind patterns and air currents to travel long distances with minimal effort. This efficient flying technique allows them to cover vast distances while expending minimal energy.
- Long Lifespan: Black-browed Albatrosses are among the longest-living birds, with some individuals reaching ages of over 70 years. This longevity is crucial for their reproductive success, as they have ample time to raise multiple offspring.
- Distinctive Plumage: These birds have striking plumage, with characteristic black eyebrows contrasting their white head and neck. This unique coloration makes them easily recognizable, even from a distance.
- Global Distribution: While they primarily breed on subantarctic islands, Black-browed Albatrosses have a widespread distribution across the Southern Ocean, foraging over vast expanses of open water and reaching as far north as the coasts of South America.
- Vocal Communicators: Black-browed Albatrosses use a variety of vocalizations for communication, including grunts, whistles, and bill-clapping sounds. These vocalizations play a crucial role in maintaining social bonds within their colonies.
- Conservation Concerns: Despite their remarkable adaptability, Black-browed Albatrosses face threats from habitat destruction, fisheries bycatch, and pollution. Conservation efforts are underway to protect their breeding colonies and reduce human impacts on their populations.
The Black-browed Albatross is a fascinating, charismatic seabird with unique traits and behaviors.
Studying and appreciating these magnificent birds enriches our understanding of marine ecosystems and underscores the importance of conservation efforts to ensure their continued survival.
Wrapping Up
The Black-browed Albatross stands as a symbol of resilience and grace in the vast expanse of the Southern Ocean.
With its impressive wingspan, striking plumage, and fascinating behaviors, this seabird captivates the hearts of birdwatchers and conservationists alike.
From their dynamic soaring flights to their intricate social dynamics within breeding colonies, Black-browed Albatrosses offer a window into the wonders of the natural world.
However, their survival is increasingly threatened by human activities such as habitat destruction, fisheries bycatch, and pollution.
Therefore, it is imperative that we continue to study, appreciate, and actively conserve these magnificent birds and their fragile marine habitats.
Through concerted conservation efforts, we can ensure a brighter future for the Black-browed Albatross and preserve its place as a cherished icon of the Southern Ocean ecosystem.