Ciconia, commonly known as storks, are majestic birds renowned for their elegant appearance and fascinating behaviors.
Belonging to the genus Ciconia, these avian wonders inhabit various habitats across the globe, from wetlands and grasslands to agricultural fields and urban areas.
With their long legs, distinctive bills, and impressive wingspans, Ciconia species captivate the imagination of bird enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Ciconia birds offer many opportunities for study and admiration, from their intricate nesting behaviors to their graceful flight patterns and cooperative social structures. So, stay focused.
Identifying Characteristics of Ciconia
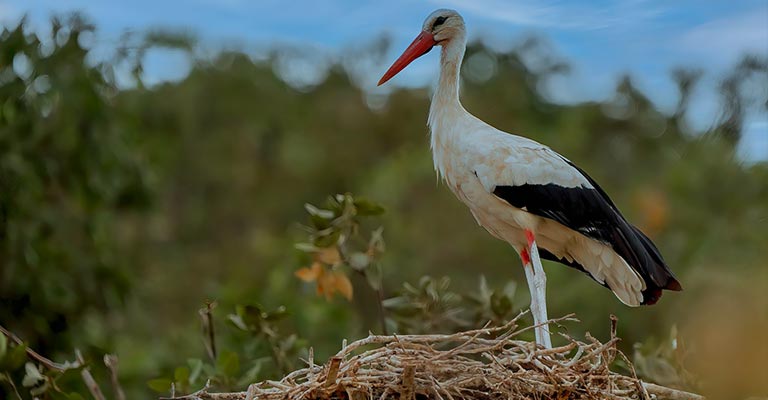

Ciconia is a genus of large wading birds comprising storks, known for their distinctive appearance and behavior.
These birds are found across various continents, inhabiting multiple habitats, from wetlands to grasslands.
Identifying Ciconia requires a keen eye for detail, as they share specific characteristics with other birds in the stork family. Here are some of the key points to aid in their identification:
Size and Shape
One of the primary characteristics of Ciconia species is their large size and distinctive shape.
They typically stand tall on long, slender legs, with a straight, sturdy neck and a broad, pointed bill. Their bodies are bulky, and they often have a hunched posture when standing.
Plumage
Ciconia storks commonly exhibit white plumage on their bodies, contrasting sharply with their black flight feathers.
This plumage pattern is especially noticeable during flight, where the white body stands out against the dark wings.
Bare Skin
Another distinguishing feature of Ciconia birds is the presence of bare skin patches on their heads and necks.
These areas are often brightly colored, ranging from red to pink or orange, and are used for communication and thermoregulation.
These bare skin patches extend down the throat in some species, such as the White Stork (Ciconia ciconia).
Flight Pattern
Ciconia storks have a distinctive flight pattern characterized by slow, powerful wingbeats interspersed with glides. They often soar on thermal currents, utilizing their large wingspan to stay aloft for extended periods.
Behavior
Observing their behavior can also aid in identifying Ciconia species. They are typically seen foraging in shallow water, using their sharp bills to catch fish, amphibians, and other aquatic prey.
They may also be spotted in grasslands, where they feed on insects, small mammals, and reptiles.
Voice
While not always reliable for identification, the vocalizations of Ciconia birds can provide clues to their presence.
They may produce a variety of calls, including guttural grunts, bill clattering, and hissing sounds during courtship and territorial displays.
Range and Distribution
Lastly, consulting range maps and distribution data can assist in identifying Ciconia species within a particular geographic area. Different species have distinct ranges, some migratory and others passive.
Identifying Ciconia species requires a combination of visual, behavioral, and habitat cues. By paying attention to these critical characteristics, birdwatchers and enthusiasts can confidently recognize these majestic storks in the wild.
Taxonomy of Ciconia

Here’s a table detailing the taxonomy of the Ciconia:
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Clade | Aequornithes |
| Order | Ciconiiformes (Bonaparte, 1854) |
| Family | Ciconiidae |
| Genus | Ciconia |
| Species | abdimii & 7 others |
The genus Ciconia encompasses eight species of storks, each possessing unique characteristics and inhabiting diverse habitats across the globe. Here’s a brief overview of these magnificent birds:
1. White Stork (Ciconia ciconia)
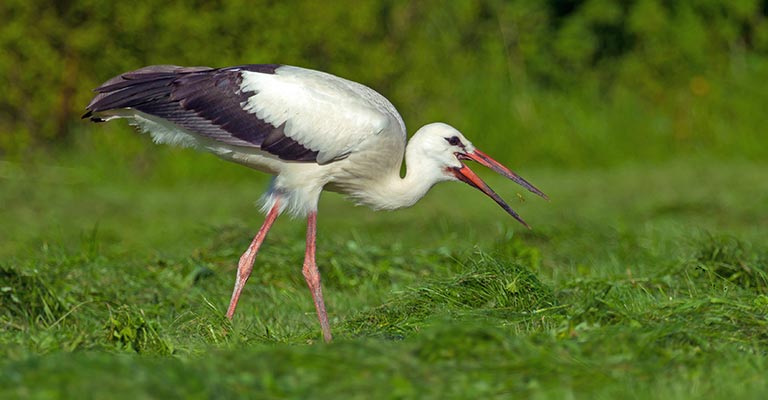

The iconic White Stork is renowned for its striking black-and-white plumage and distinctive red bill. Found in Europe, Africa, and Asia, it is known for its extensive migration patterns and cultural significance, often associated with the arrival of newborns.
2. Black Stork (Ciconia nigra)
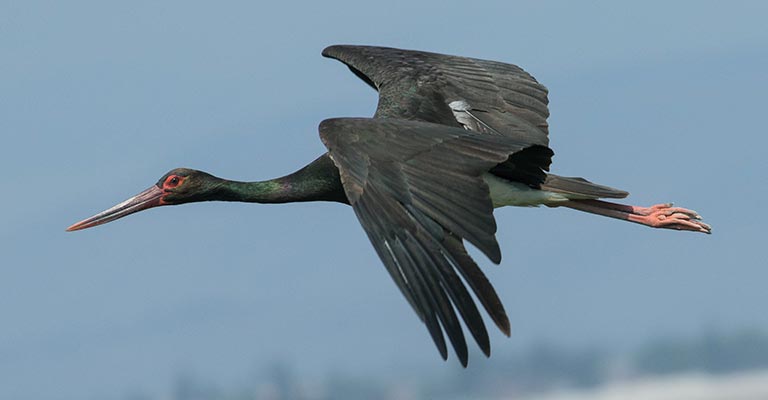

With its glossy black plumage and contrasting white underparts, the Black Stork is a majestic sight in the wetlands and forests of Europe and Asia. It is more secretive than its white counterpart and often nests in remote areas.
3. Abdim’s Stork (Ciconia abdimii)
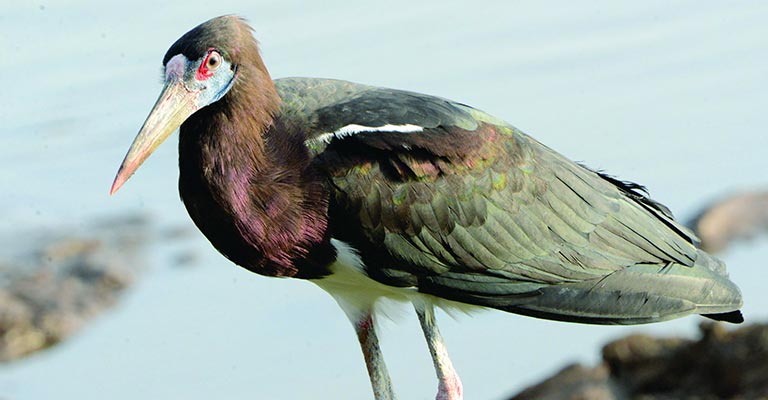

Named after the Turkish governor Abdim, this species is characterized by its black-and-white plumage and distinctive red facial skin. Abdim’s Stork is primarily found in sub-Saharan Africa, congregating in large flocks during the breeding season.
4. Woolly-necked Stork (Ciconia episcopus)
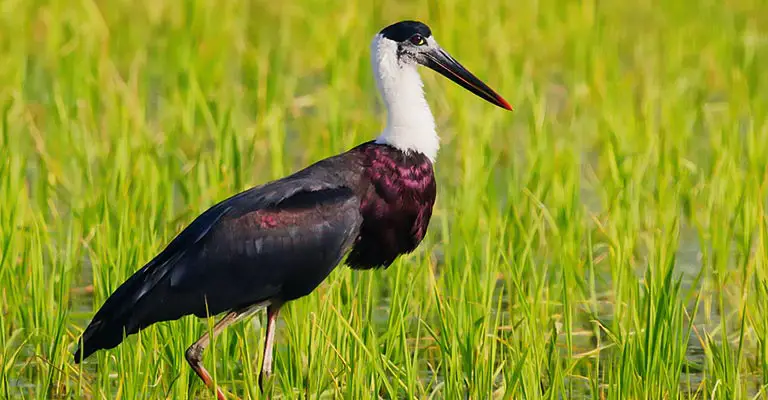

Sporting a woolly white neck and black-and-white plumage, this species is native to South and Southeast Asia. It frequents wetlands and agricultural areas, feeding fish, frogs, and insects.
5. Storm’s Stork (Ciconia stormi)
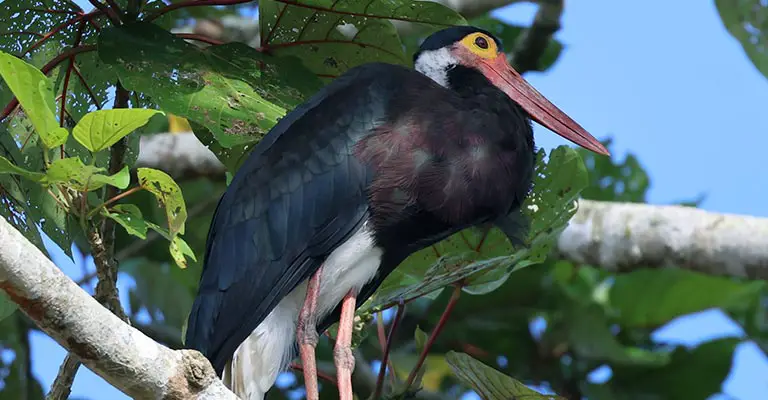

Endemic to the rainforests of Southeast Asia, Storm’s Stork is distinguished by its predominantly white plumage with black flight feathers and a vital redhead. It is considered vulnerable due to habitat loss and degradation.
Maguari Stork (Ciconia maguari)
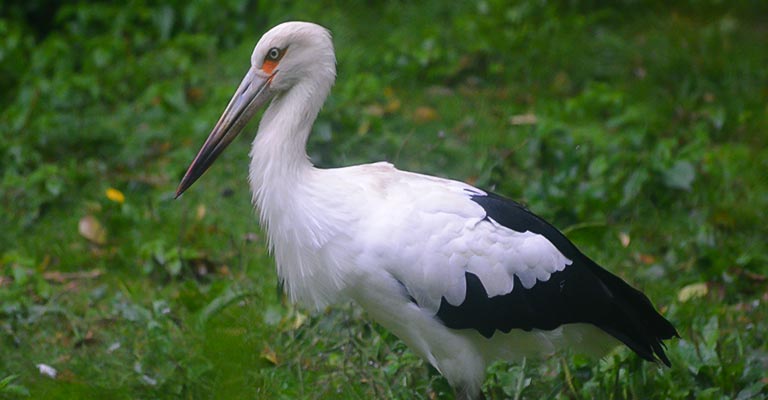

Native to South America, the Maguari Stork is characterized by its predominantly white plumage with black flight feathers and a distinctive yellow bill. It inhabits wetlands and grasslands, where it forages for fish, frogs, and crustaceans.
Asian Openbill (Ciconia boyciana)
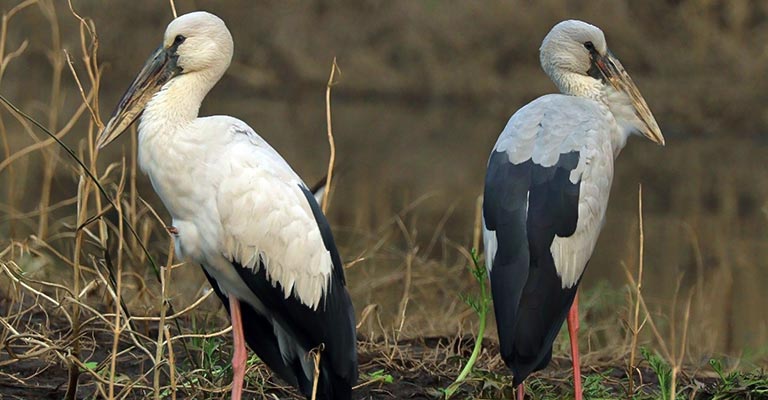

With its unique bill structure featuring a distinct gap, the Asian Openbill is found in South and Southeast Asia. It primarily feeds on snails, which it extracts from their shells using its specialized bill.
African Openbill (Ciconia abdimii)
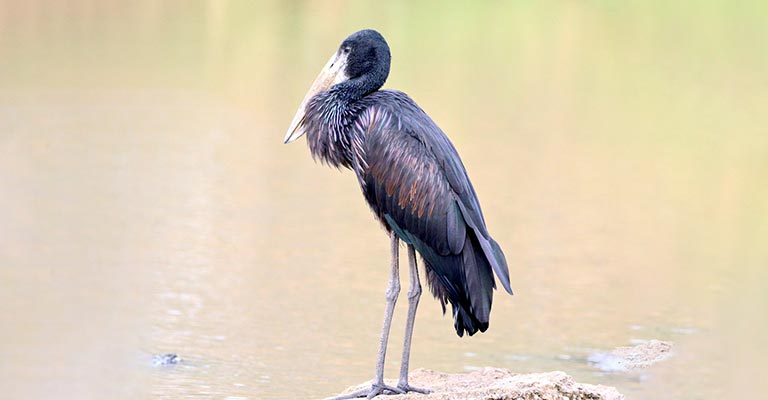

Similar in appearance to the Asian Openbill, the African Openbill is native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is often seen foraging in wetlands and rivers for mollusks and aquatic invertebrates.
Each Ciconia species plays a vital role in its respective ecosystem, contributing to the rich tapestry of biodiversity found worldwide.
Hunting Habit of Ciconia
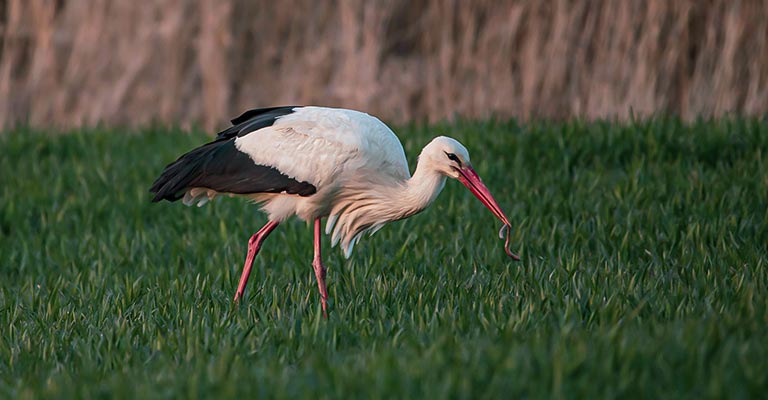

Ciconia species, primarily storks, exhibit a distinctive hunting habit characterized by their preference for shallow aquatic habitats and grasslands.
With their long legs and sharp bills, they stalk through the water or tall grass, searching for prey such as fish, amphibians, insects, and small mammals.
Utilizing their keen eyesight and patience, Ciconia birds remain motionless for extended periods, waiting for the opportune moment to strike.
When prey is detected, they swiftly jab their bills into the water or ground, precisely grasping their quarry.
This hunting strategy requires stealth, focus, and agility, enabling Ciconia to capture prey while minimizing energy expenditure effectively.
Additionally, some species engage in cooperative hunting behaviors, utilizing group dynamics to increase hunting success.
The hunting habit of Ciconia reflects their adaptability to diverse environments and their specialization in exploiting available resources for sustenance.
Ciconia Life History
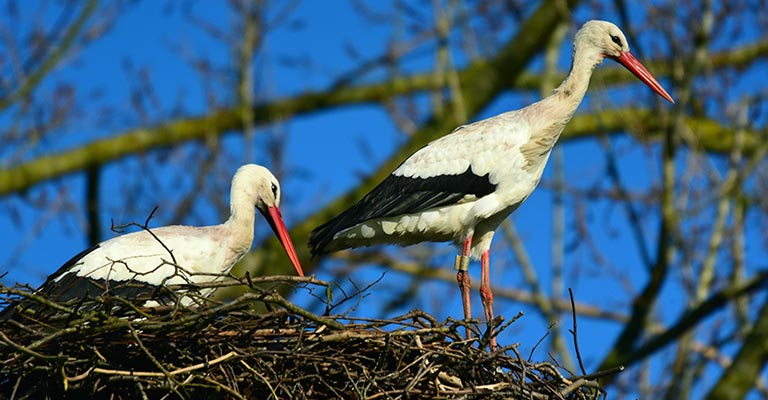

Ciconia, commonly known as storks, encompasses several species of large wading birds known for their striking appearance and fascinating life history.
These birds are found across diverse habitats worldwide and exhibit intriguing behaviors related to food acquisition, nesting, breeding, and conservation.
Understanding the life history of Ciconia species provides valuable insights into their ecological roles and conservation needs.
Food
Ciconia species are primarily carnivorous, feeding on a varied diet depending on their habitat and seasonal availability. They commonly prey on fish, amphibians, insects, small mammals, and reptiles.
Their long bills and sharp eyesight facilitate efficient hunting in shallow water bodies and grasslands. Some species also scavenge for carrion and forage in agricultural fields for insects and small vertebrates.
Habitat
Ciconia birds inhabit various habitats, including wetlands, marshes, grasslands, savannas, and agricultural areas.
They are often associated with water bodies where they forage for prey but may also utilize upland habitats for nesting and roosting.
Range Map
Ciconia species have diverse ranges across continents, some migratory and others passive.
Range maps provide valuable information on their distribution, highlighting areas of conservation concern and importance for habitat protection.
Nesting
Nesting behavior varies among Ciconia species but typically involves the construction of large stick nests in trees, cliffs, or man-made structures.
These nests are often reused year after year and may be added to over time, resulting in massive structures capable of supporting the weight of adult birds and their young.
Check out the table detailing the nesting details of Ciconia below:
| Nesting Details | Facts |
| Clutch Size | Varies by species, normally 7-10 cm |
| Number of Broods | Usually 1 per breeding season |
| Egg Length | Varies by species, typically 7-10 cm |
| Egg Width | Large stick nests built in trees, cliffs, or man-made structures, often added to over time. |
| Incubation Period | Approximately 25-35 days |
| Nestling Period | Around 60-90 days |
| Egg Description | Smooth surface, usually white with some speckling or markings depending on species |
| Nest Construction | Preferentially located near water bodies, often in colonies for communal nesting protection. |
| Parental Care | Both parents share incubation and feeding duties |
| Fledging | Chicks typically fledge around 2-3 months of age |
| Nesting Habitat | Preferentially located near water bodies, often in colonies for communal nesting protection |
This table summarizes vital nesting details of Ciconia species, highlighting aspects such as clutch size, incubation period, nest construction, and parental care behaviors.
Breeding
Breeding in Ciconia species is often characterized by elaborate courtship displays, with pairs engaging in synchronized movements and vocalizations to reinforce pair bonds.
Females typically lay a clutch of eggs, which both parents incubate. After hatching, chicks are cared for by both parents and fed regurgitated food until they fledge.
Diseases and Treatment
Ciconia species are susceptible to various diseases, including viral infections, bacterial diseases, and parasitic infestations. Common ailments include avian influenza, avian botulism, and parasitic infections such as avian malaria.
Treatment often involves veterinary intervention, including medication, supportive care, and quarantine measures to prevent the spread of disease.
Conservation
Conservation efforts for Ciconia species focus on habitat protection, population monitoring, and mitigation of threats such as habitat loss, pollution, and human disturbance.
International collaboration and legislation play a crucial role in conserving these iconic birds and ensuring their long-term survival.
The life history of Ciconia species is characterized by their diverse diet, habitat preferences, breeding behaviors, and conservation needs.
By understanding and addressing these aspects, conservationists can work towards safeguarding the future of these magnificent birds and the ecosystems they inhabit.
10 Behavioral Habits of Ciconia
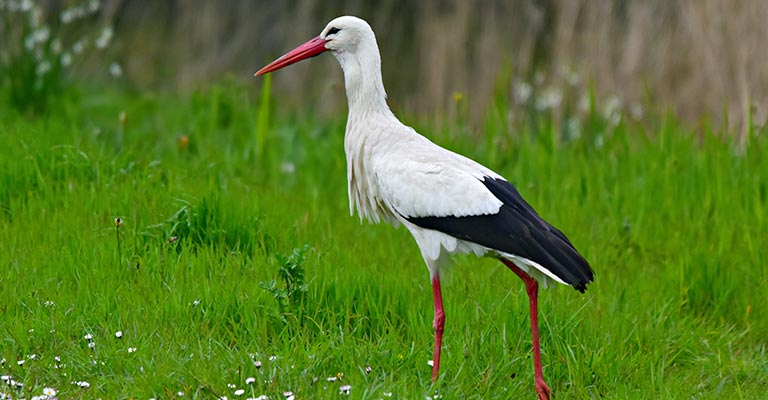

Ciconia, commonly known as storks, exhibit various behavioral habits that contribute to their survival and reproductive success.
From foraging techniques to social interactions, these behaviors are shaped by ecological factors and evolutionary adaptations. Here are ten behavioral habits of Ciconia species:
- Foraging Strategy: Ciconia birds employ a patient stalking strategy, often standing motionless in shallow water or tall grass before striking swiftly with their sharp bills to catch prey like fish, amphibians, and small mammals.
- Migratory Patterns: Many Ciconia species are migratory, undertaking long-distance journeys between breeding and wintering grounds. They navigate using celestial cues and wind patterns, displaying impressive navigational abilities.
- Courtship Displays: During the breeding season, Ciconia storks engage in elaborate courtship displays characterized by synchronized movements, bill-clattering, and vocalizations. These displays strengthen pair bonds and establish breeding territories.
- Nest Building: Ciconia constructs large stick nests in trees, cliffs, or man-made structures. Both sexes contribute to nest building, with some species refurbishing and adding to nests over successive breeding seasons.
- Parental Care: Both parents share responsibilities in incubating eggs, feeding nestlings, and protecting the nest from predators. This cooperative behavior ensures the survival of offspring and reinforces pair bonds.
- Colonial Nesting: Some Ciconia species nest in colonies, where multiple pairs build nests nearby. Colonial nesting protects predators and facilitates information sharing about foraging sites.
- Vocalizations: Ciconia birds produce a variety of vocalizations for communication, including grunts, hisses, and bill-clattering. These vocalizations maintain contact between mates, signal alarms, and coordinate breeding activities.
- Territorial Defense: During the breeding season, Ciconia vigorously defend their nesting territories from intruders. Aggressive displays and aerial pursuits deter potential threats and ensure the safety of their offspring.
- Feeding Young: Parental care extends to feeding young nestlings, with regurgitated food delivered directly to their mouths. This provisioning behavior ensures the growth and development of chicks until they are ready to fledge.
- Roosting Behavior: Outside of the breeding season, Ciconia birds gather in communal roosts, where they rest and socialize. Roosting sites provide safety in numbers and facilitate information exchange about foraging opportunities.
The behavioral habits of Ciconia species reflect their adaptability to diverse environments and their complex social dynamics.
Studying these behaviors enhances our understanding of their ecology and contributes to their conservation and management.
Wrapping Up
The behavioral habits of Ciconia species offer a captivating glimpse into the intricate lives of these iconic birds.
From foraging and nesting to social interactions and migratory patterns, each behavior is finely tuned to ensure their survival and reproductive success.
By studying and understanding these habits, we gain valuable insights into the ecological roles of Ciconia and the challenges they face in an ever-changing world.
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting their habitats and mitigating threats are essential to safeguarding the future of these majestic birds for generations to come. Thank you very much.