The Echo Parakeet (Psittacula eques) stands as a testament to the delicate balance between conservation efforts and preserving biodiversity on the island of Mauritius.
Endemic to this picturesque Indian Ocean island, the Echo Parakeet represents more than just a colorful avian species—it embodies the resilience of nature in the face of adversity.
Once teetering on the brink of extinction due to habitat loss and human interference, this charismatic bird has experienced a remarkable resurgence thanks to dedicated conservation initiatives.
With its vibrant plumage, distinctive crest, and raucous vocalizations, the Echo Parakeet captivates scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Its story is a beacon of hope for endangered species worldwide, demonstrating the transformative power of proactive conservation measures.
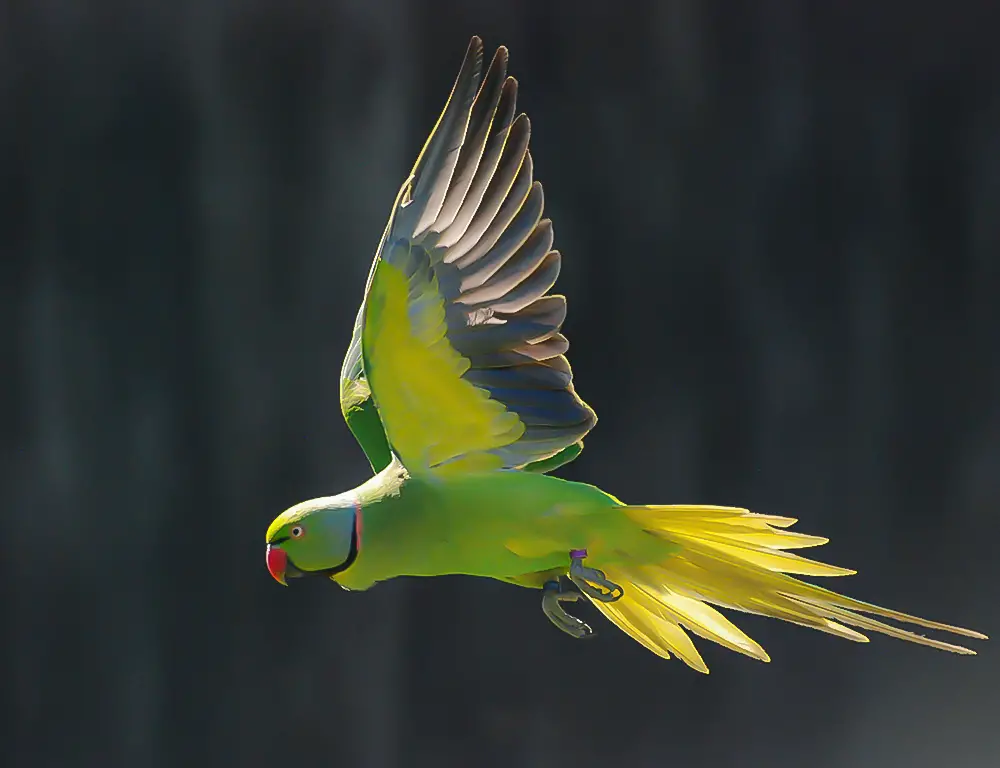

Characteristics Of Echo Parakeet
The Echo Parakeet (Psittacula eques) symbolizes Mauritius’ unique biodiversity, with its distinct physical traits and behavioral patterns. Here are common characteristics of this remarkable bird across various aspects of its life:
Physical Characteristics Of Echo Parakeet
The Echo Parakeet (Psittacula eques) is a striking bird endemic to the island of Mauritius, known for its vibrant plumage and unique physical features. Here are seven key physical characteristics that distinguish this species:
Plumage
The Echo Parakeet displays a captivating combination of colors, with predominantly bright green feathers covering its body. Its wings feature bold flashes of blue, while its tail feathers often exhibit hints of yellow and red.
This colorful plumage aids in camouflage within the lush vegetation of its native habitat.
Size
On average, Echo Parakeets measure around 40 to 45 centimeters in length, making them relatively large parrot family members. Their substantial size contributes to their presence and visibility within their forested environment.
Beak
One of the most noticeable physical attributes of the Echo Parakeet is its robust, curved beak. This beak is perfectly adapted for cracking open tough nuts and seeds, which form a significant portion of the bird’s diet.
Its powerful beak also allows it to access the pulp of fruits, aiding its nutritional needs.
Head and Crest
The Echo Parakeet features a distinctive head shape, with a slightly rounded crown and a prominent, elongated crest adorning its forehead. When excited or alarmed, this crest raises, adding to the bird’s overall appearance of alertness and readiness.
Eye Rings
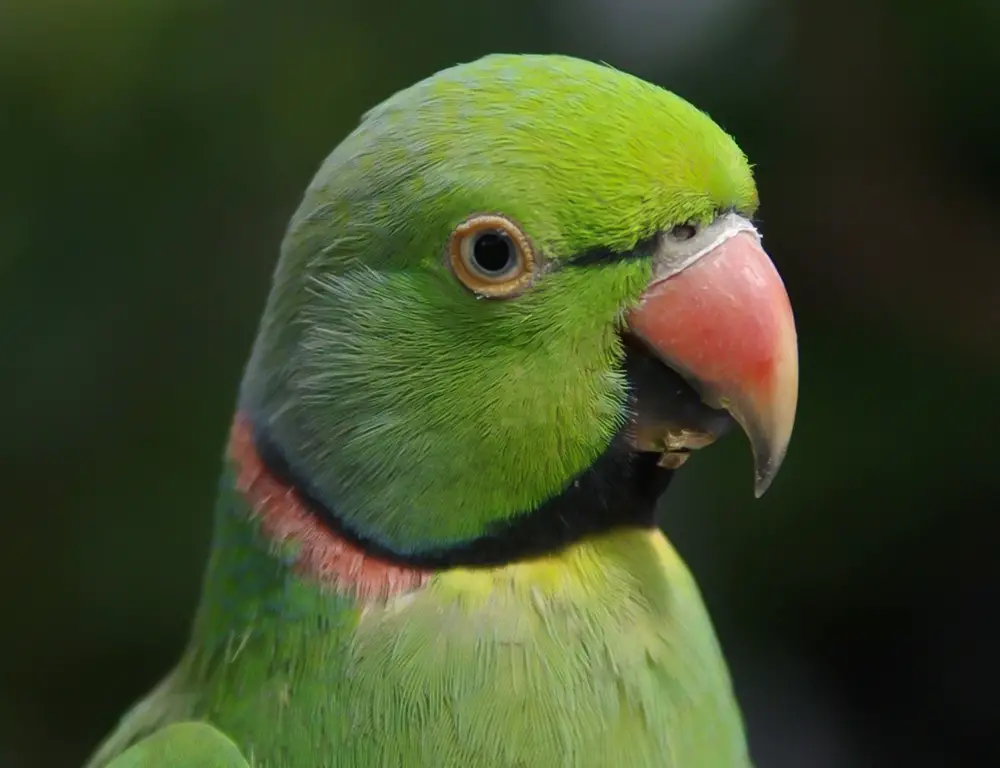

Surrounding each eye, the Echo Parakeet sports narrow, pale eye rings, contrasting beautifully against the bird’s darker facial feathers. These eye rings help accentuate the bird’s expressive gaze, adding to its visual allure.
Legs and Feet
Like many parrot species, the Echo Parakeet possesses sturdy legs and feet adapted for grasping and climbing.
Its zygodactyl feet—two toes facing forward and two feet facing backward—enable it to grip onto branches securely and easily navigate its arboreal habitat.
Vocalizations
While not a physical characteristic in the traditional sense, the Echo Parakeet’s vocalizations are integral to its identity.
These birds are known for their loud, raucous calls, which serve various purposes, including communication, territory defense, and mate attraction. Their distinctive vocal repertoire adds to the lively ambiance of Mauritius’ forests.
Distribution And Habitat
Endemic to Mauritius, the Echo Parakeet primarily inhabits the island’s upland forests and montane regions. It favors dense, evergreen forests where it can find suitable nesting sites and ample food resources.
Behaviour And Ecology
Echo Parakeets are highly social birds, often observed in small flocks or pairs. They are arboreal and spend much time foraging in the forest canopy for fruits, seeds, and nuts. These birds play a vital role in seed dispersal within their ecosystem.
Population
Once on the brink of extinction, the Echo Parakeet has remarkably recovered thanks to intensive conservation efforts. However, its population remains relatively small, with estimates suggesting a few hundred individuals in the wild.
Threats
Historically, habitat destruction, hunting, and predation by introduced species posed significant threats to the Echo Parakeet population.
While conservation efforts have mitigated some of these threats, habitat loss and fragmentation continue to endanger the species.
Conservation
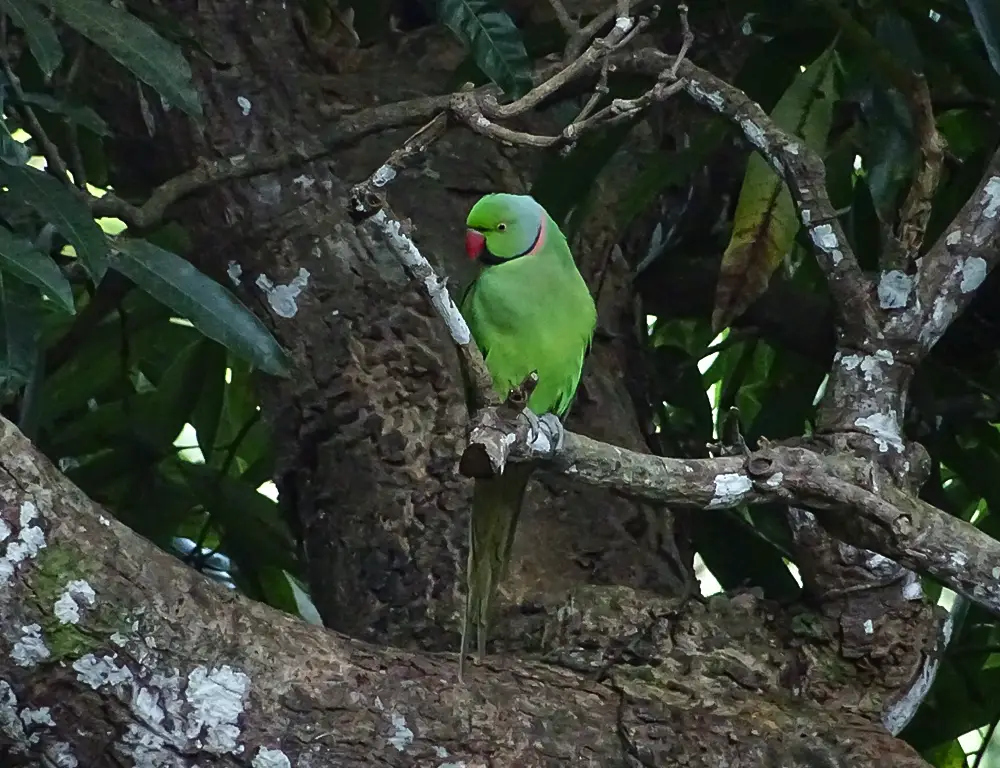

Conservation initiatives have been crucial in safeguarding the Echo Parakeet, including habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, and predator control.
Ongoing monitoring and conservation measures are essential for ensuring the long-term survival of this species.
Evolution
As an endemic species of Mauritius, the Echo Parakeet has evolved in isolation, adapting to the unique environmental conditions of the island over millennia. Its distinctive traits and behaviors reflect the evolutionary pressures it has faced in its native habitat.
Reproduction
Breeding typically occurs during the austral summer, with pairs forming solid bonds and nesting in tree hollows. Females lay a clutch of eggs, and both parents participate in incubation and chick rearing, demonstrating cooperative breeding behavior.
Vocalizations
The Echo Parakeet is known for its loud and raucous vocalizations, which serve various purposes, including communication within flocks, territory defense, and mate attraction.
These vocalizations are integral to the bird’s social interactions and behavioral repertoire.
Diet And Feeding
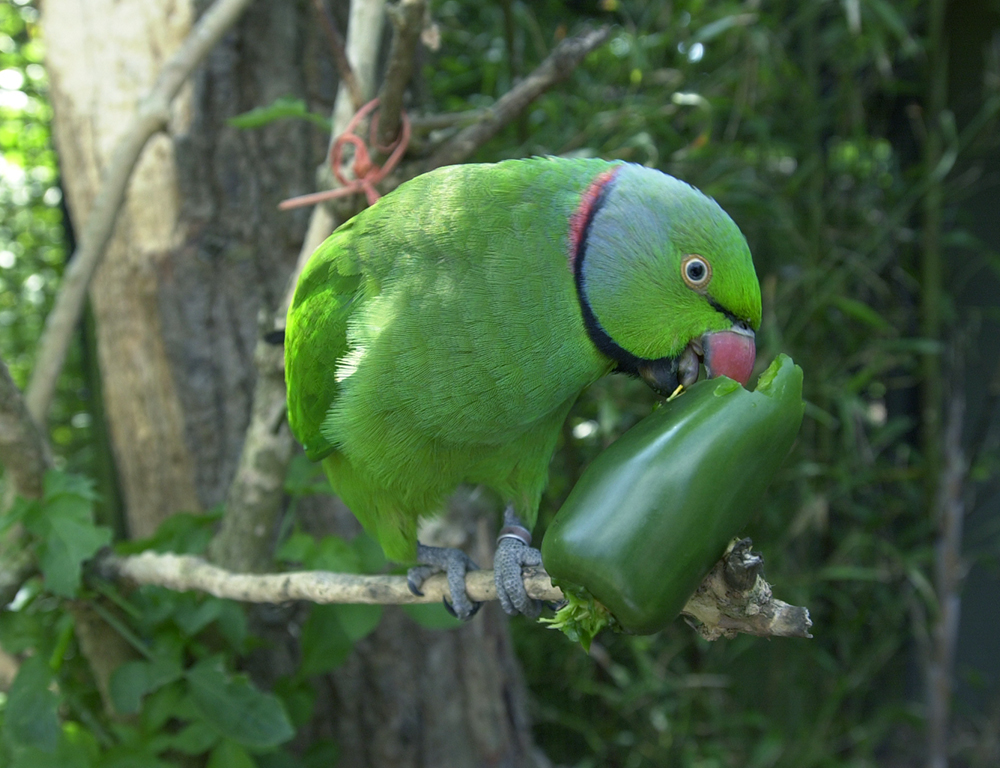

Echo Parakeets are primarily frugivorous, feeding on various fruits, seeds, and nuts in their forest habitat. Their robust beaks are well-suited for cracking open hard shells and extracting nutritious pulp from fruits.
Aggression And Competition
Echo Parakeets may exhibit aggression and competition within their social groups, particularly during mating season or when defending feeding territories.
Dominance hierarchies and displays of aggression help establish social order within flocks.
Status
The Echo Parakeet is classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List due to its small population size and ongoing threats to its habitat and survival.
Continued conservation efforts are essential for preventing further decline and ensuring the species’ persistence in the wild.
Taxonomy
Below is a table outlining the taxonomy of the Echo Parakeet:
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Order | Psittaciformes |
| Family | Psittaculidae |
| Genus | Psittacula |
| Species | Psittacula eques |
This table systematically summarizes the Echo Parakeet’s taxonomic classification, from its kingdom down to its species name.
Nesting Habit
Below is a table outlining the nesting habits of the Echo Parakeet:
| Nesting Habit | Description |
| Nest Location | Tree hollows, particularly in mature trees with suitable cavities |
| Nest Materials | Leaves, twigs, and other plant materials |
| Nest Construction | Both male and female parakeets participate in nest construction |
| Breeding Season | Typically occurs during the austral summer months (November to April) |
| Clutch Size | Usually lays 2-4 eggs per clutch |
| Incubation Period | Both parents incubate the eggs, lasting around 20-30 days |
| Chick Rearing | Both parents feed and care for the chicks until they fledge |
This table provides an overview of the nesting behavior and habits of the Echo Parakeet, including where they nest, the materials they use, and their breeding season characteristics.
Conservation Threats
Despite conservation successes, the Echo Parakeet faces persistent threats such as habitat loss, predation by invasive species, and potential disease outbreaks.
Addressing these threats requires ongoing collaboration between government agencies, conservation organizations, and local communities.
The Echo Parakeet’s resilience and conservation success story underscores the importance of proactive measures in preserving biodiversity and protecting endangered species in their natural habitats.
Ranging Map Of The Echo Parakeet
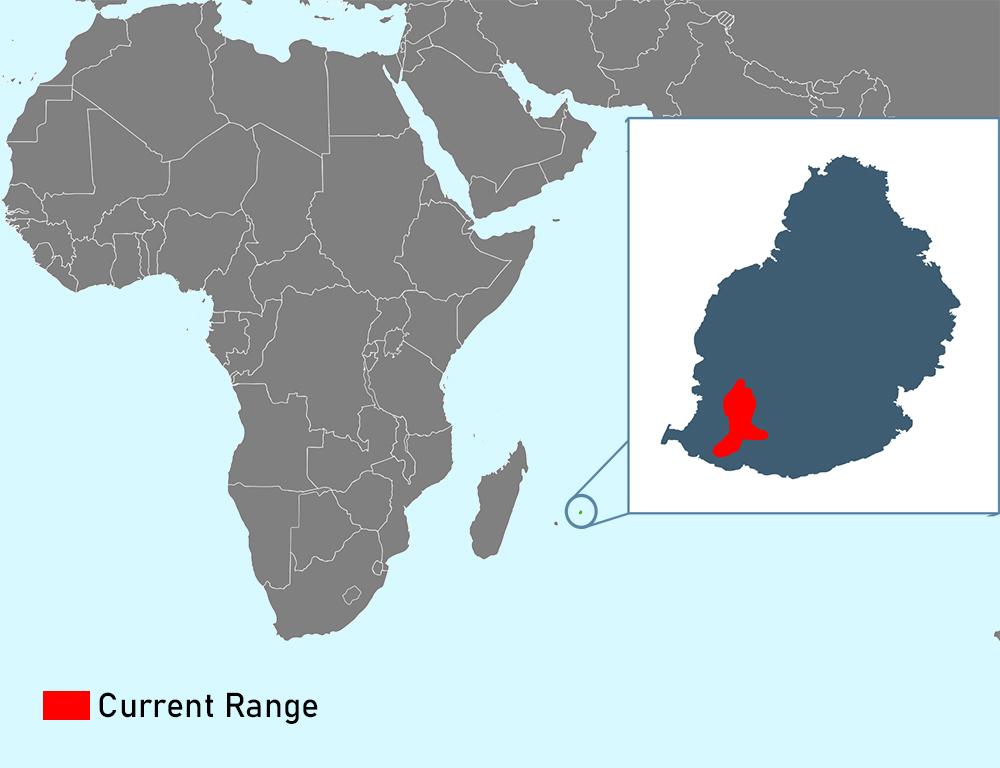
The ranging map of the Echo Parakeet (Psittacula eques) visualizes the species’ distribution and movement patterns within its native habitat on the island of Mauritius.
This map illustrates the areas where the Echo Parakeet can be found, offering valuable insights into its ecological requirements and conservation needs.
The ranging map typically depicts the distribution of Echo Parakeet populations across Mauritius, highlighting key habitats such as upland forests, montane regions, and other suitable areas where the birds reside.
These habitats are often characterized by dense vegetation, providing the necessary resources for nesting, foraging, and roosting.
By understanding the spatial dynamics of Echo Parakeet populations, researchers and conservationists can work towards ensuring the long-term survival of this iconic Mauritian bird.
How Can We Protect The Echo Parakeet?
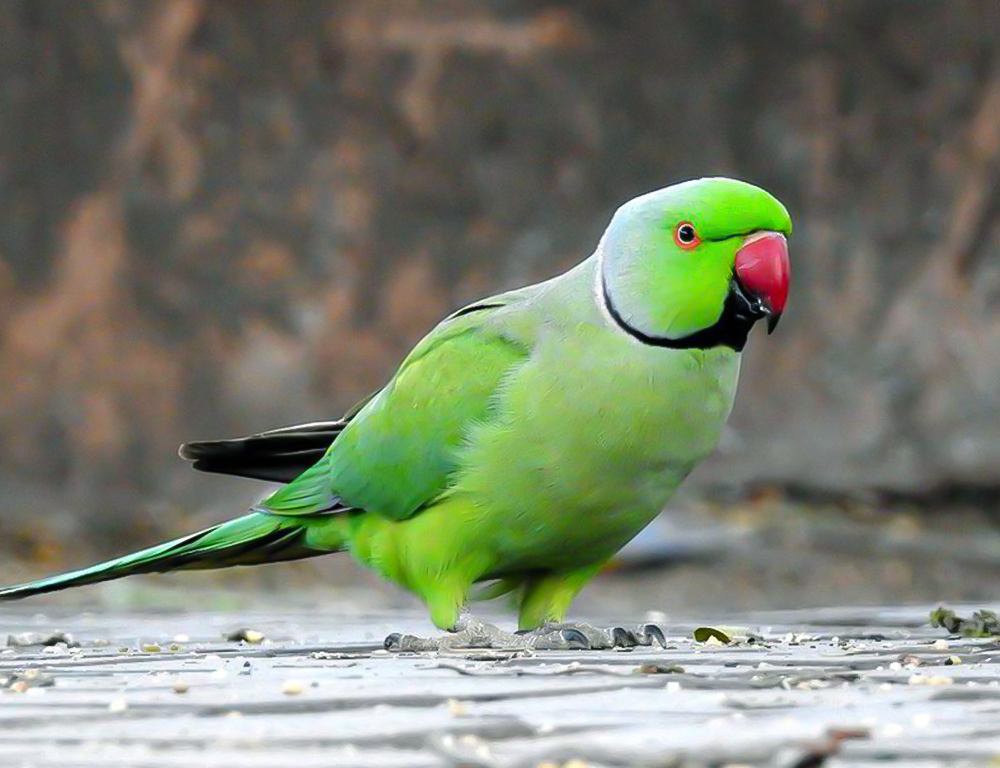

Protecting the Echo Parakeet (Psittacula eques) requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses various threats to its survival, from habitat loss to predation by invasive species.
Here are some effective strategies for safeguarding this endangered bird:
Habitat Conservation
Preserving and restoring the Echo Parakeet’s native habitat is paramount to its survival. This includes protecting remaining forests from deforestation, establishing protected areas, and reforesting degraded landscapes.
By maintaining suitable habitats, we ensure the availability of nesting sites, food resources, and roosting areas essential for the bird’s survival.
Invasive Species Management
Controlling and eradicating invasive species that prey on Echo Parakeet eggs and chicks is crucial for their protection. Introduced predators such as rats, cats, and monkeys threaten nesting sites and breeding success.
Implementing trapping programs and predator-proofing techniques can help mitigate these impacts and reduce predation pressure on Echo Parakeet populations.
Nesting Site Protection
Identifying and safeguarding natural and artificial nesting sites is essential for the Echo Parakeet’s breeding success.
This may involve installing nest boxes in suitable locations, monitoring nesting activity, and implementing measures to deter disturbance or vandalism.
Protecting nesting sites ensures the survival of chicks and contributes to population growth.
Community Engagement
Engaging local communities in Echo Parakeet conservation efforts fosters stewardship and support for protective measures.
Education and outreach programs can raise awareness about preserving the species and its habitat while involving communities in monitoring and conservation activities to promote ownership and collaboration.
Conservation Breeding Programs
Establishing and managing captive breeding programs can help augment wild populations and provide a safety net against extinction.
Breeding centers can breed Echo Parakeets for release into the wild, supplementing natural populations and increasing genetic diversity.
These programs also serve as insurance populations in case of catastrophic events in the wild.
Monitoring and Research
Regular monitoring of Echo Parakeet populations provides valuable data on population trends, habitat use, and threats. By conducting research on the species’ ecology, behavior, and genetics, scientists can better understand its needs and inform conservation strategies.
Long-term monitoring programs are essential for assessing the effectiveness of conservation efforts and adapting management plans accordingly.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration among government agencies, non-profit organizations, researchers, and local communities is essential for effective Echo Parakeet conservation.
By pooling resources, expertise, and efforts, stakeholders can implement coordinated conservation actions, leverage funding opportunities, and maximize the impact of conservation initiatives.
Working together towards a common goal ensures a unified approach to protecting this iconic Mauritian bird.
Protecting the Echo Parakeet requires a holistic approach that addresses habitat conservation, invasive species management, community engagement, breeding programs, monitoring, and collaboration.
By implementing these strategies in concert, we can safeguard the future of this endangered species and ensure its continued presence in Mauritius’ forests.
10 Interesting Facts About Echo Parakeets
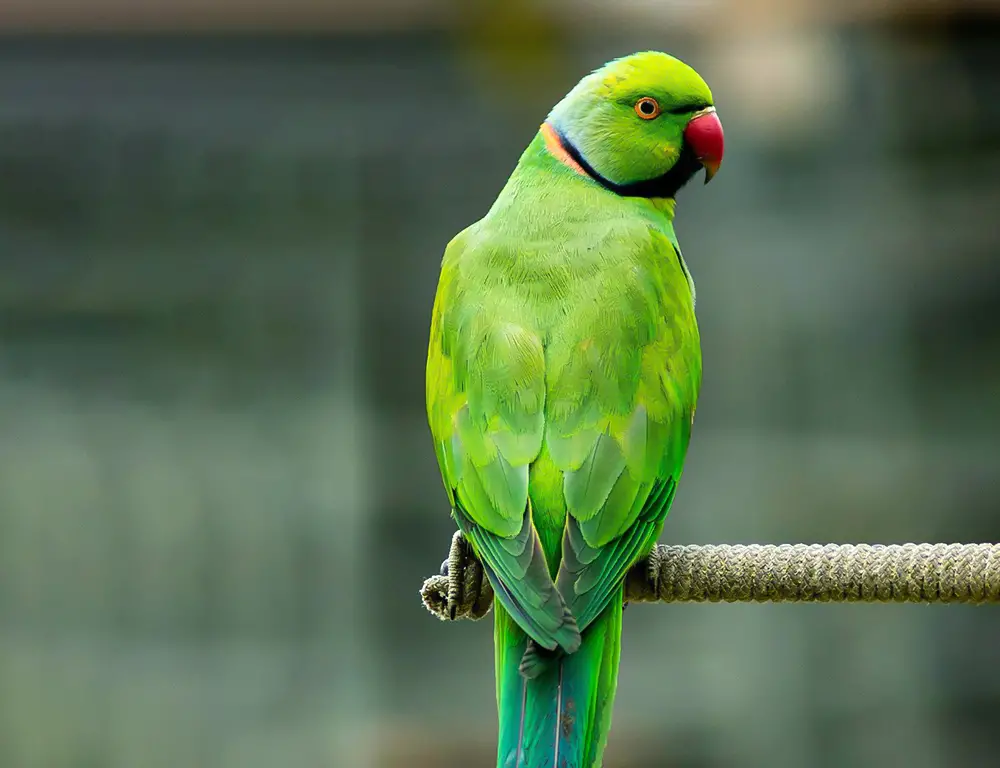

Here are 10 interesting facts about the Echo Parakeet:
1. Endemic to Mauritius
The Echo Parakeet is found only on the island of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean, making it an endemic species. It has evolved in isolation on this island over thousands of years.
2. Once Critically Endangered
Due to habitat loss and hunting, the Echo Parakeet was on the brink of extinction in the late 20th century, with only a handful of individuals remaining in the wild.
3. Conservation Success Story
Thanks to intensive conservation efforts, the population of Echo Parakeets has rebounded significantly in recent years. It serves as a remarkable example of successful species recovery.
4. Large Parakeet Species
The Echo Parakeet is one of the largest species, measuring around 40 to 45 centimeters in length. Its size distinguishes it from other parakeet species found in Mauritius.
5. Vibrant Plumage
These birds are adorned with striking plumage, featuring predominantly bright green feathers with flashes of blue on the wings and hints of yellow and red on the tail feathers.
6. Distinctive Crest
The Echo Parakeet sports a prominent, elongated crest on its forehead. When excited or alarmed, this crest rises, adding to the bird’s distinctive appearance.
7. Loud Vocalizations
Echo Parakeets are known for their loud and raucous calls, which can be heard echoing through the forests of Mauritius. These vocalizations serve various purposes, including communication within flocks and territory defense.
8. Social Behavior
These parakeets are highly social birds, often observed in small flocks or pairs. They engage in cooperative breeding, with both parents participating in incubating eggs and raising chicks.
9. Frugivorous Diet
Echo Parakeets feed on fruits, seeds, and nuts in their forest habitat. Their robust beaks are well-adapted for cracking open hard shells to access nutritious pulp.
10. Symbol of Conservation
The Echo Parakeet has become a symbol of conservation in Mauritius, representing the importance of preserving the island’s unique biodiversity. Its recovery showcases the positive impact of dedicated conservation efforts.
These fascinating facts highlight the ecological significance and conservation importance of the Echo Parakeet, a species emblematic of Mauritius’ natural heritage.
Conclusion
The Echo Parakeet is a shining example of successful conservation efforts and the importance of safeguarding endemic species in their native habitats.
Through collaborative initiatives, habitat restoration, and community engagement, the population of this iconic Mauritian bird has rebounded from the brink of extinction.
However, the work is far from over. Continued vigilance and commitment are essential to ensure the long-term survival of the Echo Parakeet and its fragile island ecosystem.
By protecting this charismatic species, we preserve a unique component of Mauritius’ natural heritage and uphold our responsibility to steward the planet’s rich biodiversity for generations to come.
The Echo Parakeet serves as a poignant reminder of the profound impact that dedicated conservation efforts can have in securing a brighter future for all living beings.