Step into the vibrant world of the Indian Peafowl (Pavo cristatus), where elegance meets grandeur amidst the lush landscapes of the Indian subcontinent.
Renowned for its iridescent plumage and captivating courtship displays, this iconic bird has long captivated the imagination of cultures worldwide.
Join us on a journey to unravel the mysteries and marvels of the Indian Peafowl, as we delve into its rich natural history, cultural significance, and ecological importance.
From the sprawling forests of India to the palatial gardens of ancient civilizations, the Indian Peafowl has left an indelible mark on human history and folklore.
Revered for its beauty and grace, it symbolizes nobility, pride, and renewal, embodying the essence of regal splendor.
As we embark on this exploration, prepare to be mesmerized by the enchanting allure of the Indian Peafowl, a true embodiment of nature’s magnificence and timeless elegance.
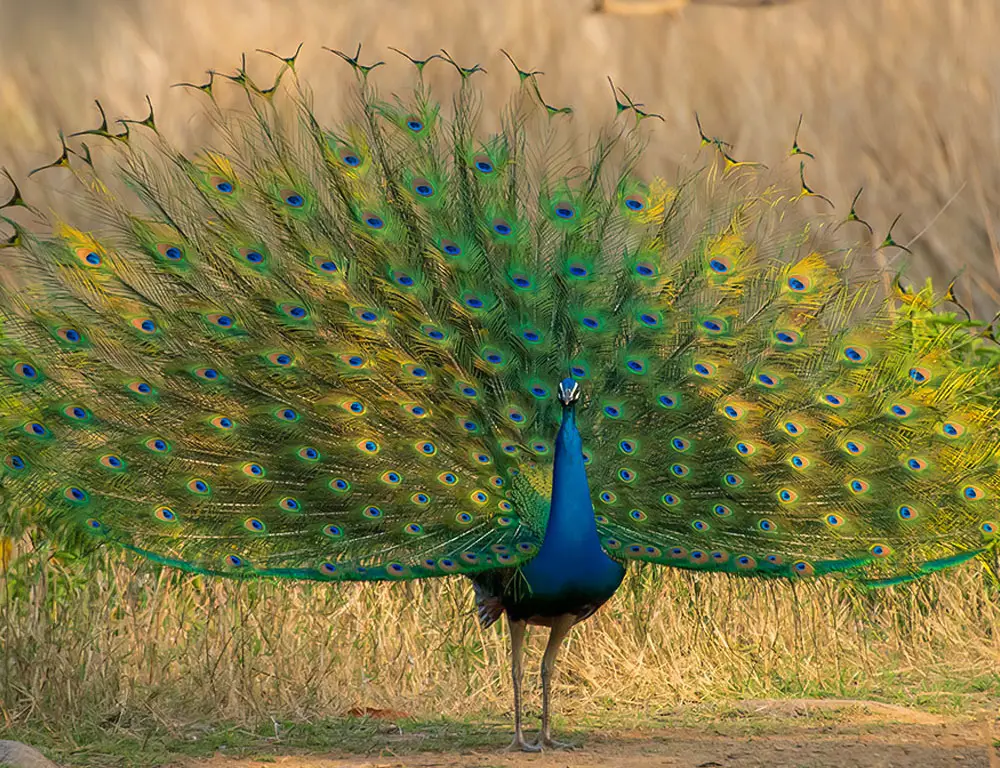

How Do You Identify the Indian Peafowl? Physical Characteristics
The Indian Peafowl, also known as the peacock, is a magnificent bird renowned for its striking appearance and elaborate courtship displays. Here, we explore the key physical characteristics that make the Indian Peafowl a distinctive and iconic species.
Plumage
The most striking feature of the Indian Peafowl is undoubtedly its vibrant plumage. Adult males, known as peacocks, display iridescent blue-green plumage on their upper body, while their lower body is adorned with long, iridescent tail feathers, or “train,” marked with eye-like spots.
These tail feathers can reach lengths of up to 6 feet (1.8 meters) and are prominently displayed during courtship displays to attract mates.
Crest
Both male and female Indian Peafowls have a distinctive crest atop their heads, which they can raise and lower depending on their mood or level of excitement.
The crest consists of a fan of feathers that adds to the bird’s regal appearance and may be raised during displays of aggression or courtship.
Facial Features
The face of the Indian Peafowl is adorned with striking features, including a prominent beak that is relatively short and stout, ideal for cracking open seeds and other food items.
Their eyes are dark and round, surrounded by bare skin that may change color depending on their emotional state.
Size and Shape
Adult males can reach lengths of up to 7 feet (2.1 meters) from beak to tail and weigh between 9 to 13 pounds (4 to 6 kilograms), while females are slightly smaller, averaging around 3 to 6 pounds (1.4 to 2.7 kilograms).
Tail Feathers
The elaborate tail feathers of male Indian Peafowls are among their most iconic features. These feathers, known as “train” feathers, are elongated upper tail coverts raised and fanned out during courtship displays to create a stunning visual spectacle.
Each feather is adorned with eye-like spots, or “ocelli,” which are thought to attract the attention of females during mating rituals.
Color Variation
While the classic image of a peacock showcases its plumage’s vibrant blue-green and bronze hues, Indian Peafowls exhibit various color variations across their range.
Some individuals may have more muted or albino plumage, while others may display variations in the intensity of their colors or the size and shape of their tail feathers.
Sexual Dimorphism
One of the most notable aspects of Indian Peafowls is their sexual dimorphism, with males and females exhibiting distinct differences in appearance.
Males are characterized by their extravagant plumage, including long tail feathers and vibrant colors, while females have a more cryptic appearance, with mottled brown plumage that provides camouflage in their forest habitat.
Voice
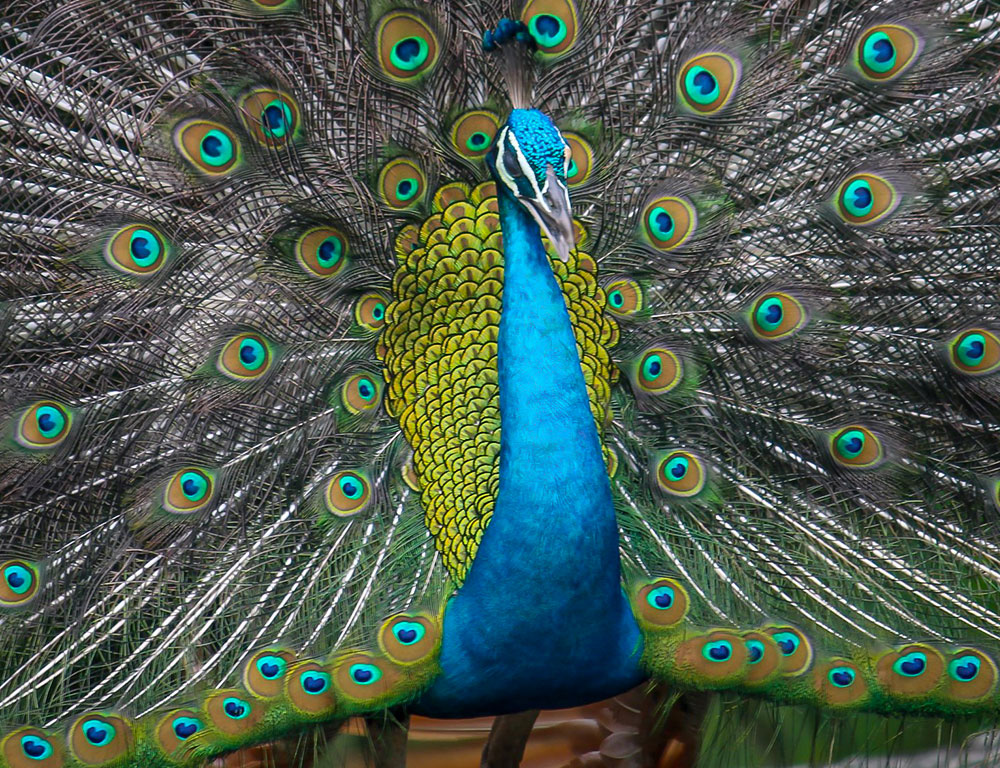

Indian Peafowls are known for their distinctive calls, which vary between males and females. Males produce loud, raucous calls, often called “peacock calls,” particularly during the breeding season when they are trying to attract mates.
In contrast, females emit softer, more musical calls used for communication within their social groups and during interactions with their offspring.
What Is the Taxonomy Level and Nesting Habits of the Indian Peafowl?
Dive into the intricate world of the Indian Peafowl as we uncover its captivating life history and behaviors. From its taxonomy to nesting habits, breeding behaviors, and more, join us to explore this iconic bird species comprehensively.
Taxonomy
| Taxonomy Level | Classification |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Order | Galliformes |
| Family | Phasianidae |
| Genus | Pavo |
| Species | Pavo cristatus |
Food Habitat
The Indian Peafowl is omnivorous, feeding on a diverse diet that includes seeds, grains, fruits, insects, small reptiles, and even small mammals. Its foraging behavior is opportunistic, and it can adapt to various habitats, including grasslands, agricultural fields, and forest edges.
Nesting Habits
| Nest Type | Description |
| Ground Nest | A typical clutch consists of 4 to 8 eggs, although clutch size may vary depending on food availability and habitat quality. |
| Location | Nests are commonly located in concealed spots on the forest floor, grasslands, or agricultural fields. The female selects the nesting site, which may be shared with other females in communal nesting areas. |
| Clutch Size | The female alone incubates the eggs, which hatch after approximately 28 days. During incubation, she relies on cryptic coloration and remains motionless to avoid detection by predators. |
| Incubation Period | The female alone incubates the eggs, which hatch after approximately 28 days. During incubation, she relies on cryptic coloration and remaining motionless to avoid detection by predators. |
| Chick Development | Chicks are precocial, capable of walking and feeding shortly after hatching. They remain under the care of the female, learning essential survival skills such as foraging and predator avoidance. |
| Parental Care | The female provides primary care for the chicks, leading them to food sources and protecting them from predators. Male Indian Peafowls may display protective behavior towards the brood but do not contribute directly to chick rearing. |
Breeding
Indian Peafowls typically breed during the monsoon season, with courtship displays involving elaborate plumage exhibitions, vocalizations, and ritualized behaviors.
Males compete for access to females, displaying their vibrant trains and performing intricate dances to attract mates.
Once paired, the female selects a nesting site, where she lays and incubates her eggs while the male defends the territory from intruders.
Roaming Behavior
Indian Peafowls are often observed roaming in small groups called parties, consisting of a mix of males, females, and juveniles. These parties forage together and provide additional safety and social interaction for the individuals within the group.
What Is the Range Map and Conservation Status of the Indian Peafowl?
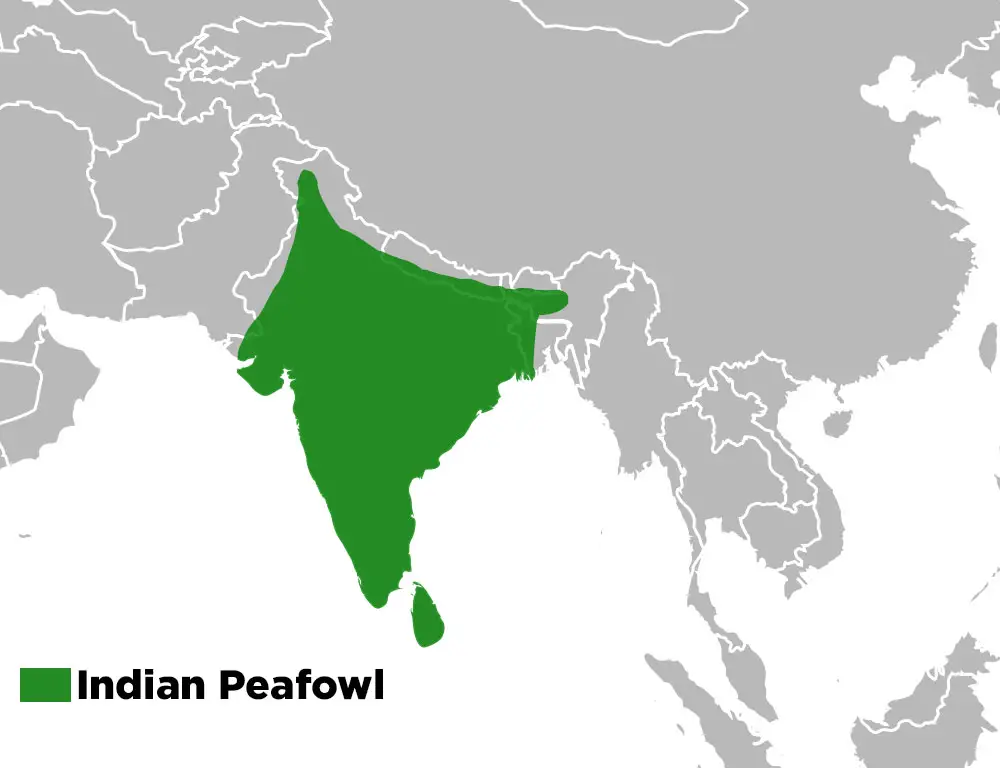
Join us as we delve into the distribution and conservation status of the majestic Indian Peafowl.
Range Map
The Indian Peafowl is native to the Indian subcontinent, where it is found across a wide range of habitats, including grasslands, forests, agricultural areas, and urban landscapes. Its distribution extends from the foothills of the Himalayas in northern India to the southern tip of the Indian peninsula.
Additionally, populations of Indian Peafowls are also present in neighboring countries such as Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka.
Conservation Status
The Indian Peafowl is classified as Least Concern (LC) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, indicating that it is not currently facing imminent threats of extinction.
Its large population size, widespread distribution, and ability to adapt to various habitats contribute to its stable conservation status. However, localized declines may occur due to habitat loss, hunting, and predation by domestic animals.
Conservation efforts focused on habitat protection, sustainable land management, and community-based conservation initiatives are essential for ensuring the continued survival of this iconic bird species.
What Are the Common Diseases and Treatments of the Indian Peafowl?
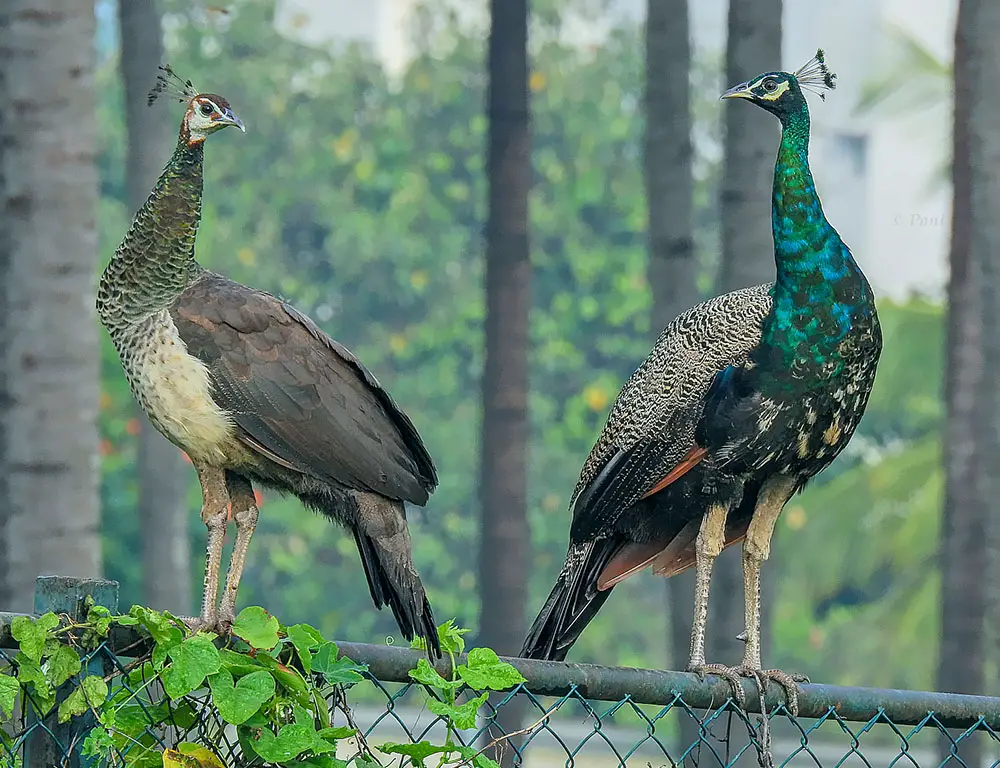

Indian Peafowls are susceptible to various diseases and health issues. Here are some common diseases and their treatments:
Newcastle Disease
A highly contagious viral disease affecting the respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems. Treatment involves supportive care and vaccination to prevent outbreaks.
Avian Pox
Caused by a virus transmitted by mosquitoes, resulting in wart-like skin and mucous membranes lesions. Treatment focuses on supportive care and preventing mosquito exposure.
Coccidiosis
A parasitic disease affecting the intestinal tract leads to diarrhea and weight loss. Treatment includes anti-parasitic medications and maintaining clean living conditions.
Aspergillosis
Fungal infection causes respiratory distress and lesions in the lungs. Treatment involves antifungal medications and improving ventilation in the enclosure.
Worm Infestations
Internal parasites such as roundworms and tapeworms can affect Indian Peafowls. Treatment includes deworming medications prescribed by a veterinarian.
Bumblefoot
A bacterial infection causes swelling and inflammation in the feet. Treatment involves antibiotics and improving perching surfaces to prevent injury.
Ectoparasites
External parasites like mites and lice can infest the feathers and skin. Treatment includes topical parasiticides and maintaining clean living conditions.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Inadequate diet can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients. Treatment involves dietary supplementation and providing a balanced diet.
Heat Stress
High temperatures can cause heat stress and dehydration. Treatment includes providing shade, fresh water, and misting to cool the birds down.
Trauma and Injuries
Injuries from fights, falls, or predator attacks require immediate veterinary care, including wound cleaning, pain management, and supportive care.
Treatment of Common Diseases in Indian Peafowls

It’s essential to consult a qualified avian veterinarian for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of any health issues affecting Indian Peafowls. However, here are some potential treatments:
Newcastle Disease
Treatment involves supportive care, fluid therapy, and administration of antiviral medications. Vaccination is crucial for prevention.
Avian Pox
Supportive care to alleviate symptoms, such as applying topical treatments to lesions and preventing mosquito exposure through insecticides or mosquito nets.
Coccidiosis
Anticoccidial medications are prescribed by a veterinarian, along with improved sanitation practices to reduce exposure to contaminated feces.
Aspergillosis
Antifungal medications are administered orally or through nebulization and environmental modifications to reduce fungal spore exposure.
Worm Infestations
Deworming medications prescribed by a veterinarian based on fecal analysis, improved hygiene practices and prevention of re-infestation.
Bumblefoot
Antibiotics to treat a bacterial infection, bandaging affected feet, and providing soft, clean bedding to reduce pressure on the feet.
Ectoparasites
Topical treatments with parasiticides, such as sprays or powders, and regular cleaning and disinfection of the enclosure to prevent re-infestation.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Dietary supplementation with vitamins and minerals as a veterinarian prescribes, along with adjusting the diet to ensure nutritional adequacy.
Heat Stress
We are providing shaded areas, misting systems, ample fresh water to prevent dehydration and heatstroke, and monitoring birds for signs of heat stress.
Trauma and Injuries
Immediate veterinary care, including wound cleaning, debridement, pain management, and antibiotic therapy to prevent infection and promote healing.
10 Fun Facts About the Indian Peafowl

Here are some interesting facts about Indian Peafowl:
1. Iconic Plumage
Male Indian Peafowls, or peacocks, boast stunning iridescent blue-green plumage, while females, or peahens, exhibit more subtle brown tones to blend in with their surroundings.
2. Spectacular Courtship
During courtship displays, peacocks fan out their extravagant train feathers into a stunning display, vibrating them to create a mesmerizing visual and auditory spectacle to attract peahens.
3. Limited Flight
Despite their large size and elaborate plumage, Indian Peafowls are relatively poor fliers and prefer to spend most of their time on the ground, using flight mainly for short bursts to escape predators.
4. Vocal Variations
Indian Peafowls are not just known for their visual displays but also for their distinctive calls. Peacocks emit loud, trumpeting calls, while peahens produce more subdued, cackling sounds.
5. Perching Preference
Despite their ground-dwelling nature, Indian Peafowls roost and nest in trees at night, using their strong legs and feet to perch on branches, where they are safer from nocturnal predators.
6. Social Behavior
Indian Peafowls are social birds and often gather in small groups called parties, consisting of several females and their offspring, led by a dominant male.
7. Cultural Significance
Revered for their beauty and grace, Indian Peafowls hold cultural significance in many societies, symbolizing beauty, prosperity, and spirituality, and are often depicted in art, mythology, and folklore.
FAQs
What is the lifespan of an Indian Peafowl?
Indian Peafowls can live up to 15-20 years in the wild, but they may have shorter lifespans due to predation, diseases, or habitat threats.
Do both male and female Indian Peafowls have elaborate plumage?
No, only male Indian Peafowls, known as peacocks, have extravagant plumage with iridescent colors and long train feathers. Females, called peahens, have more subdued plumage for camouflage.
How do Indian Peafowls protect themselves from predators?
Indian Peafowls rely on their keen eyesight and ability to blend into their surroundings for protection. They also use their loud calls and quick bursts of flight to evade predators.
What do Indian Peafowls eat?
Indian Peafowls are omnivorous and feed on various foods, including grains, seeds, fruits, insects, small reptiles, and even small mammals.
How do Indian Peafowls communicate?
Indian Peafowls communicate through a variety of vocalizations and visual displays. Male peafowls, or peacocks, produce loud calls, known as “roars” or “meows,” to attract females and establish territory.
Conclusion
The Indian Peafowl symbolizes beauty, grace, and cultural significance, enchanting observers with its majestic plumage and captivating displays.
Across the landscapes of the Indian subcontinent and beyond, this iconic bird embodies the essence of regal splendor, leaving an indelible mark on human history and folklore.
As we reflect on its rich natural history and ecological importance, we are reminded of the need to conserve and protect its habitats to ensure the continued existence of this magnificent species.
Let us cherish the Indian Peafowl for its aesthetic beauty and role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and inspiring wonder in all who behold its iridescent brilliance.
Through appreciation and conservation efforts, we can ensure that future generations continue to marvel at the timeless elegance of the Indian Peafowl. Enjoy its natural history that has fascinated us all.