Muscovy ducks captivate observers with their intricate diversity and gender-specific traits. Beyond the surface variations, these waterfowl showcase nuanced behaviors and features that distinguish males from females.
From nesting habits to aggressive tendencies, feather loss to eye color, and overall appearance to comb distinctions, the disparities provide a captivating glimpse into the intricate dynamics of Muscovy duck populations.
This exploration sheds light on the multifaceted nature of these avian species and deepens our understanding of the roles these differences play in their survival, reproduction, and interactions within their environment.
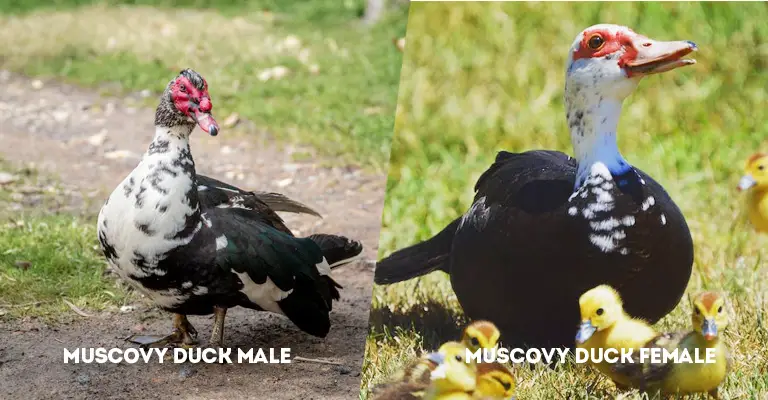

Key Differences Between Male and Female Muscovy Ducks
Male and female Muscovy ducks (Cairina moschata) exhibit several key differences in terms of physical characteristics, behavior, and sometimes even vocalizations.
Here are some of the key differences:
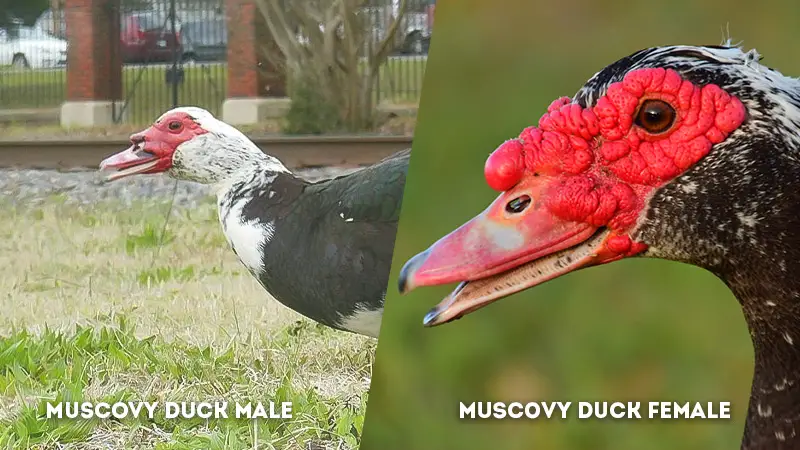
Bill Shape: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: The bill of a male Muscovy duck is a remarkable feature that sets it apart. It is characterized by a straight, flat, and wide shape.
This billing structure is designed to aid in foraging and feeding habits, allowing the male to grasp and consume a variety of aquatic organisms with ease. - Female Muscovy Duck: In contrast, the bill of the female Muscovy duck presents a distinct curvature. It is narrower and more pointed, with a noticeable ridge down the middle.
This specialized bill design is adapted to the female’s foraging requirements and plays a vital role in her diet.
Size: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: Male Muscovy ducks are generally larger in size compared to their female counterparts. This size difference is particularly evident in body mass and overall dimensions. The larger size of the males contributes to their presence and dominance within their social group.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks, on the other hand, tend to be smaller in size. This size distinction is observed not only in body mass but also in overall body proportions. The size discrepancy between males and females is often used as a primary visual indicator of their sex.
Plumage: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: The plumage of male Muscovy ducks exhibits a striking iridescence. The colors of their feathers are more vibrant and lustrous, with shades of green, black, and metallic hues. This iridescent plumage is believed to play a role in attracting potential mates during courtship displays.
- Female Muscovy Duck: In contrast, the plumage of female Muscovy ducks is less iridescent and lacks the shimmering qualities found in males. Their feathers are typically more subdued in color, often displaying shades of brown and mottled patterns.
This muted plumage serves as a form of camouflage to protect females during nesting and incubation.
Caruncles: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: Caruncles are fleshy, wrinkled protuberances found around the face and neck of Muscovy ducks.
In males, these caruncles are larger and more prominent, contributing to their distinct appearance. These facial caruncles are often used in displays of dominance and courtship rituals. - Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks possess smaller and less conspicuous caruncles in comparison to males. The size difference in caruncles is one of the external indicators that can help identify the sex of Muscovy ducks.
Head Shape: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
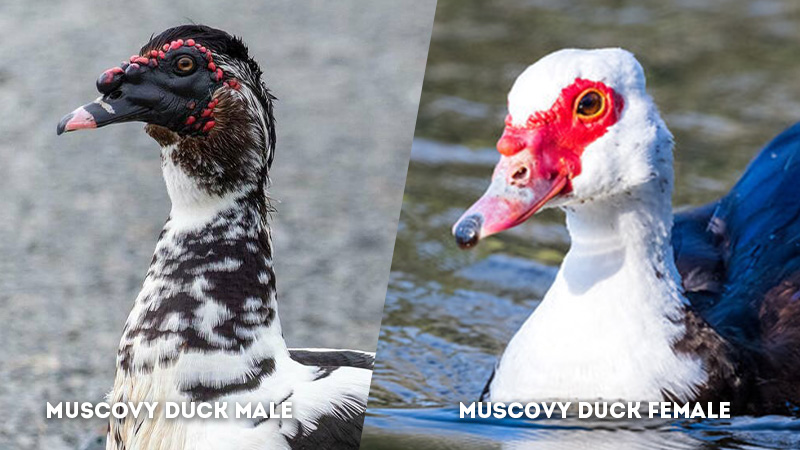

- Male Muscovy Duck: The head of a male Muscovy duck is characterized by its rounder and more robust shape.
This head structure complements their larger overall size and adds to their imposing presence. The head of the male duck is often held high during displays of dominance and mating behaviors. - Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks exhibit a sleeker and more streamlined head shape. The reduced bulkiness of their head corresponds to their smaller size and contributes to their agility during nesting and feeding activities.
Voice: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: The vocalizations of male Muscovy ducks are more pronounced and frequent. They emit loud calls that are often heard during courtship displays and territorial disputes.
The vocal range of males is broader, including various quacks, grunts, and hissing sounds that they use to assert dominance and attract females. - Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks, in contrast, tend to be quieter and emit less frequent calls. Their vocalizations are generally softer and more subdued, used primarily for communication within their social group and to maintain contact with their ducklings.
Body Shape: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
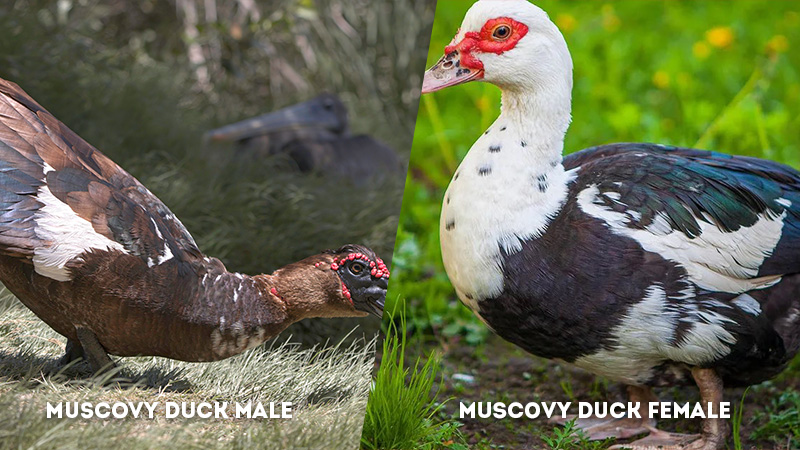

- Male Muscovy Duck: The body shape of male Muscovy ducks is characterized by bulkiness and a heavier appearance. This robust body structure contributes to their dominant presence and competitive behavior during interactions with other males.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks exhibit a sleeker and lighter body shape. Their body proportions are adapted for efficiency during nesting, incubation, and movement, allowing them to navigate water and land with greater agility.
Wing Color: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
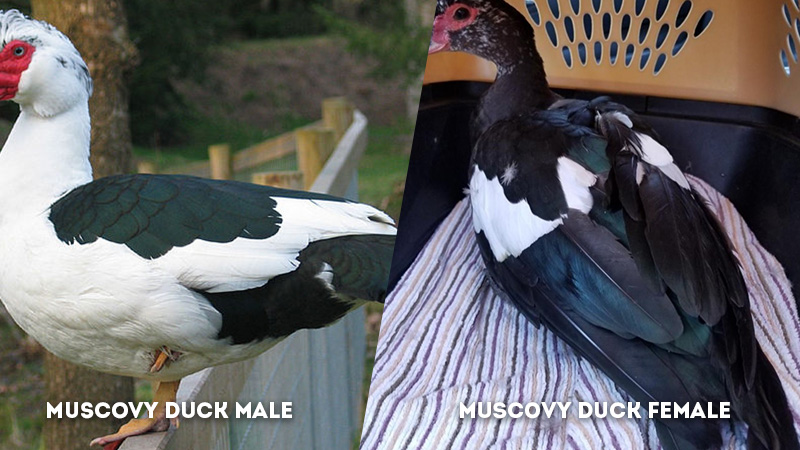

- Male Muscovy Duck: The coloration of the wing feathers in male Muscovy ducks tends to be darker and more vibrant. These bold wing colors often serve as a visual cue during courtship displays and interactions, showcasing their attractiveness and vitality.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks possess lighter and less vibrant wing colors. This subtler wing coloration helps them blend into their surroundings, offering a form of protection while engaged in nesting and caring for their young.
Tail: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
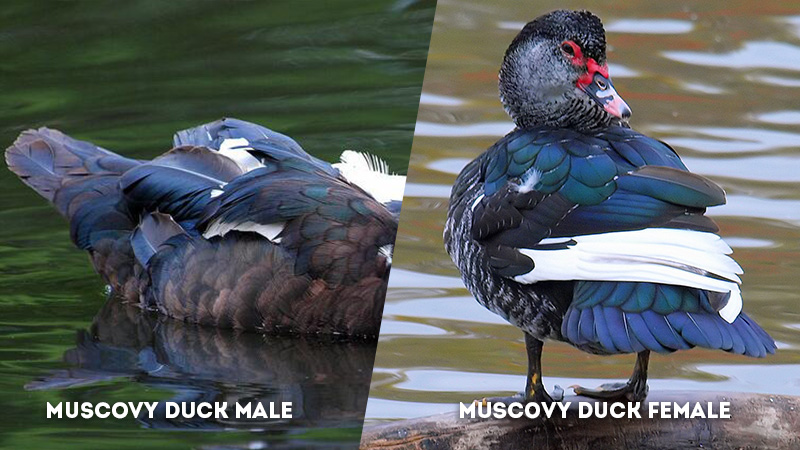

- Male Muscovy Duck: The tail of a male Muscovy duck is elongated and more pointed. This tail shape adds to their overall elegance and is often displayed prominently during courtship rituals, enhancing their visual appeal.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks have shorter and rounder tails compared to males. The tail’s shape is adapted for nesting activities, providing them with greater comfort while incubating eggs and caring for hatchlings.
Behavior: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: Male Muscovy ducks tend to exhibit more assertive and occasionally aggressive behavior. They engage in dominance displays, territorial battles, and courtship rituals involving elaborate movements and vocalizations to attract potential mates.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks are generally less confrontational and more focused on nesting and raising their offspring.
They display nurturing behavior, diligently attending to their nest and ducklings while maintaining a cooperative presence within their social group.
Nesting Behavior: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: Male Muscovy ducks are less involved in nesting activities. They typically do not engage in nest building, incubation, or caring for the eggs. Instead, males focus on displaying their dominance and courting females during the mating season.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks play a significant role in nesting. They invest time and effort in selecting suitable nesting sites, constructing nests from available materials, and laying eggs. The females are responsible for incubating the eggs and providing care to the ducklings after hatching.
Brooding Behavior: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: Male Muscovy ducks do not participate in brooding behavior. Their role in reproduction is limited to mating and displaying dominance.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks are actively engaged in brooding behavior. They incubate the eggs by sitting on the nest to regulate temperature and humidity, ensuring the proper development of the embryos.
After hatching, females continue to provide warmth, protection, and guidance to their young ducklings.
Feather Loss (Molt): Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: During molting, male Muscovy ducks generally experience less feather loss compared to females. This reduced feather loss may be attributed to their role in territorial displays, which requires a consistent and impressive appearance.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks tend to experience more extensive feather loss during molting. This phenomenon is linked to their involvement in nesting, brooding, and caring for their young. Molting is energy-intensive, and the loss of feathers allows females to allocate resources to their reproductive efforts.
Eye Color: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
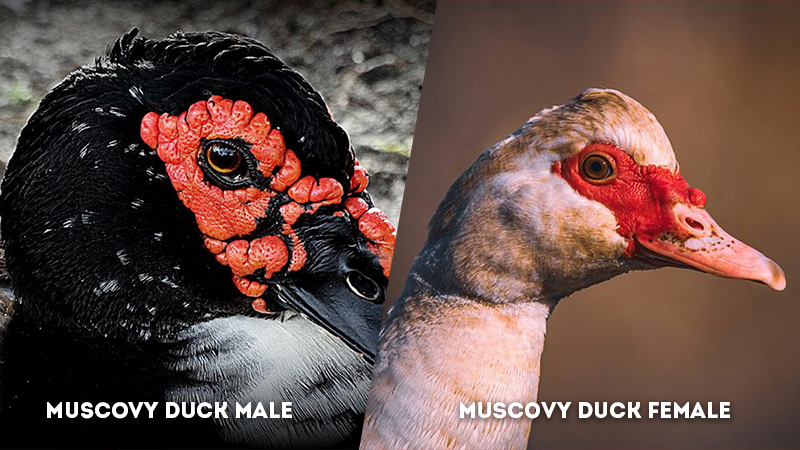

- Male Muscovy Duck: The eye color of male Muscovy ducks is often brighter and more intense. This heightened eye coloration contributes to their striking appearance and may play a role in attracting potential mates during courtship.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks typically have duller and less intense eye colors. This subtle eye coloration aligns with their camouflage-based survival strategies, allowing them to blend into their surroundings while nesting and caring for their offspring.
Comb: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: In some breeds, male Muscovy ducks may possess a more prominent and larger comb on top of their heads. The comb serves as a visual marker of their gender and may also be involved in thermoregulation.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks usually have a smaller or absent comb. This difference is another visual cue that can assist in distinguishing between males and females, especially in breeds where the comb is present in males.
Overall Appearance: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: Male Muscovy ducks boast a bolder and more striking appearance. Their larger size, prominent caruncles, and iridescent plumage make them visually captivating.
The overall appearance of males is geared towards attracting potential mates and asserting dominance within their social groups. - Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks possess a more subdued and camouflaged appearance. Their muted plumage and smaller size contribute to their ability to blend into their surroundings while nesting and caring for their young.
Bill Color: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: The bill color of male Muscovy ducks tends to be brighter and more colorful. This vibrant bill coloration is part of their courtship display and is used to attract females during mating rituals.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks exhibit duller and less colorful bill coloration. Their bill color aligns with their protective camouflage strategy and serves practical purposes during nesting and foraging.
Leg Length: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
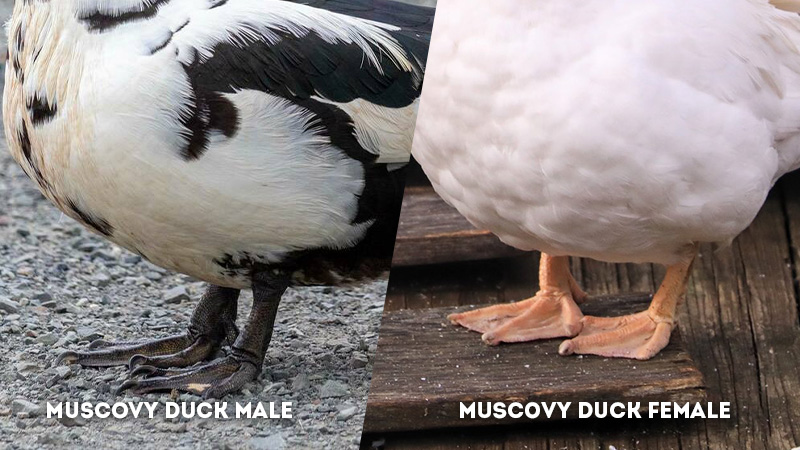
- Male Muscovy Duck: Male Muscovy ducks typically have longer legs compared to females. This difference in leg length corresponds to their larger body size and may also contribute to their confident and dominant demeanor.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks possess shorter legs, which are well-suited for efficient movement on land and in water. The leg length of females aligns with their reproductive and nurturing roles.
Sexual Maturity: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: Male Muscovy ducks achieve sexual maturity later than females. This delayed maturity is often reflected in their behaviors and physical traits, indicating their readiness for reproductive activities.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks attain sexual maturity at an earlier age compared to males. This early maturity aligns with their role in nesting and raising offspring.
Aggressive Behavior Towards Other Ducks: Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female
- Male Muscovy Duck: Male Muscovy ducks are more prone to aggressive behavior, particularly towards other males. Dominance displays, territorial disputes, and confrontations are common as males establish their position within the social hierarchy.
- Female Muscovy Duck: Female Muscovy ducks exhibit less aggressive behavior towards other ducks, including both males and females. Their interactions tend to be more cooperative, focused on nesting, and protecting their ducklings.
Muscovy Duck Male Vs Female: Comparison Table
| Feature | Male Muscovy Duck | Female Muscovy Duck |
|---|---|---|
| Bill Shape | Straight, flat, wide | Curvier, pointy, narrow, with ridge |
| Size | Generally larger | Generally smaller |
| Plumage | More iridescent colors | Duller, less iridescent colors |
| Caruncles | Larger and more prominent | Smaller and less prominent |
| Head Shape | Larger, rounder head | Smaller, sleeker head |
| Voice | Louder and more frequent calls | Quieter and less frequent calls |
| Body Shape | Bulkier and heavier | Sleeker and lighter |
| Wing Color | Darker and more vibrant | Lighter and less vibrant |
| Tail | Longer and more pointed | Shorter and rounder |
| Behavior | Aggressive towards other males | Less aggressive, more social |
| Nesting Behavior | Less involved in nesting | More involved in nest building |
| Brooding Behavior | Typically not involved | Involved in incubation and brooding |
| Feather Loss (Molt) | Less feather loss during molt | More feather loss during molt |
| Eye Color | Brighter and more intense | Duller and less intense |
| Comb | Prominent and larger in some breeds | Smaller or absent in most females |
| Overall Appearance | More aggressive toward other males | Subdued and camouflaged appearance |
| Bill Color | Brighter and more colorful | Duller and less colorful |
| Leg Length | Longer | Shorter |
| Sexual Maturity | Attained later | Attained earlier |
| Aggressive Behavior Towards Other Ducks | Less aggressive toward other females | Less aggressive towards other females |
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, male and female Muscovy ducks have distinct nesting habits. Female Muscovy ducks are primarily responsible for nest building, incubation, and caring for the eggs and ducklings. In contrast, male Muscovy ducks are less involved in nesting activities and focus more on displaying dominance and courting females.
The aggressive behavior of male Muscovy ducks is often triggered by territorial disputes and competition for mates. During the mating season, males engage in dominance displays and confrontations with other males to establish their territory and attract potential mates.
Male Muscovy ducks generally experience less feather loss during molting compared to females. This difference is related to their roles and behaviors. Males allocate more energy towards displays and interactions, requiring a consistent appearance, while females invest energy in nesting and brooding, contributing to more extensive feather loss.
Female Muscovy ducks typically attain sexual maturity at an earlier age than males. Female ducks can reach sexual maturity around 5 to 6 months old, while male ducks may take longer and become sexually mature around 6 to 7 months old.
The differences in eye color and comb contribute to the visual cues that help differentiate between male and female Muscovy ducks. Brighter and more intense eye color is often associated with males, aiding in courtship displays. The presence of a larger and more prominent comb in males (in some breeds) serves as a distinct external feature for gender identification, enhancing their overall appearance.
To Recap
The differences between male and female Muscovy ducks extend far beyond mere physical distinctions. These variances encompass behaviors, traits, and adaptations that illuminate the complex tapestry of nature’s design.
Each aspect, whether it’s in their nesting roles, feather patterns, or aggressive tendencies, contributes to the intricate dance of life within this species.
By appreciating and comprehending these unique attributes, we gain a richer comprehension of the intricate balance that shapes Muscovy ducks’ lives and their invaluable role in the broader ecosystem.