As denizens of the skies, birds navigate vast expanses of the natural world, encountering various challenges along their migratory routes or within their local habitats.
Among these challenges, roundworm infestations emerge as a prevalent and consequential concern for avian populations.
This article delves into the fascinating realm of roundworms in birds, exploring the intricate dynamics between these parasitic organisms and their feathered hosts.
From the ubiquitous sparrows in urban landscapes to majestic eagles soaring in the wild, no bird species is immune to the potential threat posed by roundworms.
Join us on a journey through the life cycle of these parasitic invaders, understanding their impact on avian health, behavior, and overall ecosystem dynamics.
As we uncover the nuances of this avian-parasite relationship, a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance within the avian world will emerge, shedding light on the ongoing efforts to mitigate the effects of roundworm infestations in our feathered companions.
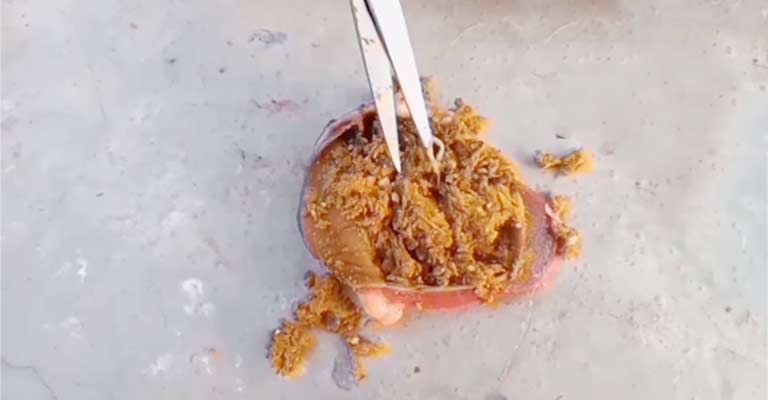

All About Roundworms in Birds
Here, we’ll explore all about roundworm infestation in birds, from how they grow and their effects on bird health.
Egg to Larva: A Covert Beginning
Nestled inconspicuously in bird habitats, roundworms embark on their clandestine journey as microscopic eggs.
Once welcomed into a host’s digestive system, these eggs undergo a transformative metamorphosis, hatching into larvae and setting the stage for a complex parasitic odyssey.
Larval Migration: Navigating the Avian Terrain
Undetected by the unsuspecting bird, the larvae embark on a migratory adventure within the avian body. Their journey, though unseen, leaves a tangible impact, affecting vital organs and potentially causing harm.
This phase becomes a perilous chapter, challenging the host’s health and altering its behavioral landscape.
Maturation in the Gut: Establishing Residence
The larvae mature into adulthood, taking residence in the bird’s gastrointestinal tract. This colonization disrupts the delicate balance of nutrient absorption, paving the way for malnutrition and compromising the bird’s overall fitness.
The once harmonious gut environment becomes a battleground for survival.
Physical Toll: Weighing Down Wings of Flight

As avian roundworms establish their dominion, the physical toll on their hosts becomes evident. Impaired flight, hindered foraging abilities, and increased vulnerability to predators ensues, creating a domino effect that jeopardizes the bird’s survival instincts and, ultimately, its place in the ecosystem.
Behavioral Alterations: The Unseen Consequences
Beyond the visible physical repercussions, roundworm infestations exert a subtle yet profound influence on bird behavior.
From disrupted feeding patterns to diminished reproductive success, these parasites manipulate the very essence of their hosts’ lives, creating a narrative of unseen consequences.
Ecological Ramifications: A Ripple Effect
The repercussions extend beyond individual birds, creating a ripple effect within the ecosystem.
Disruptions in avian populations reverberate through interconnected food webs, affecting other species and challenging the delicate equilibrium of nature. The silent drama of roundworms unfolds, casting shadows on the ecological stage.
Research Frontiers: Unraveling Mysteries

In laboratories and field studies, scientists diligently unravel the mysteries of avian roundworms.
Their investigations delve into the prevalence, transmission, and intricate dynamics of host-parasite relationships, forming the bedrock for targeted conservation strategies aimed at preserving avian biodiversity.
Preventive Measures: Safeguarding Avian Habitats
Conservationists, armed with knowledge from ongoing research, implement measures to curtail roundworm transmission.
Habitat management, meticulous bird population monitoring, and public awareness campaigns advocating responsible bird feeding practices become crucial elements in safeguarding avian habitats.
Veterinary Interventions: Healing Feathers
At the forefront of defense against roundworm infestations, veterinarians deploy deworming medications and supportive care to alleviate the impact on infected birds.
Rehabilitation efforts play a pivotal role in restoring affected individuals to their natural state, fostering hope for a healthier avian population.
What Drugs Are Used to Cure Roundworms in Birds?
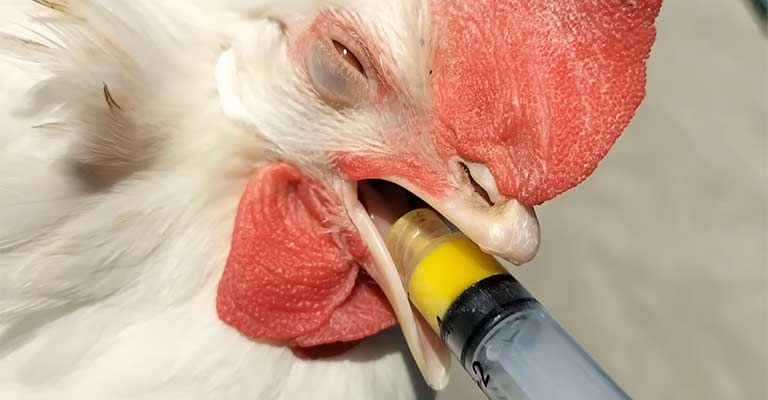
Avian deworming plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and vitality of our feathered companions.
Various antiparasitic medications are employed to combat roundworms and other internal parasites that can afflict birds. Below, we explore the commonly used drugs, their mechanisms, and the considerations involved in administering them.
Fenbendazole: A Broad-Spectrum Solution
Fenbendazole is a widely used anthelmintic drug effective against a broad spectrum of parasites, including roundworms.
Administered orally or mixed with food, fenbendazole disrupts the parasites’ ability to absorb nutrients, ultimately leading to their expulsion from the bird’s gastrointestinal tract.
Ivermectin: Targeting External and Internal Parasites
Ivermectin is a versatile medication effective against both external parasites like mites and internal parasites such as roundworms.
Administered topically, orally, or through injection, ivermectin interferes with the nervous system of parasites, rendering them immobile and ultimately causing their demise.
Praziquantel: Specialized for Tapeworms
While roundworms are a common concern, tapeworms pose a distinct challenge. Praziquantel is the drug of choice for treating tapeworm infestations in birds.
It works by disrupting the tapeworm’s integrity, making it susceptible to the bird’s digestive processes.
Levamisole: Immune System Boost and Deworming
Levamisole serves a dual purpose by not only expelling internal parasites but also stimulating the bird’s immune system.
This medication is effective against roundworms and certain types of external parasites. It is typically administered orally or added to the bird’s drinking water.
Moxidectin: Long-Lasting Protection
Moxidectin is known for its prolonged effectiveness, providing extended protection against a range of internal and external parasites.
Administered orally, moxidectin disrupts the nervous system of parasites, ensuring sustained control of infestations over an extended period.
Albendazole: An Alternative Anthelmintic
Albendazole, like fenbendazole, belongs to the benzimidazole class of anthelmintics. It is effective against various gastrointestinal parasites, including roundworms.
Administered orally, albendazole disrupts the parasites’ microtubules, inhibiting their ability to feed and reproduce.
Dosage Accuracy
Accurate dosage is crucial for the effectiveness and safety of deworming medications. Dosages are often weight-dependent, requiring knowledge of the bird’s weight or an estimation based on species-specific averages.
Route of Administration
Medications can be administered orally, topically, or through injection. The chosen route depends on the medication type, the bird species, and the severity of the infestation. Veterinary guidance is essential to determine the most appropriate method.
Repeat Treatments
Deworming may require repeated treatments to ensure the complete eradication of parasites. The frequency of treatments depends on factors such as the severity of the infestation, the lifecycle of the targeted parasites, and the specific medication used.
Monitoring for Side Effects
While deworming is essential, monitoring for potential side effects is equally important. Birds may exhibit transient changes in behavior or appetite after treatment. Consulting a veterinarian helps address any concerns and ensures a balanced approach to parasite control.
How Do You Clean Roundworm Eggs?
Roundworm eggs can persist in the environment, posing a potential risk to birds and other animals. Proper cleaning and decontamination are crucial to reduce the transmission of these parasitic eggs.
Below, we delve into effective strategies for cleaning roundworm eggs, emphasizing key steps and considerations.
Identify Contaminated Areas
Start by identifying areas where roundworm eggs are likely to be present. These areas often include bird feeding stations, roosting sites, and places with bird droppings. Regular inspections are essential to promptly address potential contamination.
Wear Protective Gear
Before initiating the cleaning process, don appropriate protective gear. This may include disposable gloves, a mask, and if working in an enclosed space, protective eyewear. These precautions minimize the risk of direct contact with potentially harmful pathogens.
Remove Visible Debris
Begin by removing visible debris such as bird droppings, feathers, and nesting materials. Use a scraper or shovel to carefully collect the material, placing it in a sealed plastic bag for proper disposal.
Dampen the Area
Before cleaning, dampen the affected area with water. This helps prevent the release of airborne particles during the cleaning process. Use a spray bottle or hose to moisten the surfaces where roundworm eggs may be present.
Cleaning Solutions
Several cleaning solutions are effective in neutralizing roundworm eggs. Common options include a 10% bleach solution (1 part bleach to 9 parts water) or specialized disinfectants recommended for use in outdoor environments. Apply the chosen solution generously to the dampened surfaces.
Scrubbing and Brushing
Employ a stiff brush or scrubbing tool to thoroughly agitate the cleaning solution on the surfaces. Pay extra attention to crevices, cracks, and areas where droppings may have accumulated.
The mechanical action of scrubbing aids in dislodging and breaking down the egg material.
Allow Dwell Time
After scrubbing, allow the cleaning solution to remain on the surfaces for an appropriate dwell time. This period ensures the disinfectant has sufficient contact time to neutralize the roundworm eggs effectively. Refer to the product instructions for recommended dwell times.
Rinse and Repeat
Rinse the treated surfaces with clean water to remove residual cleaning solution and debris. Repeat the cleaning process if necessary, especially in areas with persistent contamination. Thoroughness is key to achieving effective decontamination.
Preventive Measures
Implement preventive measures to minimize the risk of recontamination. This includes regularly cleaning and disinfecting bird feeders, rotating feeding areas, and maintaining a clean and hygienic environment. Consider using removable liners in bird baths for easier cleaning.
Dispose of Cleaning Materials
Dispose of used cleaning materials, such as gloves and brushes, in sealed plastic bags. Properly discard these bags according to local waste disposal guidelines. This prevents the spread of contaminants during disposal.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regularly monitor and maintain cleaned areas to ensure ongoing cleanliness. Establish a routine for inspection and cleaning to promptly address any signs of recontamination. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of roundworm transmission.
Cleaning roundworm eggs requires a systematic and thorough approach to effectively eliminate potential sources of contamination.
By wearing protective gear, using appropriate cleaning solutions, and implementing preventive measures, you can contribute to creating a safer environment for birds and reduce the risk of parasitic infestations.
FAQs
How do birds contract roundworm infections?
Birds commonly contract roundworm infections by ingesting contaminated food, water, or intermediate hosts. Infected birds shed roundworm eggs into the environment, where they can persist and be ingested by other birds, perpetuating the cycle.
What are the visible signs of roundworm infestations in birds?
Symptoms of roundworm infestations vary but may include weight loss, lethargy, changes in plumage quality, and behavioral alterations such as decreased foraging or impaired flight. Veterinary consultation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Can roundworms in birds affect human health?
While the roundworm species affecting birds typically do not pose a direct threat to humans, some precautions are necessary. Practicing good hygiene, especially when handling bird droppings, and avoiding consumption of undercooked game birds can reduce any potential risk.
How can bird enthusiasts contribute to the prevention of roundworm infestations?
Bird enthusiasts can play a pivotal role by maintaining clean bird feeders, practicing responsible bird feeding to minimize crowding, and participating in habitat conservation efforts.
Are there natural predators or controls for avian roundworms?
Various natural controls exist, including predators such as certain insects and other birds that consume roundworm-infected hosts. Additionally, maintaining a healthy ecosystem with diverse flora and fauna contributes to a balanced environment that can naturally regulate roundworm populations.
Conclusion
The intricate interplay between birds and roundworms unveils a complex narrative of survival and adaptation in the avian realm.
As we’ve explored the life cycle and impact of these parasitic invaders, it becomes evident that addressing roundworm infestations is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of our avian counterparts.
The challenges posed by roundworms extend beyond individual birds, influencing entire ecosystems and even posing potential threats to human health in some instances.
However, ongoing research and conservation initiatives underscore our commitment to understanding and mitigating the effects of these parasitic organisms.
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the natural world, our appreciation for the delicate balance between hosts and parasites grows.
The study of roundworms in birds serves as a microcosm of the broader ecological intricacies at play, highlighting the interconnectedness of all living organisms in the intricate tapestry of life.