The Snowy Albatross, or Diomedea exulans, is a majestic seabird renowned for its impressive size, elegant flight, and iconic presence in the Southern Ocean.
With a wingspan reaching up to 3.5 meters, it ranks among Earth’s most giant flying birds, embodying a remarkable blend of power and grace.
Named for its predominantly white plumage contrasting with striking black markings, the Snowy Albatross navigates vast oceanic expanses with remarkable ease, utilizing dynamic soaring techniques to cover thousands of kilometers in search of food and suitable breeding grounds.
As a symbol of resilience and adaptation to life in harsh marine environments, the Snowy Albatross captivates the imagination and inspires awe, highlighting the intricate beauty and interconnectedness of the Southern Ocean ecosystem. Stay sharp.
Identifying Criteria of Snowy Albatross
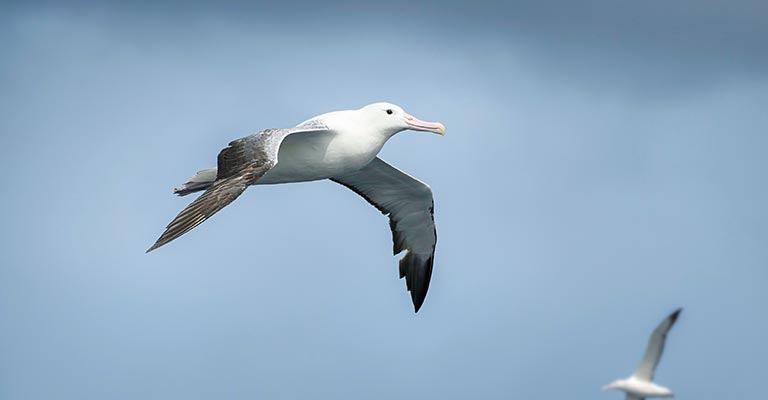

The Snowy Albatross, scientifically known as Diomedea exulans, is a magnificent seabird belonging to the albatross family.
Identifying this specific bird can be challenging due to its similarity to other albatross species, but distinct characteristics set it apart. Here are some key points to help identify the Snowy Albatross:
Size and Shape
Snowy Albatrosses are large birds with wingspan reaching up to 3.5 meters (11 feet).
They have long, narrow wings that allow them to glide effortlessly for long distances over the ocean. Their body shape is streamlined, aiding in efficient flight.
Plumage
The Snowy Albatross gets its name from its predominantly white plumage.
However, unlike other albatross species, they have dark tips on their wings and a dark back. This contrast between white and dark coloring is a crucial feature for identification.
Head and Neck
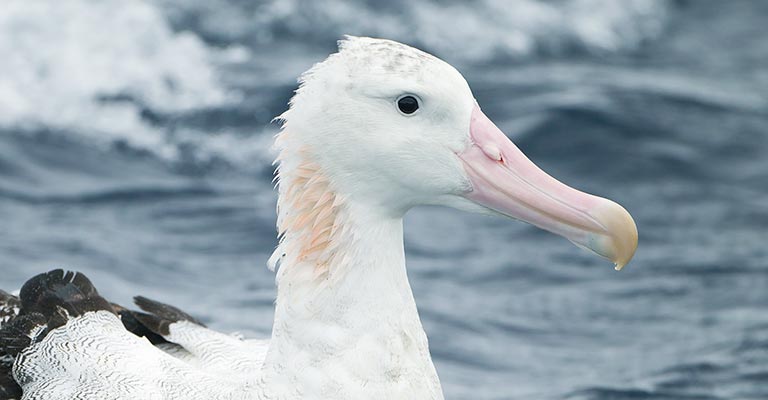

Snowy Albatrosses have a distinctive black patch around their eyes, which contrasts sharply with the white plumage of their face. Additionally, they have a pale yellow or pinkish bill with a dark tip.
Flight Pattern
Snowy Albatrosses exhibit a graceful gliding motion when in flight, rarely flapping their wings. They often soar low over the water, occasionally dipping their wings or skimming the surface with their feet.
Behavior
These birds are known for their ability to travel vast distances over the open ocean, often following ships or scavenging for food. They can sometimes be observed circling fishing vessels, attracted by discarded fish or bait.
Habitat
Snowy Albatrosses are primarily found in the Southern Ocean, breeding on remote islands such as South Georgia, Crozet, and Kerguelen.
Outside the breeding season, they roam widely across the southern oceans, from Antarctica to the subtropics.
Breeding Season
Breeding colonies of Snowy Albatrosses are typically located on steep coastal cliffs or grassy slopes of subantarctic islands. They breed biennially, with nesting sites often densely packed with pairs of birds.
Vocalizations
While not particularly vocal, Snowy Albatrosses may emit low grunts or croaks during courtship displays or interactions at breeding colonies. Their vocalizations are not as prominent as those of some other albatross species.
Identifying the Snowy Albatross requires careful attention to its size, plumage, facial markings, flight pattern, behavior, habitat, breeding season, and vocalizations.
By observing these key characteristics, birdwatchers and researchers can confidently distinguish this magnificent seabird from other species within the albatross family.
Taxonomy of Snowy Albatross
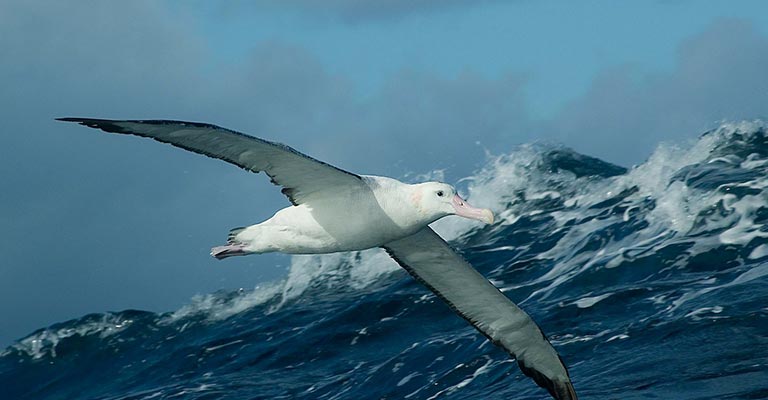

Below is the table detailing the taxonomy of the Snowy Albatross:
| Taxonomic Rank | Classification |
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Order | Phaethontiformes |
| Family | Diomedeidae |
| Genus | Diomedea |
| Species | D. exulans |
The wandering albatross, known as Diomedea exulans, comprises a species complex including several proposed species.
These birds are renowned for their impressive wingspan, graceful flight, and extensive range across the Southern Ocean. Here are brief descriptions of the proposed species within the wandering albatross complex:
- Diomedea exulans (Snowy Albatross): This subspecies, often called the Snowy Albatross, is characterized by its predominantly white plumage with dark wingtips and back. It inhabits subantarctic islands and spends much of its life soaring over the open ocean, hunting for fish and squid.
- Diomedea antipodensis (Antipodean Albatross): The Antipodean Albatross is found primarily in the waters surrounding New Zealand’s subantarctic islands. It has a darker plumage than the Snowy Albatross, with more extensive black markings on the head and neck.
- Diomedea dabbenena (Tristan Albatross): Endemic to the Tristan da Cunha archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean, its dark plumage and yellowish bill distinguishes it. It nests on remote cliffs and feeds mainly on squid and fish.
- Diomedea gibsoni (Gibson’s Albatross): Gibson’s Albatross, named after bird biologist John Lewis Gibson, inhabits the waters around New Zealand’s Chatham Islands. It has a similar appearance to the Antipodean Albatross but is slightly smaller in size.
These proposed species within the wandering albatross complex share many similarities in appearance and behavior but exhibit subtle differences that reflect their respective ranges and evolutionary histories.
Studying and understanding these distinctions are crucial for conservation efforts to protect these magnificent seabirds and their fragile ecosystems.
Hunting Habit of Snowy Albatross
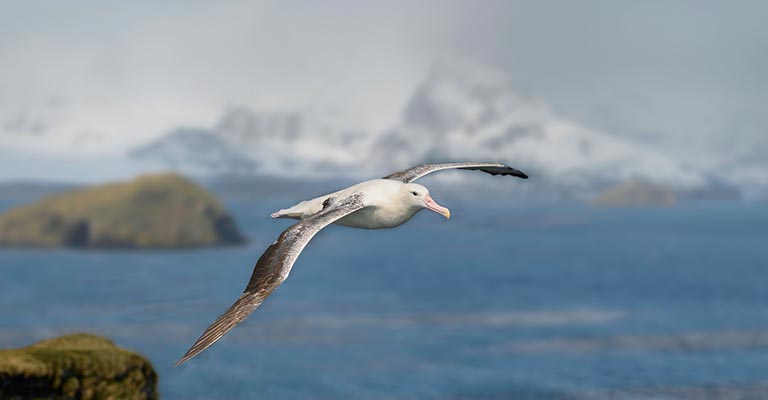

The Snowy Albatross is a highly skilled predator, primarily feeding on fish, squid, and crustaceans.
Utilizing its exceptional soaring abilities, it hunts by gliding effortlessly over the ocean surface, scanning for prey with keen eyesight.
When it spots potential food, it may dip to snatch it from the water’s surface or even plunge into the water from a height, using its long, robust bill to capture prey.
Additionally, Snowy Albatrosses are known to scavenge for food, often following ships or congregating around fishing vessels to feed on discarded fish or offal.
Their hunting habits are adapted to the open ocean’s vast and often challenging environments, allowing them to locate and capture prey while in flight efficiently.
Snowy Albatross Life History
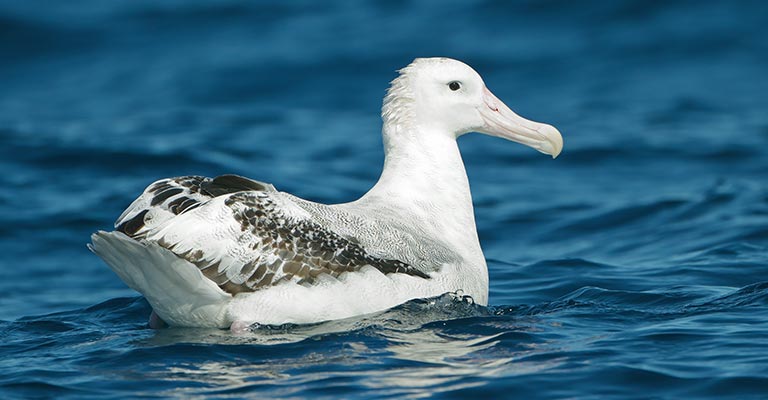

The Snowy Albatross (Diomedea exulans) is a magnificent seabird renowned for its impressive wingspan and graceful flight.
With its predominantly white plumage and striking black markings, this species navigates the vast expanses of the Southern Ocean in search of food and breeding grounds.
Understanding the life history of the Snowy Albatross involves delving into various aspects of its biology and ecology, including its feeding habits, habitat preferences, breeding behavior, and conservation status.
Food
Snowy Albatrosses are skilled predators, primarily feeding on fish, squid, and crustaceans. They employ various hunting techniques, including surface dipping and plunge diving, to capture prey while gliding over the ocean.
Habitat
These seabirds are primarily found in the Southern Ocean, inhabiting remote islands such as South Georgia, Crozet, and Kerguelen.
They often fly over open ocean waters, occasionally visiting coastal areas during breeding seasons.
Range Map
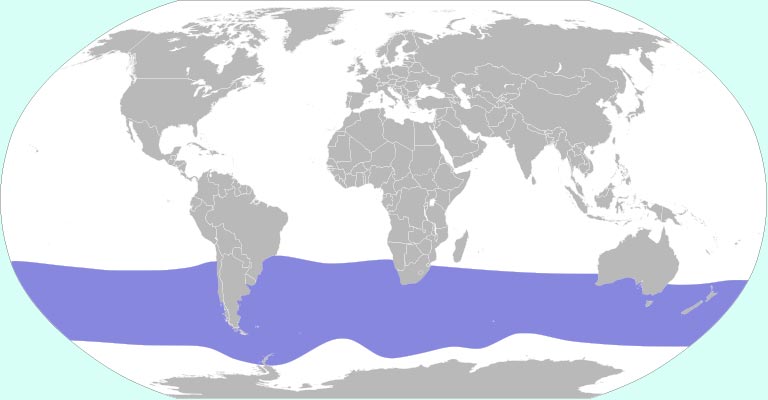
Snowy Albatrosses have a circumpolar distribution, with breeding colonies on subantarctic islands and foraging grounds extending across the southern oceans.
A range map illustrates their extensive migratory routes and breeding sites.
Nesting
Breeding colonies of Snowy Albatrosses are typically situated on steep coastal cliffs or grassy slopes of subantarctic islands.
These birds construct large, bowl-shaped nests using grass, moss, and other vegetation, often in densely packed colonies.
Here’s a table detailing the nesting details of the Snowy Albatross:
| Nesting Details | Facts |
| Clutch Size | Usually 1 egg |
| Number of Broods | Typically 1 every 2 years |
| Egg Length | Approximately 12.7 – 13.2 cm |
| Egg Width | Approximately 7.3 – 7.8 cm |
| Incubation Period | Around 2 months (60-70 days) |
| Nestling Period | About 9 months |
| Egg Description | Large, oval-shaped, white egg with a slightly rough texture |
These nesting details provide insight into the reproductive behavior and characteristics of Snowy Albatrosses, highlighting their unique adaptations for breeding and raising offspring in their remote island habitats.
Breeding
Snowy Albatrosses breed biennially, with pairs engaging in elaborate courtship displays before forming long-term monogamous bonds.
Females lay a single egg, which both parents take turns incubating for approximately two months. Chicks fledge after around nine months and may not return to breed until several years old.
Diseases and Treatment
Like many seabird species, Snowy Albatrosses are susceptible to diseases and parasites, including avian pox and parasitic infections.
Conservation efforts may involve monitoring and treating individuals affected by such ailments to prevent population declines.
Conservation
Snowy Albatross populations face threats from habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, and fisheries bycatch.
Conservation measures focus on protecting breeding sites, reducing human impacts on foraging grounds, and implementing measures to mitigate bycatch in fishing operations.
International agreements and protected area designations are crucial in safeguarding these majestic birds for future generations.
10 Fun Facts About Snowy Albatross
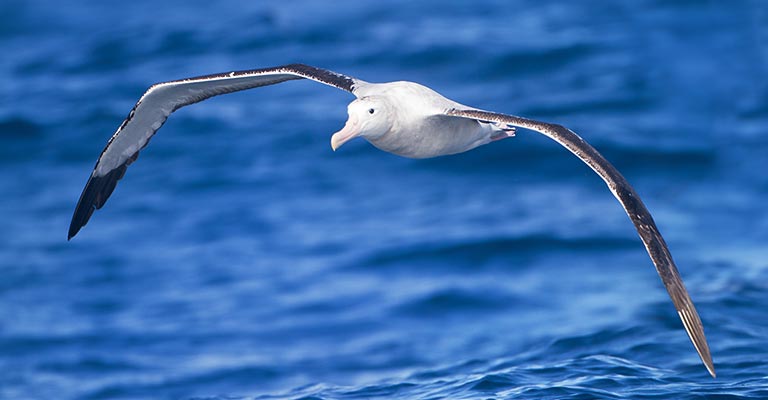

The Snowy Albatross is a fascinating seabird that roams the Southern Ocean with its majestic presence and remarkable capabilities.
Here are 10 fun facts that shed light on the intriguing characteristics and behaviors of this remarkable species:
- Wingspan Wonder: Snowy Albatrosses boast one of the most enormous wingspans of any bird, reaching up to an impressive 3.5 meters (11 feet). This immense wingspan allows them to glide effortlessly over the open ocean for hours.
- Nomadic Navigators: These birds are true wanderers of the sea, traveling thousands of kilometers in search of food and suitable breeding grounds. Their extensive range spans the vast expanse of the Southern Ocean.
- Longevity Legends: Snowy Albatrosses have an impressive lifespan, with some individuals living over 50 years old. Their ability to survive and thrive in harsh marine environments contributes to their remarkable longevity.
- Elegant Gliders: Snowy Albatrosses are masters of aerial acrobatics, utilizing dynamic and slope soaring techniques to conserve energy during long-distance flights. Their graceful gliding motion is a sight to behold.
- Oceanic Olympians: These seabirds are well-adapted to life on the high seas, spending most of their lives far from land. They can drink seawater and extract freshwater from their food, allowing them to remain hydrated during extended periods at sea.
- Monogamous Mates: Snowy Albatrosses form strong pair bonds lasting for life. During courtship displays, they perform elaborate dances and vocalizations to strengthen their bond and synchronize their breeding efforts.
- Egg-cellent Parents: Both parents take turns incubating the single egg laid each breeding season. Once the chick hatches, they work together to feed and care for it until it flees, which can take up to nine months.
- International Icons: Snowy Albatrosses are iconic symbols of the Southern Ocean ecosystem and are featured in numerous cultural and artistic representations. Their majestic presence has inspired admiration and awe for centuries.
- Conservation Concerns: Despite their remarkable adaptations, Snowy Albatross populations face threats from habitat destruction, pollution, and fisheries bycatch. Conservation efforts are underway to protect their breeding sites and foraging grounds.
- Ambassadors of the Antarctic: As ambassadors of the Antarctic and Southern Ocean, Snowy Albatrosses play a crucial role in raising awareness about preserving these remote and pristine ecosystems for future generations.
Wrapping Up
The Snowy Albatross stands as a magnificent ambassador of the Southern Ocean, captivating hearts with its immense wingspan, graceful flight, and remarkable adaptations for life at sea.
From its nomadic wanderings across vast oceanic expanses to its enduring monogamous bonds and dedicated parenting, this seabird embodies resilience, elegance, and the interconnectedness of marine ecosystems.
However, it also faces significant conservation challenges, underscoring the urgent need for concerted efforts to safeguard its habitats and mitigate threats such as habitat destruction and fisheries bycatch.
By recognizing and protecting the Snowy Albatross, we ensure the survival of a remarkable species and contribute to preserving the delicate balance of life in the Antarctic and Southern Ocean regions. Thank you so much.