The Plain-capped Starthroat (Heliomaster constantii) emerges as a jewel among hummingbirds, captivating ornithologists, and enthusiasts alike.
This dazzling species, belonging to the family Trochilidae, is enchanted with its striking appearance and unique behaviors.
Characterized by an iridescent plumage, the male boasts metallic greens and vivid violets, while the eponymous white cap adorns its head.
Found across diverse habitats in Central and South America, from southern Mexico to Panama and extending into countries like Colombia and Venezuela, the Plain-capped Starthroat thrives in open woodlands, gardens, and forest edges.
Its agile flight, characterized by hovering and rapid movements, complements its specialized feeding habits. Nectar from a variety of flowering plants constitutes its primary diet, emphasizing its role as a vital pollinator.
As an emblem of biodiversity, the Plain-capped Starthroat beckons exploration into the intricacies of avian life, fostering an appreciation for the delicate ecosystems it inhabits. Stay focused.
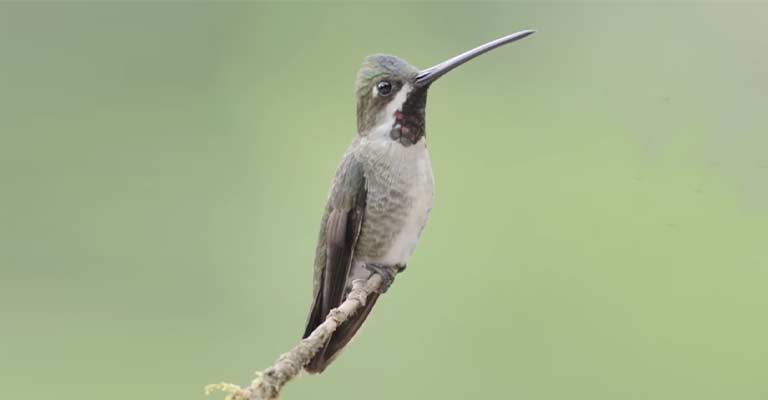

Identifying Characteristics of Plain-capped Starthroat
The Plain-capped Starthroat (Heliomaster constantii) is a striking and distinctive hummingbird species found in Central and South America.
Identifying this bird requires careful observation of its physical characteristics, behavior, and habitat.
Here, we will delve into the key features that make the Plain-capped Starthroat stand out in the avian world.
Physical Appearance

One of the most distinguishing features of the Plain-capped Starthroat is its vibrant plumage.
The male exhibits a captivating iridescence with metallic green feathers covering its upperparts, while its throat and breast display a brilliant violet hue.
The crown, as the name suggests, is plain and adorned with a contrasting white cap, setting it apart from other hummingbird species.
The female, on the other hand, is generally less vibrant, with a more subdued coloration but still possesses the distinct white cap.
Size and Shape

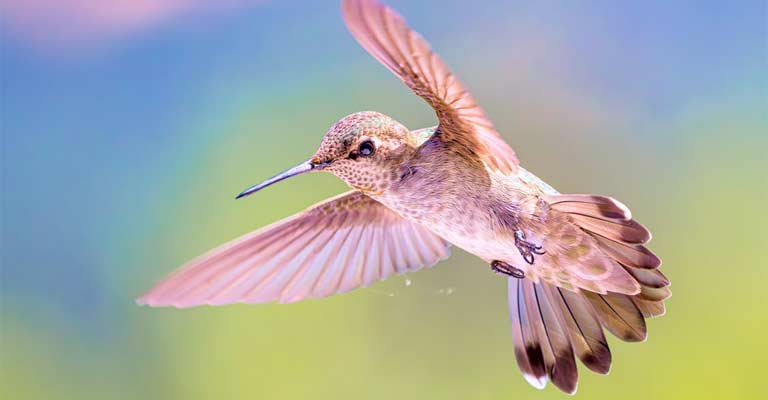
In terms of size, the Plain-capped Starthroat is a medium-sized hummingbird, typically measuring around 10 to 12 centimeters in length.
Its slender body is designed for agile flight, and its long, pointed bill is adapted for reaching nectar deep within flowers.
The tail is forked and extends beyond the wingtips, contributing to its overall aerodynamic form.
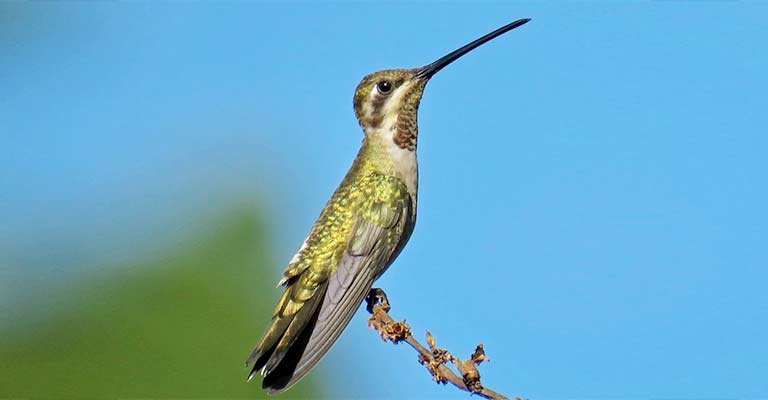
Distinctive Flight Patterns
Observing the flight patterns of the Plain-capped Starthroat can also aid in identification.
Like other hummingbirds, it is known for its rapid and agile flight, capable of hovering in mid-air and maneuvering with precision. Its wings beat at an astonishing rate, creating a distinct humming sound.
The ability to hover and move rapidly from flower to flower is a characteristic behavior exhibited by hummingbirds in general.
Habitat and Range
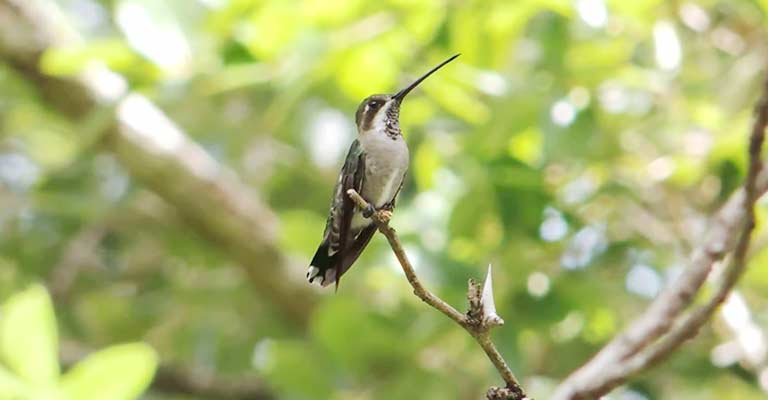

Understanding the habitat and range of the Plain-capped Starthroat is crucial for identification. These birds are primarily found in open woodlands, gardens, and forest edges, preferring areas with abundant flowering plants.
Their range extends from southern Mexico through Central America to western Panama and parts of South America, including Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela.
Observing them in these specific habitats can increase the likelihood of correctly identifying them.
Vocalizations
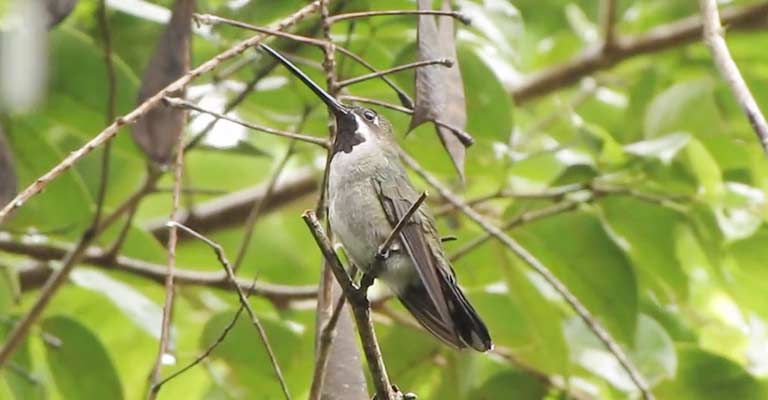

The Plain-capped Starthroat produces distinctive vocalizations that can aid in identification. While their calls are not as melodious as some other bird species, they are often sharp and high-pitched.
These vocalizations are used for communication, especially during territorial disputes or courtship rituals.
Identifying the Plain-capped Starthroat involves a comprehensive assessment of its physical characteristics, flight patterns, habitat, and vocalizations.
Taxonomy of Plain-capped Starthroat

Here’s a table outlining the taxonomy details of the Plain-capped Starthroat (Heliomaster constantii):
| Taxonomic Level | Classification |
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Clade | Strisores |
| Order | Apodiformes |
| Family | Trochilidae |
| Genus | Heliomaster |
| Species | H. constantii |
This table reflects the hierarchical classification of the Plain-capped Starthroat, from the broadest taxonomic levels such as Domain and Kingdom down to the specific Genus and Species.
This systematic arrangement is based on the bird’s evolutionary relationships and shared characteristics within the animal kingdom.
The Plain-capped Starthroat (Heliomaster constantii) exhibits three distinct subspecies, each with its unique characteristics and geographical distribution.
- Heliomaster constantii constantii (Nominate Subspecies): The nominate subspecies is found in various regions, ranging from southern Mexico through Central America. It shares the general features of the Plain-capped Starthroat, with vibrant plumage and the characteristic white cap on its head.
- Heliomaster constantii pinicola: This subspecies is known to inhabit specific regions, contributing to the overall range of the Plain-capped Starthroat. While sharing the core characteristics of the species, regional variations may be present, reflecting adaptations to the local environment.
- Heliomaster constantii leocadiae: The leocadiae subspecies is part of the Plain-capped Starthroat’s range, contributing to the species’ diversity. Similar to the other subspecies, it displays the signature white cap and vibrant plumage, with potential variations influenced by its specific habitat.
These subspecies, though variations of the same species, play a vital role in the overall biodiversity and adaptability of the Plain-capped Starthroat.
Their distinct distributions and potential differences in physical traits contribute to the intricate mosaic of avian life in the regions they inhabit.
Plain-capped Starthroat Life History
The life history of the Plain-capped Starthroat (Heliomaster constantii) unveils a fascinating narrative of survival, adaptation, and ecological interdependence.
As a species of hummingbird, the Plain-capped Starthroat’s life is intricately woven into the tapestry of its environment.
From its dietary preferences to nesting habits, breeding behaviors, and conservation challenges, exploring the various facets of its life history provides valuable insights into the delicate balance of nature.
Food
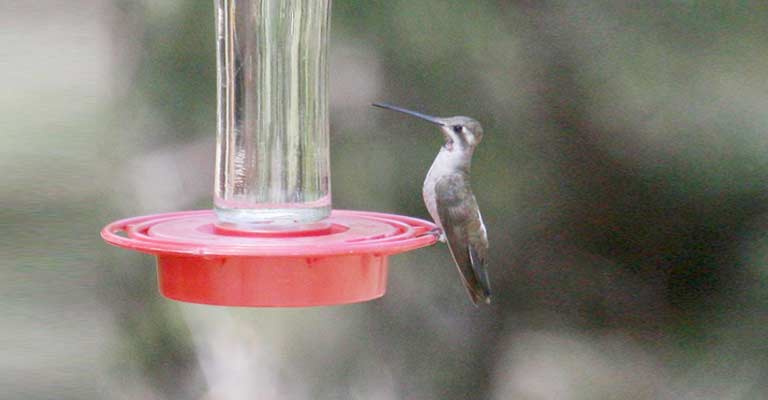

The primary sustenance for the Plain-capped Starthroat revolves around nectar obtained from a diverse array of flowering plants.
Equipped with a specialized long, slender bill and a tubular tongue, these hummingbirds excel at extracting nectar from deep within the blossoms.
Their high metabolism is sustained not only by nectar but also by the consumption of small insects and spiders, providing essential proteins and nutrients.
Habitat
The Plain-capped Starthroat exhibits a preference for open woodlands, gardens, and forest edges. This adaptable species thrives in a variety of environments, from lowland tropical areas to montane regions.
Their choice of habitat is closely tied to the availability of flowering plants, which serve as a crucial source of nectar for their survival.
Range Map
The species’ range extends from southern Mexico through Central America to western Panama and further south into parts of South America, including Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela.
The distribution map showcases the geographical areas where these birds can be found, highlighting the importance of diverse ecosystems in supporting their populations.
Nesting and Breeding
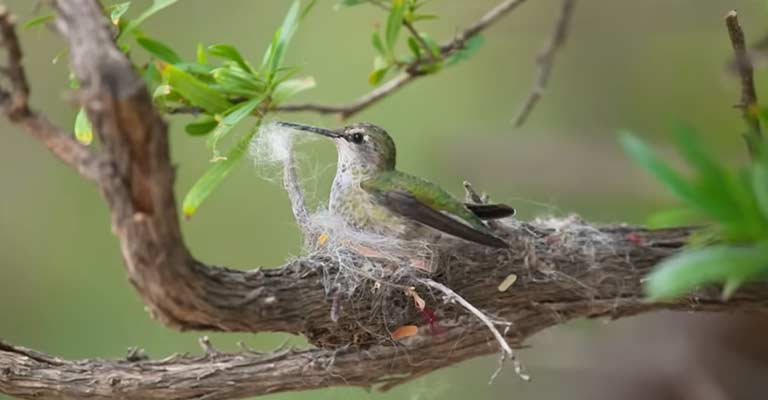

Plain-capped Starthroats are meticulous in their nesting habits. Females construct small cup-shaped nests using plant fibers, spider silk, and feathers, often attaching them to horizontal branches.
These nests serve as a safe haven for the development of their two eggs. The incubation period is relatively short, and once hatched, the chicks are fed a diet of regurgitated nectar and insects by both parents.
Here’s a table summarizing the nesting details of the Plain-capped Starthroat (Heliomaster constantii):
| Nesting Details | Facts |
| Clutch Size | Typically 2 eggs |
| Number of Broods | Often raises multiple broods in a season |
| Egg Length | Approximately 1.5 centimeters (0.6 inches) |
| Egg Width | Around 1 centimeter (0.4 inches) |
| Incubation Period | Approximately 15 to 19 days |
| Nestling Period | About 20 days |
| Egg Description | White or creamy, small and elliptical |
| Nest Construction | Cup-shaped nest made of plant fibers, spider silk, and feathers, attached to horizontal branches |
| Parental Involvement | Both males and females participate in incubation and feeding |
| Feeding the Nestlings | Chicks are fed a diet of regurgitated nectar and insects |
| Nesting Site | Positioned in trees or shrubs, often in open woodlands, gardens, or forest edges |
| Nest Height | Varies but often within 1 to 3 meters above the ground |
| Predation and Threats | Vulnerable to predators such as snakes, birds of prey, and larger insects |
| Nest Reuse | May reuse nests from previous seasons, with repairs and additions |
This table provides a comprehensive overview of the nesting habits and reproductive characteristics of the Plain-capped Starthroat, offering key insights into its breeding biology.
Diseases and Treatment
Like many bird species, Plain-capped Starthroats are susceptible to various diseases, including avian malaria and other infections.
Maintaining the health of their environment and providing a consistent food supply can contribute to disease prevention.
In captivity, if symptoms of illness are observed, prompt veterinary care may be necessary, with treatments ranging from antibiotics to supportive care.
Conservation
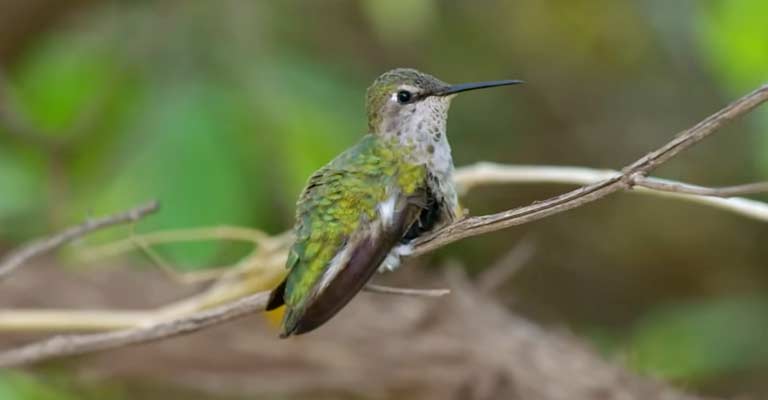

The conservation status of the Plain-capped Starthroat is currently of least concern, as per the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, their survival is intricately linked to the health of their habitats.
Conservation efforts should focus on preserving natural landscapes, preventing deforestation, and promoting sustainable practices that protect the ecosystems crucial to their existence.
The life history of the Plain-capped Starthroat unveils a remarkable journey of adaptation and resilience.
From foraging for nectar to nesting and breeding, understanding the intricacies of their lives provides a deeper appreciation for the role these hummingbirds play in the ecosystems they inhabit.
10 Fun Facts About Plain-capped Starthroat
Here are some fun facts about the Plain-capped Starthroat:
- Distinctive White Cap: As the name suggests, the Plain-capped Starthroat is known for the conspicuous white cap on its head, setting it apart from other hummingbird species. This unique feature adds to its charm and makes it easily recognizable.
- Agile Aerial Acrobats: Like all hummingbirds, Plain-capped Starthroats are expert aerial acrobats. They can hover in mid-air, fly backward, and make rapid, precise movements, showcasing their agility in flight.
- Iridescent Plumage: The males of this species boast vibrant, iridescent plumage with metallic green upperparts and a dazzling violet throat and breast. The play of light on their feathers creates a stunning visual display during courtship rituals.
- Migratory Behavior: While some populations of Plain-capped Starthroats are considered resident, others are known to undertake seasonal migrations. This behavior may vary based on factors such as food availability and environmental conditions.
- High Metabolism: Hummingbirds, including the Plain-capped Starthroat, have an exceptionally high metabolism. They need to consume large amounts of nectar and supplement their diet with insects to meet their energy requirements.
- Unique Feeding Technique: Their specialized long, slender bills and extendable, tube-like tongues allow them to feed on nectar deep within flowers. This unique feeding adaptation facilitates their role as important pollinators in their ecosystems.
- Vocal Communicators: While their calls may not be as melodious as songbirds, Plain-capped Starthroats use sharp and high-pitched vocalizations for communication. These calls are often employed during territorial disputes and courtship displays.
- Flexible Nesting Habits: The Plain-capped Starthroat is adaptable in its nesting habits. It may reuse nests from previous seasons, making repairs and additions as needed. This flexibility showcases their resourcefulness in breeding.
- Territorial Nature: During the breeding season, males can be particularly territorial, defending feeding and nesting territories vigorously. This behavior is a common trait among hummingbird species, ensuring access to critical resources.
- Conservation Status: As of now, the Plain-capped Starthroat is categorized as being of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, ongoing conservation efforts are crucial to maintaining their populations, as their survival is closely linked to the health of their habitats.
These fun facts highlight the remarkable characteristics and behaviors of the Plain-capped Starthroat, contributing to its status as a captivating and ecologically significant bird species.
Wrapping Up
In the intricate tapestry of avian life, the Plain-capped Starthroat emerges as a captivating protagonist. Its vibrant plumage, agile flight, and unique nesting habits illuminate the wonders of nature.
From foraging for nectar in open woodlands to defending territories with sharp calls, the life history of this hummingbird unveils a story of adaptation and resilience.
Conservation efforts become imperative to sustain the delicate balance of ecosystems and ensure the continued flourishing of this charismatic species. Thank you.