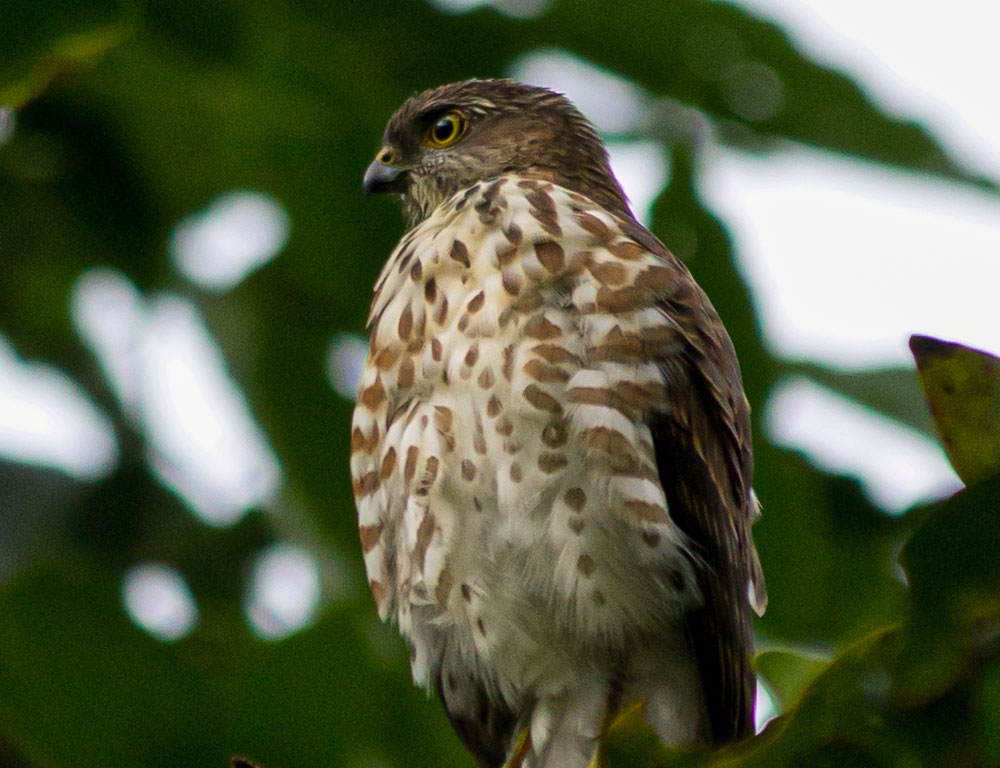
The Besra (Accipiter virgatus) is a captivating bird of prey renowned for its agility, stealthy hunting skills, and adaptability to forested habitats across Asia.
With its compact size, streamlined body, and acute vision, the Besra is a formidable predator capable of navigating dense vegetation with remarkable precision.
From its specialized flight capabilities to its versatile diet and breeding adaptations, each aspect of the Besra’s biology reflects its role as a top predator in its ecological niche.
As we delve into the fascinating world of the Besra, we uncover its remarkable specialties and importance in maintaining the balance of Asia’s diverse ecosystems.
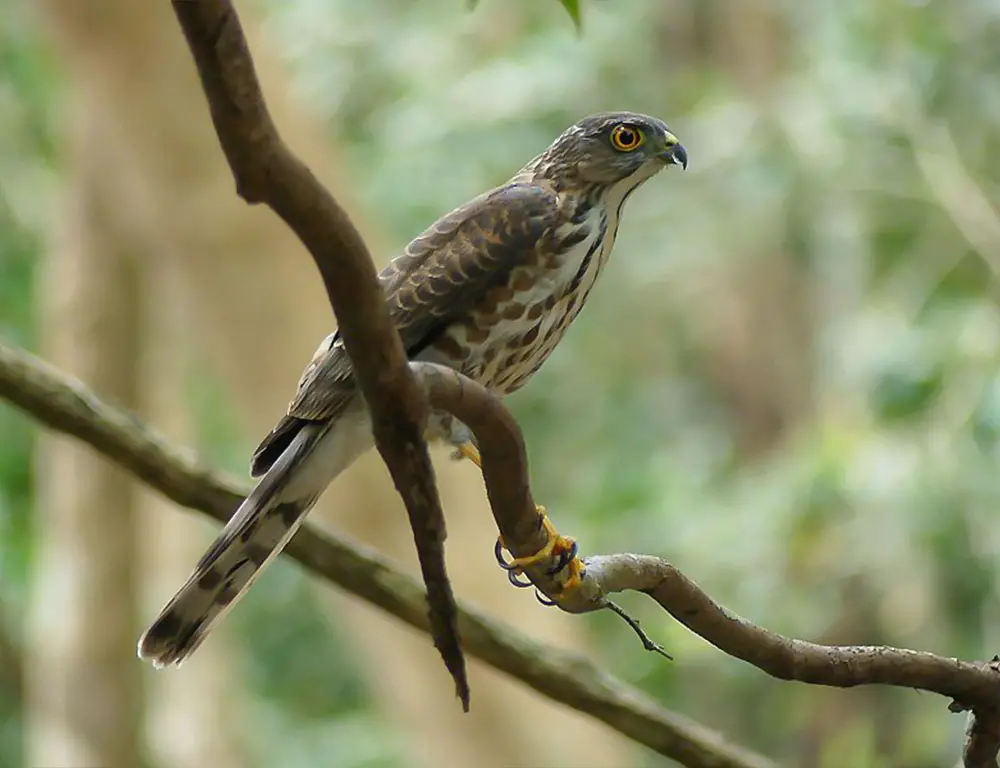

Interesting Characteristics Of Besra
The Besra (Accipiter virgatus) is a small bird of prey known for its agility and predatory prowess, inhabiting forests and wooded areas across Asia. Here are some common characteristics of this species:
Physical Characteristics Of Besra
The Besra (Accipiter virgatus) is a small bird of prey found across Asia, known for its agile flight and predatory prowess. Here are seven physical characteristics that distinguish this raptor:
Size
The Besra is relatively small compared to other raptors, measuring around 30 to 40 centimeters in length, with a wingspan of approximately 60 to 70 centimeters. This compact size allows it to navigate through dense vegetation with ease.
Plumage
It has a striking appearance with dark brown or slate-gray upperparts and finely barred underparts. The plumage provides effective camouflage in its forested habitat, allowing it to blend seamlessly with its surroundings while hunting.
Shape
The Besra has a sleek and streamlined body adapted for swift and agile flight. Its long tail and rounded wings enable quick maneuvers and precise control during pursuit of prey.
Beak and Talons
Like all raptors, the Besra possesses a sharp, hooked beak and powerful talons, which are used to grasp and dispatch prey swiftly. These formidable weapons are essential for capturing and subduing small birds and mammals.
Eyesight
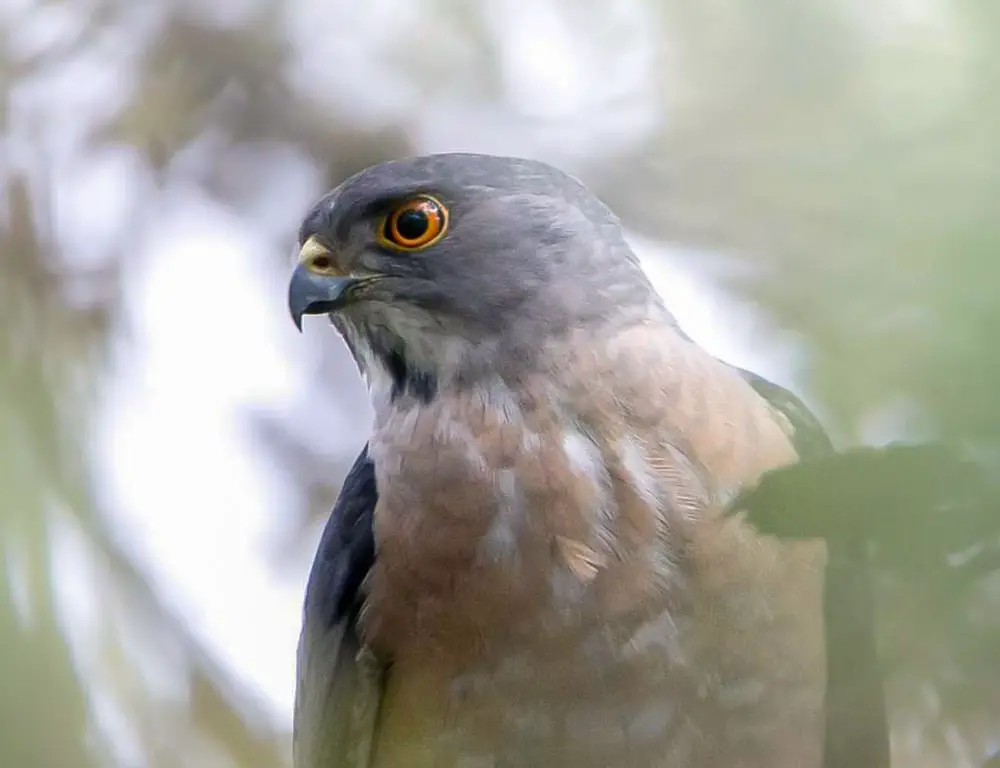

With large, forward-facing eyes, the Besra has exceptional visual acuity, allowing it to spot prey from a considerable distance while in flight. Its keen eyesight is vital for locating and targeting fast-moving prey.
Crest
Some individuals may exhibit a distinctive crest of feathers on the crown of the head, which can be raised or lowered depending on the bird’s mood or level of alertness. This crest adds to the Besra’s striking appearance.
Sexual Dimorphism
In terms of physical appearance, male and female Besras are similar, with slight variations in size. However, females may be slightly larger and heavier than males, a common trait observed in many bird species.
Distribution And Habitat
Besras are widely distributed across Asia, from the Indian subcontinent to Southeast Asia and East Asia. They inhabit various forested habitats, including tropical rainforests, deciduous woodlands, and montane forests, where they hunt for prey amidst dense vegetation.
Aviculture
While not as commonly kept in aviculture as larger raptor species, Besras have been bred in captivity for falconry and educational purposes. Their small size and agile flight make them fascinating subjects for bird enthusiasts and falconers.
Survival
Besras are skilled hunters, preying on small birds, mammals, and insects. Their agility and speed enable them to pursue prey through dense vegetation with remarkable precision, making them efficient hunters in their forested habitats.
Status
The conservation status of Besras varies across their range, with some populations facing threats from habitat loss, deforestation, and illegal hunting. In some areas, they may benefit from protected areas and conservation efforts to preserve their forest habitats.
Besras are small but formidable predators, well-adapted to life in Asia’s diverse forests.
From their distribution and habitat preferences to their survival strategies and conservation status, each characteristic underscores the importance of protecting these agile raptors and their forested homes.
Taxonomy
Here’s a simplified table outlining the taxonomy and classification of the Besra (Accipiter virgatus):
| Taxonomy Level | Classification |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Order | Accipitriformes |
| Family | Accipitridae |
| Genus | Accipiter |
| Species | Accipiter virgatus |
The Besra belongs to the Animalia kingdom, Chordata phylum, Aves class, Accipitriformes order, Accipitridae family, Accipiter genus, and its specific species name is Accipiter virgatus.
This classification reflects its evolutionary relationships and taxonomic placement among other bird species.
Nesting Habit Of Besra
Here’s a simplified table outlining the nesting habits of the Besra (Accipiter virgatus):
| Nesting Habit | Description |
| Nest Type | The Besra builds a platform-style nest of sticks, twigs, and other plant materials, often lined with softer materials like leaves or moss. |
| Nest Placement | Nests are typically located high in the canopy of trees, providing protection and concealment from predators. |
| Breeding Season | The breeding season for Besras typically occurs during the spring and early summer months, varying slightly across different regions. |
| Clutch Size | Besras generally lay a clutch of 2-4 eggs, although clutch size may vary depending on food availability and environmental conditions. |
| Incubation Period | Both male and female Besras participate in incubating the eggs, which hatch after approximately 30-35 days. |
| Parental Care | Both parents share responsibilities in incubating the eggs, caring for the hatchlings, and providing food and protection until the young fledge. |
This table provides an overview of the nesting habits of the Besra, including nest type, placement, breeding season, clutch size, incubation period, and parental care.
These nesting behaviors reflect the species’ reproductive strategies and adaptation to its forest habitat.
Ranging Map Of Besra
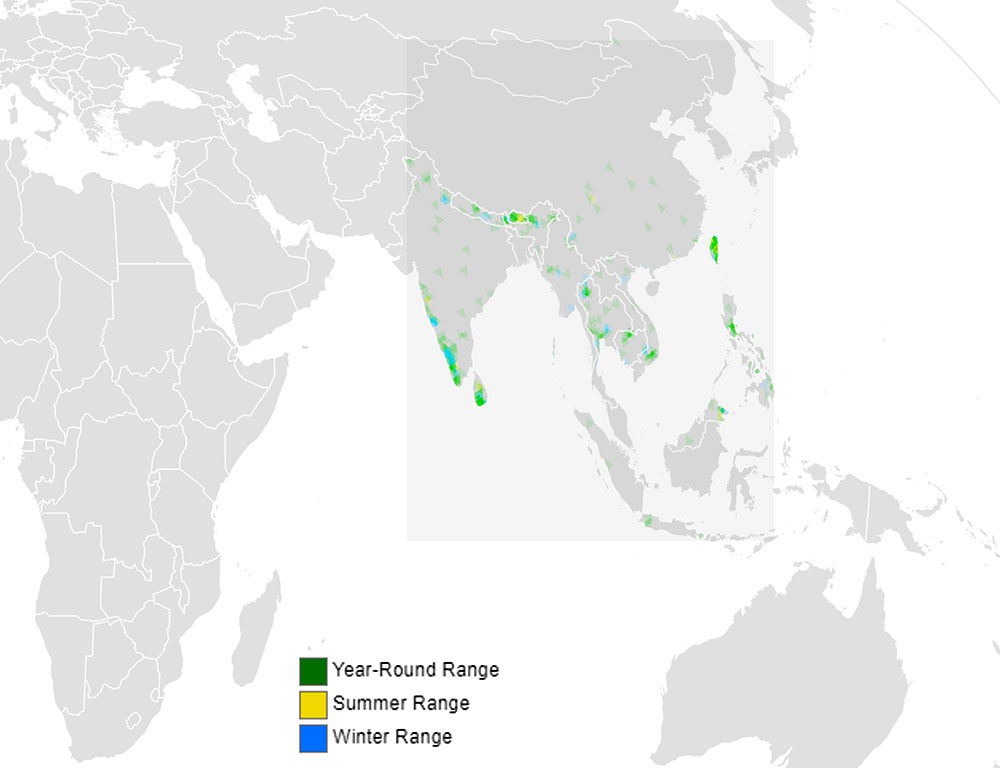
The ranging map of the Besra (Accipiter virgatus) illustrates the distribution of this tiny bird of prey across Asia.
From the Indian subcontinent to Southeast Asia and East Asia, the Besra is found in various forested habitats, including tropical rainforests, deciduous woodlands, and montane forests.
This species’ adaptable nature allows it to thrive in diverse environments, where it hunts for prey amidst dense vegetation.
While its range may vary slightly within different regions, the Besra’s presence is often associated with areas abundant in small birds, mammals, and insects, which serve as its primary food sources.
Conservation efforts aimed at preserving its forest habitats are crucial for ensuring the continued existence of the Besra and maintaining the ecological balance of Asia’s diverse ecosystems.
What Is The Speciality Of Besra?
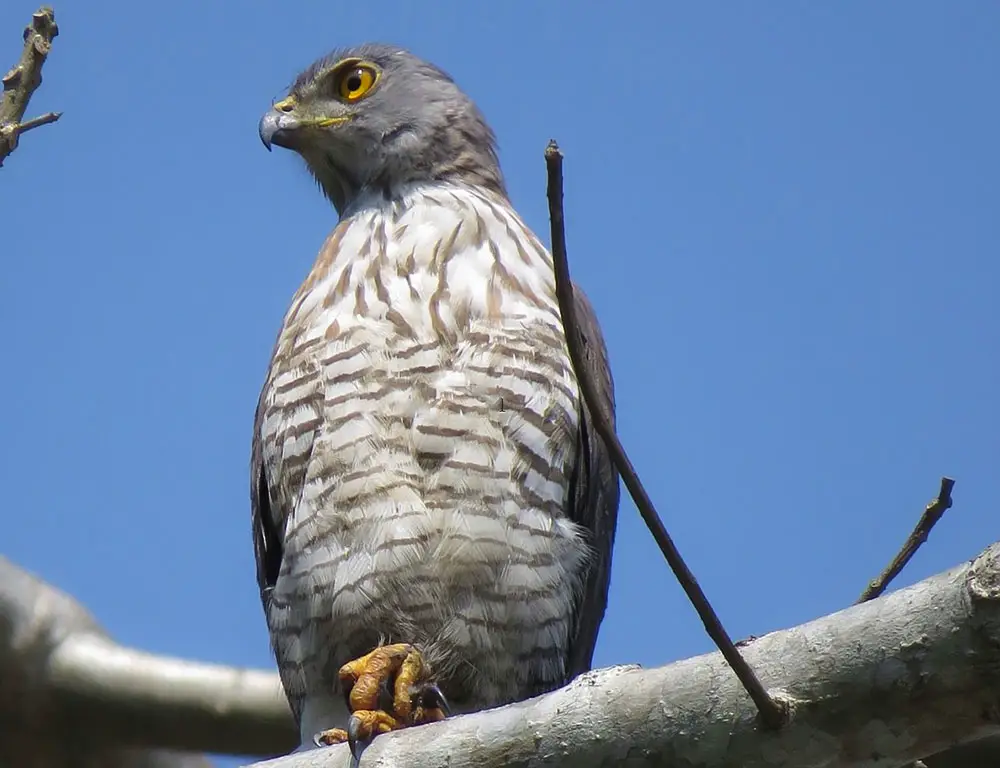

The Besra (Accipiter virgatus) possesses several remarkable specialties that distinguish it as a unique bird of prey in the avian world. Here are seven notable specialties:
Agile Flight
One of the Besra’s most remarkable specialties is its incredibly agile flight capabilities. With its streamlined body and long tail, this raptor can maneuver swiftly through dense vegetation with noteworthy precision, making it a formidable hunter in its forested habitat.
Stealthy Hunting
The Besra specializes in stealthy hunting techniques, using its sharp vision and silent flight to surprise and capture prey. It can approach its target undetected, relying on camouflage and strategic positioning to ensure a successful hunt.
Versatile Diet
Despite its small size, the Besra has a diverse diet that includes small birds, mammals, and insects. This adaptability allows it to exploit a wide range of prey species, ensuring survival even in challenging environments.
Acute Vision
Another specialty of the Besra is its acute vision, which enables it to spot prey from a considerable distance while in flight. Its large, forward-facing eyes provide excellent binocular vision, allowing it to assess potential prey’s movements accurately.
Breeding Adaptations
During the breeding season, Besras exhibit specialized behaviors and adaptations to ensure the survival of their offspring. Both parents participate in nest-building, incubating the eggs, and caring for the young chicks until they are ready to fledge.
High Speeds
Despite its small size, the Besra can reach impressive speeds during pursuit flights. Its streamlined body and mighty wings allow it to accelerate quickly and execute sharp turns with agility, enabling it to outmaneuver agile prey species.
Adaptation To Forested Habitats
The Besra’s specialization in forested habitats sets it apart from other raptor species.
It is uniquely adapted to navigating through dense vegetation, utilizing its agility and keen senses to hunt effectively in the complex and challenging environments of the forest canopy.
The Besra’s specialties encompass a range of adaptations that enable it to thrive as a skilled predator in Asia’s diverse forests.
Each specialty contributes to its success as a top predator in its ecological niche, from its agile flight and stealthy hunting techniques to its versatile diet and breeding adaptations.
FAQs
What does a Besra eat?
Besras primarily feed on small birds, mammals, and insects. Their versatile diet allows them to adapt to various prey species in their forested habitats, making them efficient hunters in dense vegetation.
How does a Besra hunt?
Besras employ stealthy hunting techniques, utilizing their sharp vision and silent flight to surprise and capture prey. They often ambush their prey from concealed perches or pursue them through dense vegetation with swift and agile maneuvers.
Where does a Besra live?
Besras, including tropical rainforests, deciduous woodlands, and montane forests, inhabit forests and wooded areas across Asia. They are often found in areas with abundant prey and dense vegetation, where they can hunt and nest effectively.
Are Besras threatened?
The conservation status of Besras varies across their range, with some populations facing threats from habitat loss, deforestation, and illegal hunting. However, in areas with protected habitats, they may thrive and contribute to the ecosystem’s balance.
How can I spot a Besra?
Spotting a Besra can be challenging due to its secretive nature and preference for dense vegetation. However, keen observers may catch glimpses of these agile raptors flying swiftly through the forest canopy or perched stealthily on tree branches, scanning for prey.
Conclusion
The Besra emerges as a remarkable species of bird of prey, uniquely adapted to thrive in the forested habitats of Asia.
Through its agile flight, stealthy hunting techniques, and versatile diet, the Besra plays a crucial role in regulating prey populations and maintaining the health of forest ecosystems.
As we continue to appreciate and study the Besra, let us also recognize the importance of conserving its habitat and protecting this magnificent bird for future generations to enjoy and admire.
