The Bumblebee Hummingbird (Selasphorus heloisa) emerges as a captivating jewel in the avian kingdom, earning its distinction as the smallest bird species on Earth.
Endowed with diminutive proportions, these enchanting creatures showcase vibrant plumage, resembling the hues of a bumblebee, thus earning their whimsical name.
Inhabiting the highland and montane regions of Central and South America, the Bumblebee Hummingbird navigates the skies with unparalleled agility, employing rapid wing beats that allow it to hover effortlessly.
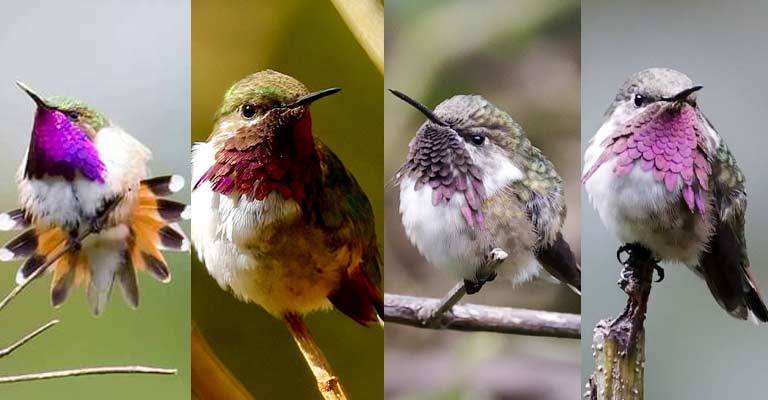
The males’ resplendent colors, featuring iridescent greens and fiery throat patches, contrast with the subtler hues of the females.
Their intricate nesting habits, migratory feats, and unique adaptations for nectar feeding contribute to the allure of this tiny marvel, inviting exploration into the delicate yet resilient world of the Bumblebee Hummingbird. Stay focused.
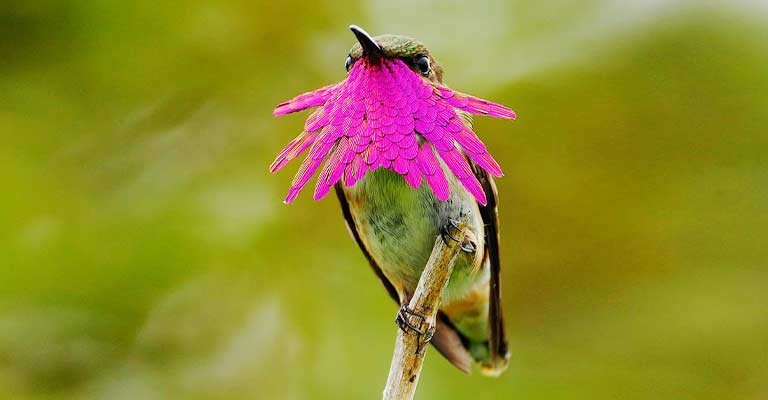

Identifying Characteristics of Bumblebee Hummingbird
The Bumblebee Hummingbird (Selasphorus heloisa) is a fascinating and diminutive bird that holds the title of being the smallest bird species in the world.
Identifying this tiny marvel requires a keen eye and an understanding of its distinctive characteristics. Here are some key points to help you identify the Bumblebee Hummingbird:
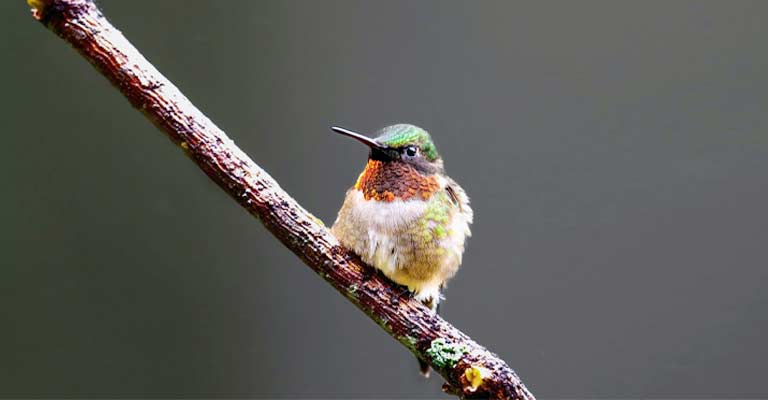
Size and Proportions
The most striking feature of the Bumblebee Hummingbird is its miniature size. With an average length of 2 to 2.4 inches (5 to 6 cm), it is comparable to the size of a large bumblebee, hence its name.
Additionally, its body proportions are compact, with a short bill and tail, making it distinct from other hummingbird species.
Coloration
The Bumblebee Hummingbird exhibits vibrant and iridescent plumage. The males typically showcase a brilliant combination of iridescent greens, blues, and fiery red or orange throat patches, known as gorgets.
Females, on the other hand, have more subdued colors, often featuring greens and grays, allowing them to blend into their surroundings for nesting.
Throat Patch

One of the most identifiable features of the male Bumblebee Hummingbird is its colorful throat patch. During courtship displays or territorial encounters, these patches flare up, creating a dazzling display of colors.
The intensity and brilliance of this throat patch are key in distinguishing between individual males.
Flight Pattern
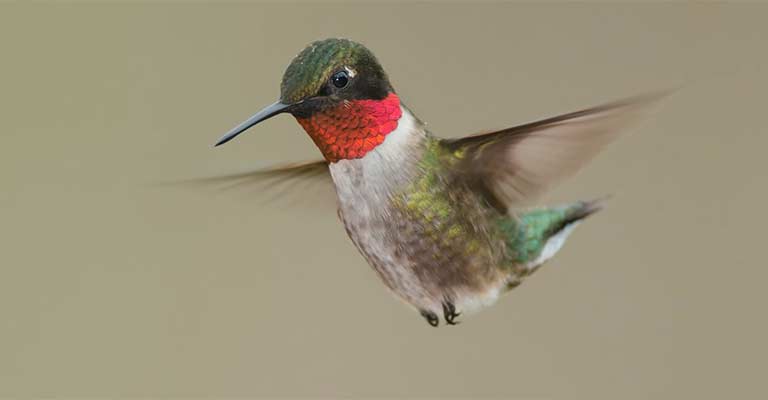

Bumblebee Hummingbirds have a distinctive and rapid flight pattern, hovering in mid-air with remarkable agility.
Their wings beat at an astonishing rate, often exceeding 80 beats per second, allowing them to stay suspended while feeding on nectar from flowers.
Habitat
These tiny hummingbirds are typically found in highland and montane regions of Central and South America.
Their preferred habitats include cloud forests, mountain meadows, and areas with abundant flowering plants. Observing their habitat preference can aid in narrowing down potential species.
Vocalizations
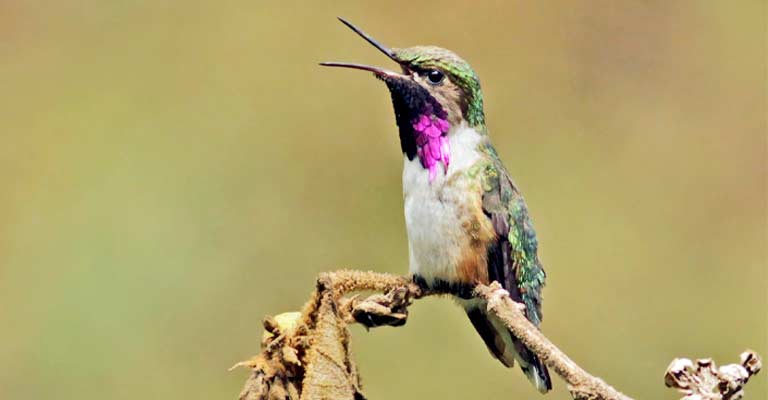

While their vocalizations are not as conspicuous as their larger hummingbird counterparts, Bumblebee Hummingbirds do emit high-pitched, insect-like calls.
These vocalizations can help identify their presence, especially in dense vegetation.
Feeding Behavior
The feeding behavior of the Bumblebee Hummingbird is distinctive. They primarily feed on nectar from small flowers, and their long, specialized bills allow them to access deep-seated blossoms.
Observing their feeding habits, including their ability to hover and extract nectar with precision, is a key characteristic.
Migratory Patterns
Bumblebee Hummingbirds are known for their remarkable migratory journeys. They undertake extensive migrations, covering large distances between their breeding grounds and wintering areas.
Tracking their migratory patterns, which can vary among individuals, can aid in identification during specific times of the year.
Identifying the Bumblebee Hummingbird requires a holistic approach, considering factors such as size, coloration, behavior, and habitat.
Being aware of these distinctive characteristics enhances the joy of encountering this extraordinary bird in its natural environment.
Taxonomy of Bumblebee Hummingbird

Here’s a table outlining the taxonomy details of the Bumblebee Hummingbird (Selasphorus heloisa):
| Taxonomic Level | Classification |
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Clade | Strisores |
| Order | Apodiformes |
| Family | Trochilidae |
| Genus | Selasphorus |
| Species | S. heloisa |
This table summarizes the hierarchical classification of the Bumblebee Hummingbird, providing insights into its taxonomic position within the animal kingdom, chordates, avian class, and the specific order, family, genus, and species to which it belongs.
The Bumblebee Hummingbird (Selasphorus heloisa) exhibits remarkable diversity within its species, as taxonomic systems recognize two distinct subspecies: the nominate S. h. heloisa (formerly A. h. heliosa) and S. h. margarethae (formerly A. h. margarethae).
These subspecies showcase subtle yet noteworthy variations, contributing to the overall richness of the Bumblebee Hummingbird population.
- S. h. heloisa (Nominate Subspecies): The nominate subspecies is found across a broad range, spanning from southern Mexico to western Panama. Males display vibrant iridescent plumage, including greens, blues, and fiery red or orange throat patches. Females exhibit more subdued colors, blending into their diverse habitats.
- S. h. Margarethae: This subspecies inhabits distinct regions, specifically the highlands of Nicaragua, Honduras, and Costa Rica. Males and females of S. h. margarethae share similarities with the nominate subspecies in terms of size and general appearance.
However, subtle differences in coloration and markings may exist due to geographic and environmental factors.
These subspecies distinctions underscore the adaptability and evolution of the Bumblebee Hummingbird in response to varied environmental conditions across its range.
Studying these subtle variations enhances our understanding of the species’ biology, ecology, and the intricate interplay between genetics and environmental factors.
Bumblebee Hummingbird Life History
The Bumblebee Hummingbird (Selasphorus heloisa) captivates bird enthusiasts worldwide with its diminutive size and vibrant colors.
This miniature marvel, native to the highland and montane regions of Central and South America, has a fascinating life history marked by its unique adaptations for survival and reproduction.
Food
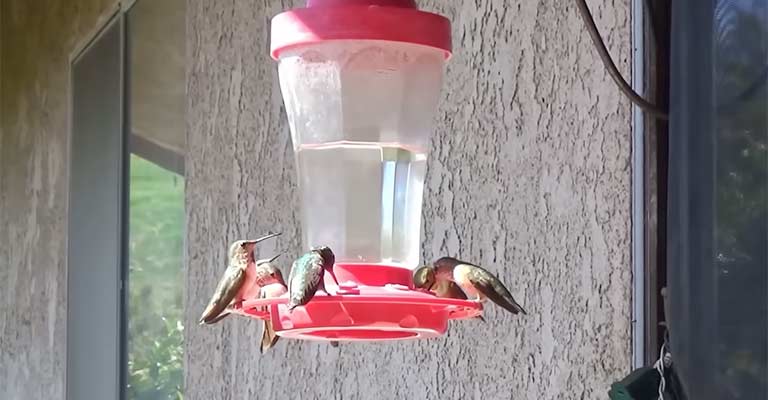

The primary dietary focus of the Bumblebee Hummingbird centers around nectar from various flowering plants.
With its long, specialized bill and rapid wing beats, this hummingbird adeptly hovers to extract nectar from deep-seated blossoms.
Additionally, they supplement their diet with small insects and spiders, providing essential proteins and nutrients.
Habitat
Bumblebee Hummingbirds inhabit diverse landscapes, including cloud forests, mountain meadows, and areas rich in blooming flora.
Their choice of habitat is closely tied to the availability of nectar-producing plants, a crucial resource for sustaining their high metabolism.
Range Map
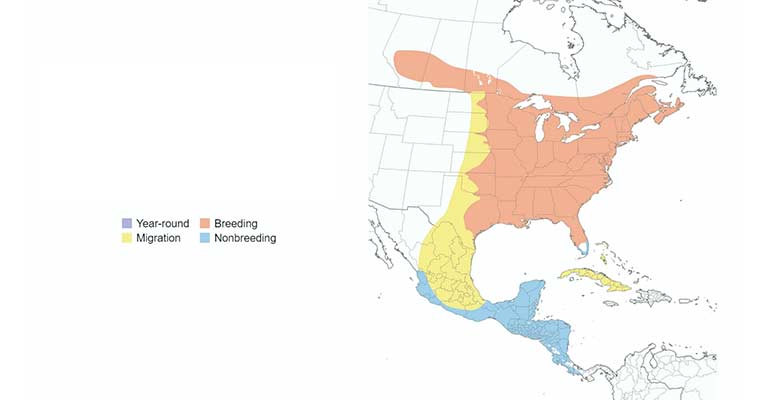
The species’ range spans from southern Mexico to western Panama, with specific populations found in the highlands of Nicaragua, Honduras, and Costa Rica.
A detailed range map aids researchers and conservationists in understanding the distribution of these birds and implementing targeted conservation efforts.
Nesting
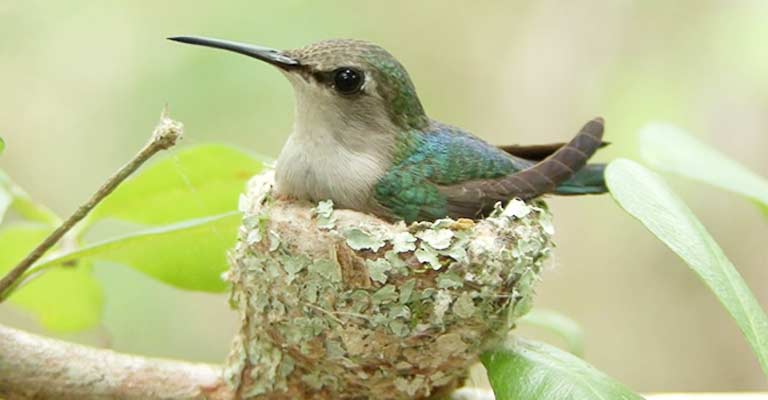

Bumblebee Hummingbirds construct intricate cup-shaped nests often adorned with lichens for camouflage.
Females meticulously select sheltered locations, such as the undersides of leaves, to safeguard their delicate nests from predators and the elements.
Here’s a table summarizing the nesting details of the Bumblebee Hummingbird:
| Nesting Details of Bumblebee Hummingbird | Facts |
| Clutch Size | Usually two eggs |
| Number of Broods | Typically one per breeding season |
| Egg Length | Approximately 1.0 cm (0.4 inches) |
| Egg Width | Around 0.6 cm (0.2 inches) |
| Incubation Period | 16-18 days |
| Nestling Period | Approximately 20-22 days |
| Egg Description | White, tiny, and elliptical |
| Nest Type | Cup-shaped, made of plant fibers, moss, and lichens |
| Nest Placement | Undersides of leaves, often sheltered locations |
| Parental Care | Female responsible for incubation; both parents feed and care for nestlings |
These details offer insights into the reproductive behaviors and adaptations of the Bumblebee Hummingbird during the nesting phase.
The small clutch size and meticulous nest construction highlight the species’ strategy to balance reproductive success with the challenges of its environment.
Breeding
Breeding behaviors of the Bumblebee Hummingbird are characterized by elaborate courtship displays. Males showcase their vibrant throat patches in aerial displays to attract females.
After mating, the female takes on the responsibility of incubating the tiny eggs, usually two, for about 16-18 days.
Diseases
While hummingbirds, including the Bumblebee Hummingbird, are relatively resilient, they can be susceptible to diseases such as avian pox and fungal infections.
These diseases may impact their overall health and reproductive success, underscoring the importance of monitoring and conservation efforts.
Treatment
Addressing diseases in Bumblebee Hummingbirds involves a multi-faceted approach.
Monitoring for signs of illness, providing a clean and disease-free environment, and, when necessary, administering veterinary care are essential components of ensuring the well-being of these delicate creatures.
Conservation

The conservation status of the Bumblebee Hummingbird highlights the need for concerted efforts to protect their habitats and mitigate threats such as deforestation and climate change.
Conservation initiatives should focus on preserving the diverse ecosystems they inhabit and promoting sustainable practices that benefit both the hummingbirds and the surrounding environment.
The life history of the Bumblebee Hummingbird is a testament to nature’s intricate design and the delicate balance necessary for the survival of these extraordinary birds.
Understanding and appreciating their unique characteristics and the challenges they face is crucial for effective conservation and the continued enjoyment of their presence in the wild.
10 Fun Facts About Bumblebee Hummingbird
The Bumblebee Hummingbird, Selasphorus heloisa, holds the enchanting distinction of being the world’s smallest bird, and its diminutive size is just one facet of its fascinating nature.
Here are 10 fun facts about this extraordinary hummingbird:
- Miniature Marvel: Weighing in at just about two grams, the Bumblebee Hummingbird is a feather-light wonder, resembling the size of a large bumblebee. Its petite frame adds to the allure of spotting this tiny creature in its natural habitat.
- Vibrant Plumage: Despite its small size, the Bumblebee Hummingbird boasts stunning and iridescent plumage. Males dazzle with a mix of greens, blues, and fiery red or orange throat patches, while females exhibit more subdued, yet equally beautiful, colorations.
- Aerial Acrobatics: These tiny birds are skilled aerial acrobats. With wing beats that can exceed 80 per second, they can hover in mid-air with remarkable precision while feeding on nectar from flowers.
- Migratory Marvels: Bumblebee Hummingbirds are migratory wonders, traveling vast distances between their breeding grounds in Central and South America and their wintering areas. Their migratory journeys showcase their endurance and navigational prowess.
- Courtship Displays: During the breeding season, male Bumblebee Hummingbirds engage in elaborate courtship displays to attract females. These displays involve intricate aerial maneuvers and the flamboyant flaunting of their iridescent throat patches.
- Nest Construction: Despite their size, Bumblebee Hummingbirds construct intricate cup-shaped nests adorned with lichens for camouflage. These nests are often placed on the undersides of leaves, providing shelter and protection.
- Rapid Metabolism: To sustain their energy-intensive lifestyles, Bumblebee Hummingbirds have incredibly fast metabolisms. They feed multiple times their body weight in nectar each day, a feat necessary to fuel their constant activity.
- High-Pitched Vocalizations: While not as loud as some other bird species, Bumblebee Hummingbirds emit high-pitched, insect-like vocalizations. These subtle sounds play a role in communication and can be an indicator of their presence.
- Tongue Structure: Bumblebee Hummingbirds have specialized tongues with brush-like tips, allowing them to lap up nectar from deep within flowers. This adaptation enhances their efficiency in extracting nectar during feeding.
- Conservation Concerns: Despite their remarkable adaptability, Bumblebee Hummingbirds face conservation challenges due to habitat loss and climate change. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring the continued survival and well-being of this extraordinary species.
The Bumblebee Hummingbird, with its petite size and vibrant personality, is a testament to the wonders of the avian world.
Observing these tiny creatures in action provides a glimpse into the intricate and remarkable life of one of nature’s smallest marvels.
Wrapping Up
In the intricate tapestry of the avian world, the Bumblebee Hummingbird emerges as a tiny yet vibrant masterpiece.
Its diminutive size, aerial prowess, migratory feats, and captivating courtship displays paint a portrait of resilience and beauty.
From the delicate construction of cup-shaped nests to the rapid flutter of iridescent wings, each facet of the Bumblebee Hummingbird’s life tells a story of adaptation and survival.
As we delve into the nuances of their nesting habits, feeding behaviors, and conservation challenges, we gain a deeper appreciation for these miniature marvels.
Ensuring the preservation of their habitats becomes not just a conservation effort but a commitment to safeguarding the delicate balance of nature. Thank you for your time.