The Green-Breasted Mango (Anthracothorax prevostii) emerges as a living kaleidoscope in the avian realm, captivating observers with its resplendent plumage and enchanting presence.
Found in the tropical and subtropical lowland forests of southern Mexico through Central America to western Panama, this hummingbird species stands out for its vibrant green and blue iridescence.
The male’s striking colors, coupled with intricate aerial displays, play a pivotal role in courtship rituals, adding a layer of fascination to its behavior.
Not confined to the depths of the forest, the Green-Breasted Mango adapts to human-altered landscapes, gracing gardens and plantations.
As agile flyers and expert foragers, these hummingbirds contribute to pollination and the delicate balance of their ecosystems.
Delving into the world of the Green-Breasted Mango unveils a story of beauty, adaptability, and ecological importance in the tapestry of nature.
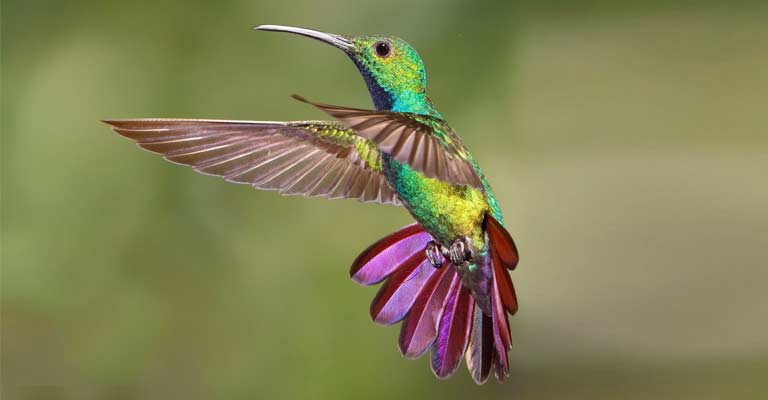

Identifying Characteristics of Green-Breasted Mango
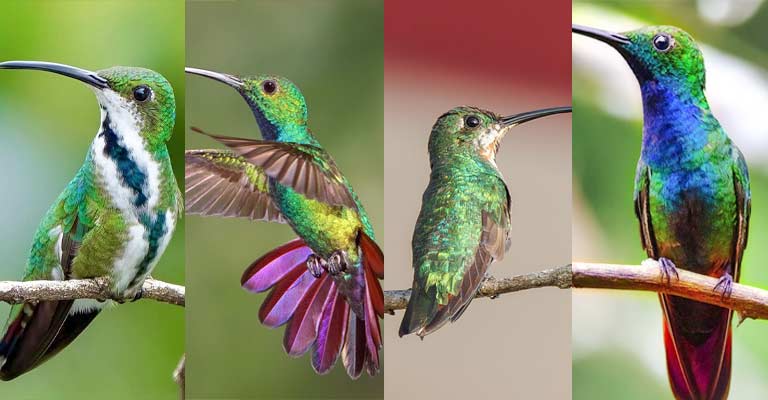
The Green-breasted Mango (Anthracothorax prevostii), a dazzling and distinctive hummingbird, is renowned for its vibrant plumage and agile flight.
Identifying this specific bird involves keen observation of various physical characteristics and behaviors unique to the species.
Plumage
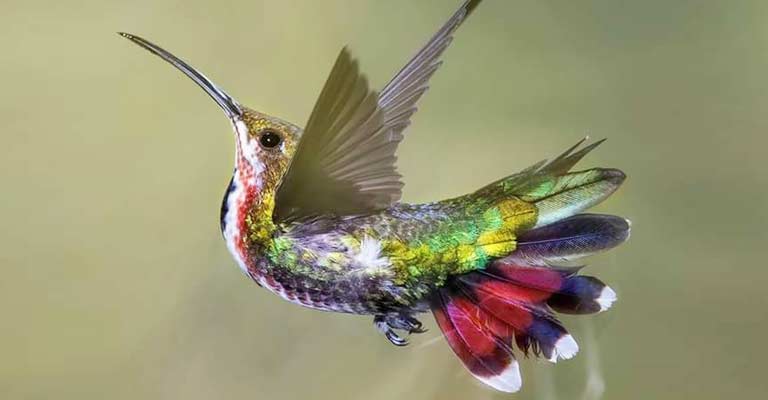

The most striking feature of the Green-breasted Mango is its iridescent plumage. Males exhibit a brilliant green coloration on their upperparts and a contrasting metallic blue or violet on their throats.
The green extends to the breast and abdomen, forming a striking contrast with the white undertail coverts. The female, on the other hand, lacks vivid iridescence, featuring more subdued colors, such as green and gray-brown, with a white ventral area.
Size and Shape
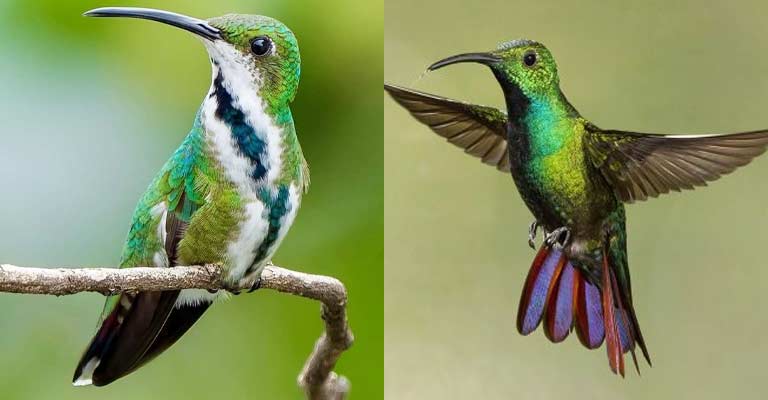

Green-breasted Mango hummingbirds are of moderate size, measuring approximately 4 to 4.5 inches (10-11 cm) in length. Their bodies are compact and streamlined, typical of hummingbirds, allowing for swift and agile flight.
The long, slender bill is adapted for extracting nectar from flowers, a primary component of their diet.
Tail
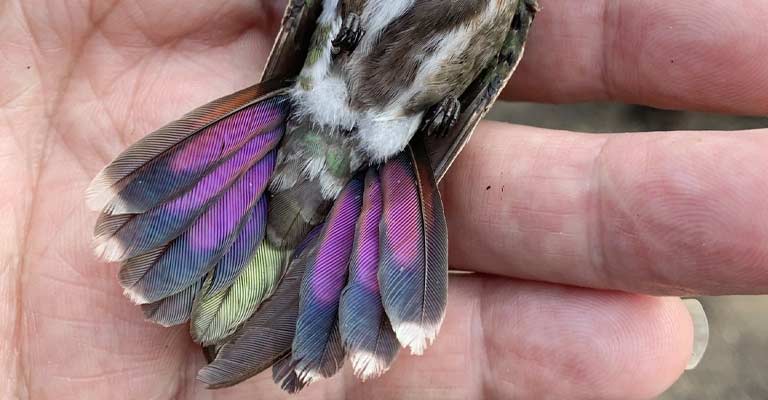

The tail of the Green-breasted Mango is deeply forked, a distinguishing characteristic that aids in its precise and maneuverable flight.
The outer tail feathers may have white tips, contributing to the overall elegance of its appearance.
Flight Pattern
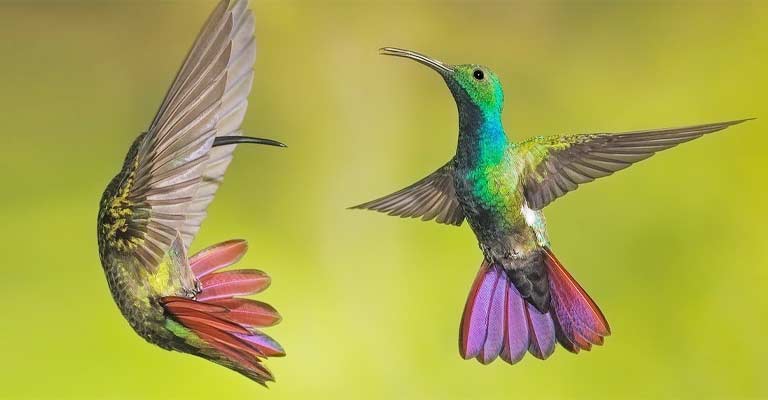

These hummingbirds are known for their acrobatic flight patterns, capable of hovering in mid-air and rapid aerial maneuvers.
Their wings beat rapidly, creating a distinct humming sound. Observing this distinctive flight behavior can be a key factor in identifying the Green-breasted Mango.
Habitat and Range
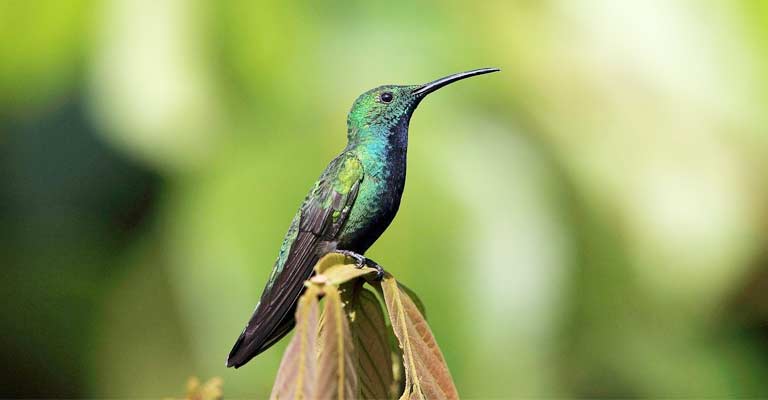

Understanding the habitat preferences and geographical range of the Green-breasted Mango is crucial for identification.
They are commonly found in tropical and subtropical lowland forests, gardens, and plantations. Their range extends from southern Mexico through Central America to western Panama.
Vocalization

While not as vocal as some other bird species, Green-breasted Mango hummingbirds do produce faint chirping or buzzing sounds during flight.
Familiarizing oneself with their soft vocalizations can aid in their identification, especially in dense foliage where visual cues may be limited.
Seasonal Migration
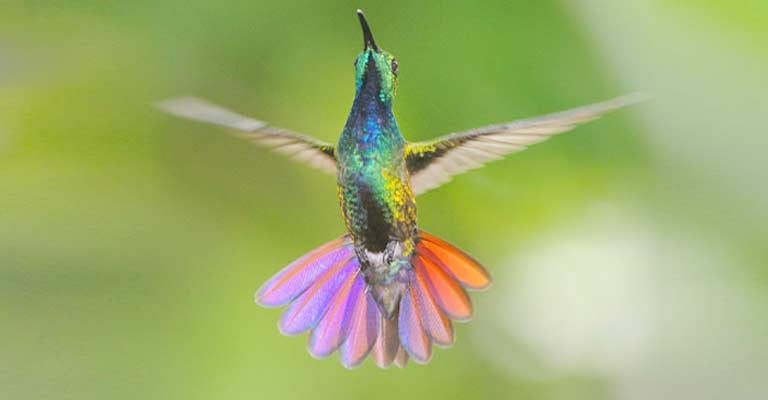

In some regions, Green-breasted Mango hummingbirds may exhibit seasonal migration patterns, moving to more suitable climates for breeding or feeding.
Understanding these migration patterns can contribute to accurate identification during specific times of the year.
Identifying the Green-breasted Mango involves a holistic approach, considering a combination of physical characteristics, behaviors, and habitat preferences.
A patient and attentive observer armed with knowledge of these key features will be well-equipped to distinguish this captivating hummingbird from its avian counterparts in the vibrant landscapes it calls home.
Taxonomy of Green-Breasted Mango

Here’s a table outlining the taxonomy details of the Green-Breasted Mango (Anthracothorax prevostii):
| Taxonomic Level | Classification |
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Clade | Strisores |
| Order | Apodiformes |
| Family | Trochilidae |
| Genus | Anthracothorax |
| Species | A. prevostii |
This taxonomy table outlines the hierarchical classification of the Green-Breasted Mango, from the broad domain level down to the specific species.
Each level provides insights into the bird’s evolutionary relationships and its place in the overall scheme of biological diversity.
The Green-Breasted Mango (Anthracothorax prevostii) belongs to the Animalia kingdom within the Chordata phylum. As a member of the Aves class, it falls under the Strisores clade and the Apodiformes order.
The bird is further classified in the Trochilidae family, commonly known as hummingbirds. The genus Anthracothorax encompasses various hummingbird species, with A. prevostii specifically denoting the Green-Breasted Mango.
This taxonomy reflects the evolutionary relationships of the species, highlighting its place in the diverse and fascinating world of avian life.
Green-Breasted Mango Life History
The Green-breasted Mango (Anthracothorax prevostii) stands as a testament to nature’s artistry, with its resplendent plumage and agile flight.
Delving into the life history of this charismatic hummingbird reveals a fascinating tapestry of behaviors, adaptations, and challenges that define its existence.
Food

Central to the Green-breasted Mango’s life is its diet, predominantly consisting of nectar from a variety of flowering plants. Using their specialized bills and long, extendable, tube-like tongues, they extract nectar with remarkable precision.
In addition to nectar, they also consume small insects and spiders, providing essential proteins and nutrients to supplement their energy requirements.
Habitat
These enchanting hummingbirds are inhabitants of tropical and subtropical lowland forests, where an abundance of flowering plants offers a ready source of nectar.
They also adapt to human-altered environments, often frequenting gardens, plantations, and areas with a profusion of blooming flora.
Range Map
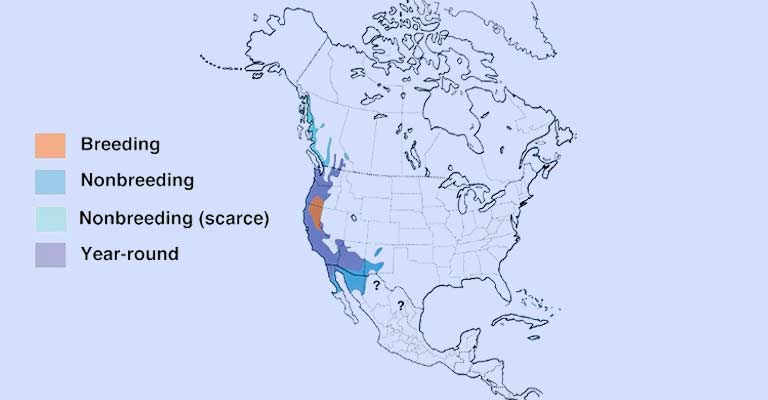
The Green-breasted Mango’s range spans from southern Mexico through Central America to western Panama.
Consulting a range map is invaluable for understanding their distribution, migration patterns, and local variations in habitat suitability.
Nesting
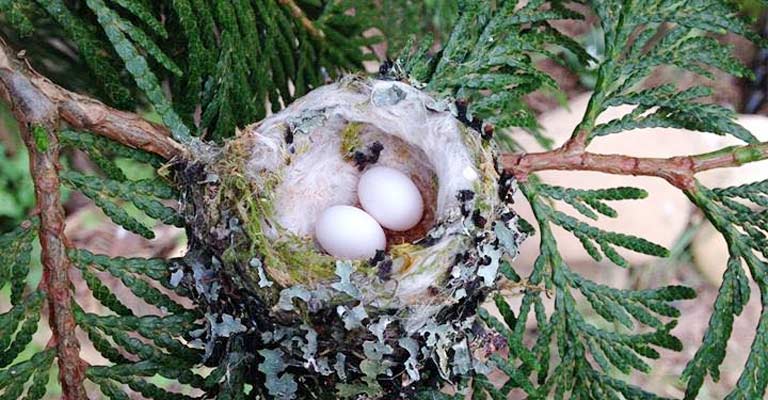

Green-breasted Mango hummingbirds are meticulous nest builders. Constructed with plant fibers, moss, and spider silk, their nests are often well-hidden in dense vegetation.
The female typically lays two eggs, and the incubation period lasts about two weeks. Nest location and construction are integral aspects of their life history, contributing to the survival of their offspring.
Here’s a table summarizing nesting details of the Green-Breasted Mango (Anthracothorax prevostii):
| Nesting Details | Green-Breasted Mango Facts |
| Clutch Size | Typically 2 eggs |
| Number of Broods | Often raises one brood per season |
| Egg Length | Approximately 1 cm (0.4 inches) |
| Egg Width | Around 0.6 cm (0.24 inches) |
| Incubation Period | About 14 to 17 days |
| Nestling Period | Approximately 20 days |
| Egg Description | Small, white or slightly off-white, |
| elliptical shape | |
| Nest Construction | Woven with plant fibers, moss, and |
| spider silk | |
| Nest Location | Hidden in dense vegetation |
| Parental Involvement | Both male and female contribute to nest building and care |
Breeding
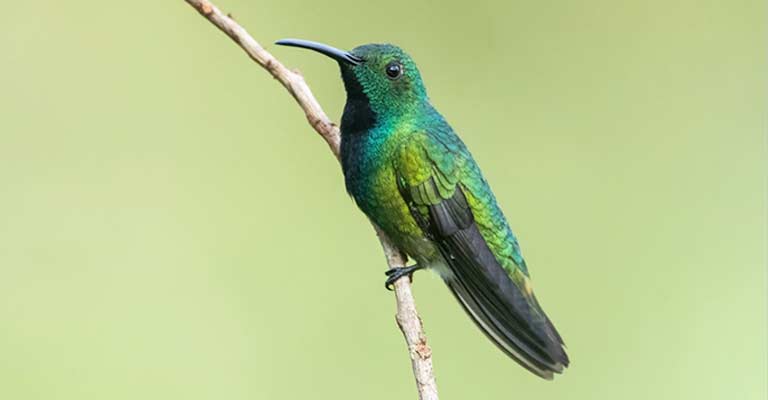

Breeding behaviors are characterized by elaborate courtship displays, with males showcasing their vibrant plumage and engaging in aerial acrobatics to attract females.
The male’s iridescent green and blue colors play a pivotal role in this courtship, serving as a visual indicator of health and genetic fitness.
Diseases
Hummingbirds, including the Green-breasted Mango, are susceptible to various diseases, including fungal infections and parasites.
Common ailments may include aspergillosis and mites. Monitoring for signs of illness, such as lethargy or abnormal behaviors, is crucial for their overall health.
Treatment
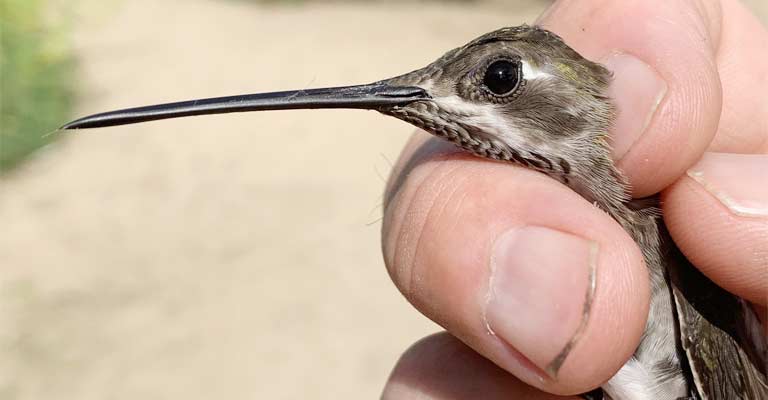

In cases of disease or parasitic infestations, prompt and appropriate treatment is essential. Veterinary care may include antifungal medications, antibiotics, or other specific treatments depending on the diagnosed ailment.
Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment around feeders is also crucial in preventing the spread of diseases.
Conservation
Despite their adaptability, Green-breasted Mango hummingbirds face threats from habitat loss due to deforestation, climate change, and human development.
Conservation efforts should focus on preserving their natural habitats, promoting sustainable land use practices, and raising awareness about the importance of protecting these remarkable birds.
Understanding the intricate life history of the Green-breasted Mango offers a glimpse into the delicate balance of nature and underscores the need for conservation initiatives to ensure the continued existence of this captivating species.
From foraging for nectar to engaging in elaborate courtship displays, each facet of their life contributes to the vibrant tapestry of biodiversity in the tropical regions they call home.
10 Fun Facts of Green-Breasted Mango
The Green-breasted Mango (Anthracothorax prevostii) is a fascinating hummingbird species with a range of captivating features. Here are some fun facts about this vibrant bird:
- Iridescent Beauty: The male Green-breasted Mango boasts a stunning display of iridescence, showcasing vibrant green and blue hues on its plumage. This visual spectacle is not only aesthetically pleasing but also serves as a key element in courtship displays to attract potential mates.
- Agile Flyers: Green-breasted Mangos are agile and adept flyers, capable of intricate aerial maneuvers. Their ability to hover in mid-air and swiftly change direction is not only a remarkable feat of aerodynamics but also a crucial skill for accessing nectar from flowers with precision.
- Forked Tail Elegance: One distinctive feature of the Green-breasted Mango is its deeply forked tail. The outer tail feathers may have white tips, adding an extra touch of elegance to its appearance. This tail structure enhances the bird’s maneuverability during flight.
- Tropical Dwellers: These hummingbirds are predominantly found in tropical and subtropical lowland forests. However, they are adaptable and can also thrive in human-altered environments such as gardens and plantations, where flowering plants provide an abundant source of nectar.
- Migratory Habits: In some regions, Green-breasted Mango hummingbirds exhibit seasonal migration, moving to different areas to find suitable climates for breeding or feeding. Observing their migration patterns adds another layer of intrigue to their life history.
- Tiny but Mighty: Despite their diminutive size, with a length of around 4 to 4.5 inches, Green-breasted Mangos are powerful and efficient foragers. Their high metabolism requires frequent feeding, and they can visit numerous flowers in a short period, sustaining themselves with nectar and small insects.
- Synchronized Nest Building: The construction of nests by Green-breasted Mango pairs is a synchronized effort. The female, with occasional assistance from the male, weaves intricate nests using plant fibers, moss, and spider silk. The concealed and well-crafted nests serve as protective homes for their eggs and chicks.
- Distinctive Vocalizations: While not as vociferous as some bird species, Green-breasted Mangos produce soft chirping or buzzing sounds during flight. These subtle vocalizations may serve as communication signals between individuals.
- Important Pollinators: Like other hummingbirds, Green-breasted Mangos play a crucial role in pollination. As they feed on nectar, their heads come into contact with the reproductive parts of flowers, facilitating the transfer of pollen and contributing to the reproduction of flowering plants.
- Conservation Concerns: Despite their adaptability, Green-breasted Mangos face threats from habitat loss due to deforestation and human development. Conservation efforts are crucial to preserving the habitats these hummingbirds rely on for survival.
The Green-breasted Mango’s life is a blend of beauty, adaptability, and ecological significance, making it a captivating subject for bird enthusiasts and nature lovers alike.
Wrapping Up
In the intricate tapestry of nature, the Green-breasted Mango emerges as a jewel, captivating with its iridescence, agility, and ecological importance.
From its vibrant plumage and agile flight to its synchronized nest-building and vital role as a pollinator, the life history of this hummingbird unfolds as a testament to the wonders of the avian world.
As we explore its habitat, behaviors, and conservation needs, we gain not just knowledge but a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance that sustains these remarkable creatures.
Preserving the habitats and addressing the challenges they face becomes not just a necessity but a shared responsibility to ensure the continued existence of this mesmerizing species.