The Puerto Rican Mango (Anthracothorax aurulentus), a jewel of the Caribbean avian realm, captures hearts with its vibrant plumage and unique ecological role.
Endemic to the lush landscapes of Puerto Rico, this hummingbird species stands as a testament to the island’s rich biodiversity.
With an iridescent mix of metallic green and gold, the male Puerto Rican Mango dazzles observers, particularly during courtship displays.
Its petite stature, measuring around 4 inches, belies its importance as a pollinator, showcasing agile hovering skills while foraging for nectar.
Beyond its aesthetic allure, the Puerto Rican Mango plays a vital role in the island’s ecosystems, contributing to the reproduction of flowering plants.
As conservation efforts intensify to safeguard its habitats, exploring the life history and distinctive features of the Puerto Rican Mango unveils a captivating story of adaptation and resilience in the Caribbean’s natural tapestry.
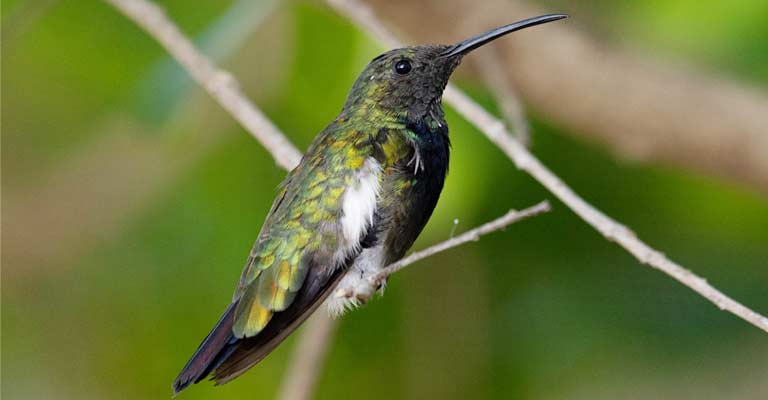

Identifying Characteristics of Puerto Rican Mango
The Puerto Rican Mango (Anthracothorax aurulentus) is a mesmerizing and distinctive bird native to the island of Puerto Rico. This species belongs to the family Trochilidae, commonly known as hummingbirds.
Renowned for its vibrant plumage and unique physical features, the Puerto Rican Mango is a captivating sight for birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts.
Size and Shape
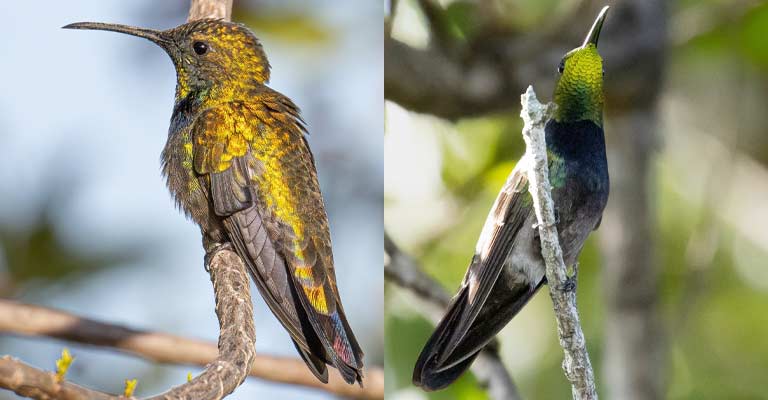

Measuring approximately 4 inches in length, the Puerto Rican Mango is a small-sized hummingbird. Its slender and streamlined body is well-adapted for swift and agile flight, a characteristic common among hummingbirds.
The bird’s long, pointed wings enable it to hover effortlessly and dart from flower to flower, showcasing its remarkable aerial abilities.
Distinctive Plumage
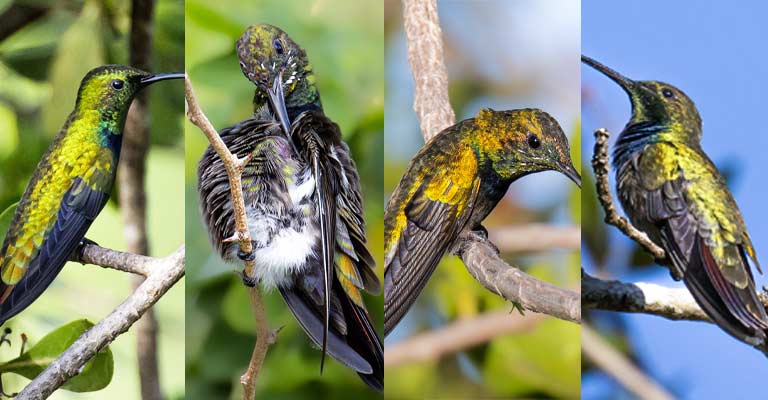
One of the most striking features of the Puerto Rican Mango is its iridescent plumage. Males exhibit a dazzling combination of metallic green and gold feathers on their upperparts, creating a radiant and captivating appearance.
The throat or gorget of the male is particularly noteworthy, showcasing brilliant iridescence that varies from turquoise to deep blue.
In contrast, females lack the vibrant colors of the male, displaying a more subdued palette of greens and browns.
Facial Characteristics
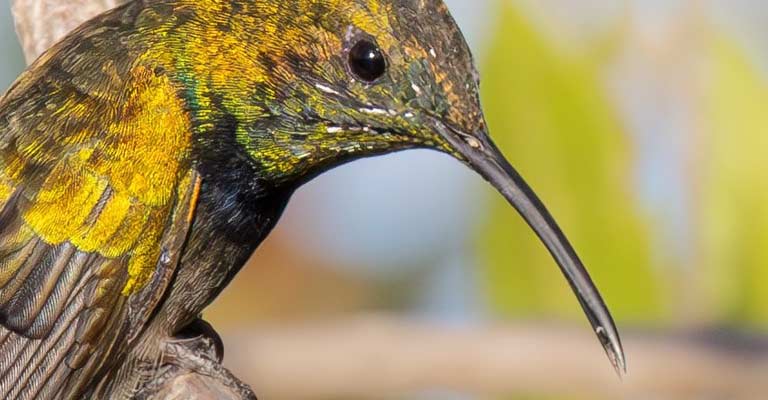

The bird’s head features a relatively short, straight bill that is adapted for sipping nectar from flowers.
The bill is dark and slender, aiding in precise feeding. The eyes are relatively large, positioned on the sides of the head, providing a wide field of view to detect predators and potential food sources.
Behavioral Traits
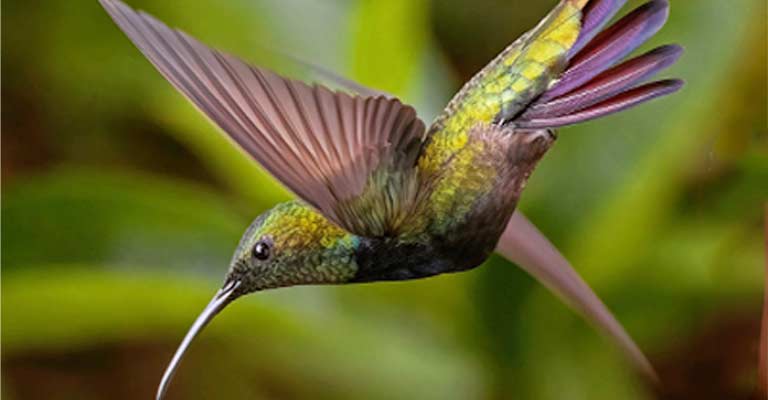

The Puerto Rican Mango is highly active, especially during the daylight hours when it forages for nectar from various flowering plants.
It is known for its territorial behavior, fiercely defending its feeding areas from other hummingbirds. The species is also characterized by its distinctive vocalizations, emitting a series of high-pitched chirps and buzzing sounds during flight.
Habitat and Range
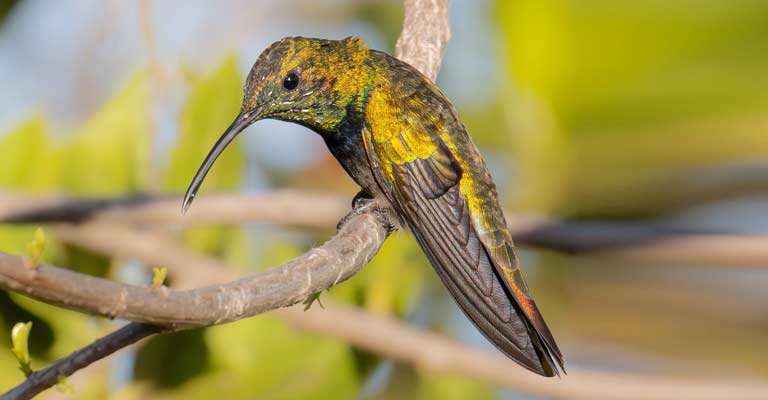

This hummingbird species is endemic to Puerto Rico, meaning it is found nowhere else in the world. Its preferred habitats include subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, where it can find an abundance of flowering plants for nectar.
The Puerto Rican Mango is often observed near forest edges, gardens, and areas with a profusion of blooming flowers.
Conservation Status
Despite its captivating presence, the Puerto Rican Mango faces conservation concerns due to habitat loss and environmental changes.
Efforts to protect and restore its natural habitats are crucial for ensuring the continued survival of this unique species.
The Puerto Rican Mango stands out not only for its vibrant plumage and distinctive physical characteristics but also for its role as an endemic species integral to the biodiversity of Puerto Rico.
Birdwatchers and conservationists alike value the opportunity to observe and protect this enchanting hummingbird in its natural habitat.
Taxonomy of Puerto Rican Mango

Here is a table outlining the taxonomy details of the Puerto Rican Mango (Anthracothorax aurulentus):
| Taxonomic Level | Classification |
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Aves |
| Clade | Strisores |
| Order | Apodiformes |
| Family | Trochilidae |
| Genus | Anthracothorax |
| Species | A. aurulentus |
This table provides a hierarchical overview of the bird’s taxonomy, ranging from the broad domain level to the specific species level.
The Puerto Rican Mango is classified within the Animalia kingdom, Aves class, and Trochilidae family, among other taxonomic ranks. The Puerto Rican Mango (Anthracothorax aurulentus) belongs to the Animalia kingdom, Chordata phylum, and Aves class.
It is classified under the Apodiformes order, specifically in the Trochilidae family, which encompasses hummingbirds. The genus of this bird is Anthracothorax, and its species name is aurulentus.
As a member of the Strisores clade, the Puerto Rican Mango showcases its unique position within the avian taxonomy, highlighting its evolutionary and ecological connections with other bird species in the diverse and captivating world of avifauna.
Puerto Rican Mango Life History
The life history of the Puerto Rican Mango (Anthracothorax aurulentus) is a fascinating journey, intricately woven with its unique adaptations and interactions within its environment.
From its feeding habits to nesting behaviors, the Puerto Rican Mango’s life history provides insights into the challenges it faces and the conservation efforts necessary to ensure its continued existence.
Food

The primary diet of the Puerto Rican Mango revolves around nectar extracted from various flowering plants.
Equipped with a specialized bill adapted for sipping nectar, this hummingbird is also known to consume small insects and spiders for protein.
Its efficient hovering capabilities allow it to access nectar from flowers that might be inaccessible to other birds.
Habitat
The Puerto Rican Mango is endemic to the island of Puerto Rico, making its home in subtropical or tropical moist montane forests.
These lush environments provide an abundance of flowering plants, crucial for the bird’s sustenance. Additionally, they are often found near forest edges, gardens, and areas with diverse flora.
Range Map
The range of the Puerto Rican Mango is limited to the island of Puerto Rico, and a detailed range map illustrates its distribution across different regions of the island.
Understanding its range is crucial for conservation efforts, helping researchers identify key habitats and implement protective measures.
Nesting
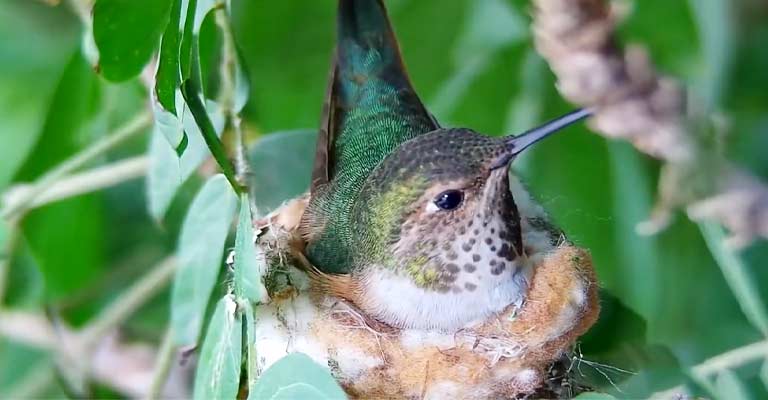

The hummingbird’s nesting behavior is a meticulous process. Females construct cup-shaped nests using plant fibers, spider silk, and other materials. These nests are often situated on the horizontal branches of trees.
The female lays two small white eggs, and after an incubation period, the chicks hatch and are cared for by the mother.
Here’s a table outlining the nesting details of the Puerto Rican Mango (Anthracothorax aurulentus):
| Nesting Details | Facts |
| Clutch Size | Usually 2 eggs |
| Number of Broods | Typically 1 per breeding season |
| Egg Length | Approximately 1.0 to 1.2 cm |
| Egg Width | Around 0.6 to 0.7 cm |
| Incubation Period | Approximately 15 to 18 days |
| Nestling Period | About 21 to 25 days |
| Egg Description | Small, white, and elliptical |
| Nest Construction | Cup-shaped, made of plant fibers, spider silk, and other materials. Placed on horizontal branches of trees. |
Breeding
Breeding activities are influenced by seasonal changes and the availability of resources.
Males engage in elaborate courtship displays, showcasing their vibrant plumage and performing aerial maneuvers to attract females. Successful courtship leads to the formation of monogamous pairs during the breeding season.
Diseases
Like many avian species, the Puerto Rican Mango is susceptible to various diseases. Common threats include parasites, fungal infections, and viral illnesses.
Monitoring and understanding disease dynamics are essential for wildlife health management.
Treatment
Efforts to combat diseases among Puerto Rican Mango populations involve a combination of research, monitoring, and intervention strategies.
Veterinarians and conservationists may implement measures such as habitat restoration, disease surveillance, and targeted medical interventions to mitigate health risks.
Conservation
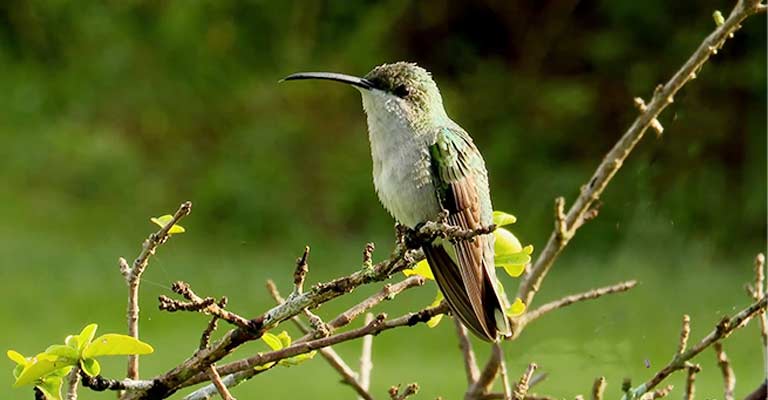

The conservation status of the Puerto Rican Mango is a matter of concern due to habitat loss, climate change, and other anthropogenic factors.
Conservation initiatives focus on preserving and restoring its natural habitat, raising awareness, and implementing protective measures to safeguard this endemic species.
Engaging local communities and policymakers is vital for the success of these conservation efforts.
The life history of the Puerto Rican Mango is a testament to the delicate balance between its ecological requirements and the challenges it faces in the ever-changing environment.
Efforts to understand and protect this unique hummingbird contribute not only to its survival but also to the overall biodiversity and health of Puerto Rico’s ecosystems.
10 Fun Facts about Puerto Rican Mango
The Puerto Rican Mango (Anthracothorax aurulentus) is a captivating bird with unique features and behaviors. Here are some fun facts about this charming hummingbird:
- Endemic Marvel: The Puerto Rican Mango is exclusive to the island of Puerto Rico, making it an endemic species. This means it is not found anywhere else in the world, adding to its significance and making it a point of pride for Puerto Rican biodiversity.
- Radiant Plumage: Male Puerto Rican Mangos boast an impressive display of iridescent plumage, showcasing a vibrant mix of metallic green and gold. The throat or gorget of the male can shimmer with brilliant iridescence, ranging from turquoise to deep blue, creating a dazzling spectacle during courtship displays.
- Expert Hoverer: Like all hummingbirds, the Puerto Rican Mango is an exceptional hoverer. Its ability to suspend itself mid-air allows it to access nectar from flowers with precision. The swift and agile flight of this bird is a testament to its remarkable aerial skills.
- Territorial Guardians: Puerto Rican Mangos are known for their territorial behavior. They fiercely defend their feeding areas from other hummingbirds, engaging in aerial chases and displays to establish dominance. This territoriality is vital for ensuring a steady supply of nectar-rich resources.
- Tiny Titans: Measuring around 4 inches in length, the Puerto Rican Mango is a petite hummingbird. Despite its small size, it plays a crucial role in pollination as it visits flowers in search of nectar, inadvertently transferring pollen and contributing to the reproduction of plant species.
- Island Adaptations: The species has adapted to the specific environmental conditions of Puerto Rico. Its presence in subtropical or tropical moist montane forests reflects its ability to thrive in diverse habitats, emphasizing its ecological flexibility.
- Monogamous Mates: During the breeding season, Puerto Rican Mangos form monogamous pairs. Male birds engage in intricate courtship displays to attract females. Once paired, they collaborate in nest-building and caring for the offspring, showcasing a cooperative and devoted breeding partnership.
- Distinctive Vocalizations: The Puerto Rican Mango communicates through a series of high-pitched chirps and buzzing sounds. These vocalizations serve various purposes, including territorial announcements, courtship signals, and general communication among individuals.
- Conservation Concerns: Despite its captivating presence, the Puerto Rican Mango faces conservation challenges due to habitat loss and environmental changes. Conservation efforts are underway to protect and restore its natural habitats, emphasizing the importance of preserving Puerto Rico’s unique biodiversity.
- Economic and Ecological Value: Beyond their aesthetic appeal, hummingbirds like the Puerto Rican Mango play a crucial role in ecosystems by aiding in pollination.
These fun facts showcase the fascinating aspects of the Puerto Rican Mango, from its dazzling appearance to its ecological significance, making it a species of great interest and importance in the natural world.
Wrapping Up
The Puerto Rican Mango (Anthracothorax aurulentus) stands as a symbol of biodiversity and endemism in Puerto Rico.
From its radiant plumage and territorial behaviors to its unique nesting habits, this hummingbird reveals a captivating life history.
Conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring the survival of this species, emphasizing the delicate balance between its ecological requirements and the challenges it faces in its native habitat.
Understanding and appreciating the Puerto Rican Mango contributes not only to the preservation of a remarkable bird but also to the overall health and diversity of Puerto Rico’s ecosystems.