The captivating world of biology is a tapestry woven with intricate threads of evolutionary history. One such captivating connection lies in the relationship between birds and reptiles.
At first glance, the idea that birds are descendants of reptiles might seem counterintuitive, but delving into the depths of paleontology and comparative anatomy reveals a fascinating tale of shared ancestry and adaptation.
Understanding why are birds reptiles offers a glimpse into the dynamic process of evolution that has shaped the diversity of life on our planet.
Why Are Birds Reptiles? [9 Popular Reasons]
Birds are reptiles, but not in the way you might think. Birds are not reptiles in the sense that they have scales, lay hard-shelled eggs, or are cold-blooded.
Birds are reptiles in the sense that they share a common ancestry with reptiles and are more closely related to some reptiles than others.
Here are nine popular reasons why birds are reptiles:
Birds Evolved From Dinosaurs
Birds are the living descendants of a group of feathered dinosaurs called theropods, which include famous species such as Tyrannosaurus rex and Velociraptor.
Birds are not just closely related to dinosaurs, they are actually dinosaurs themselves!
This is why birds have many features that are similar to dinosaurs, such as hollow bones, three-toed feet, and wishbones.
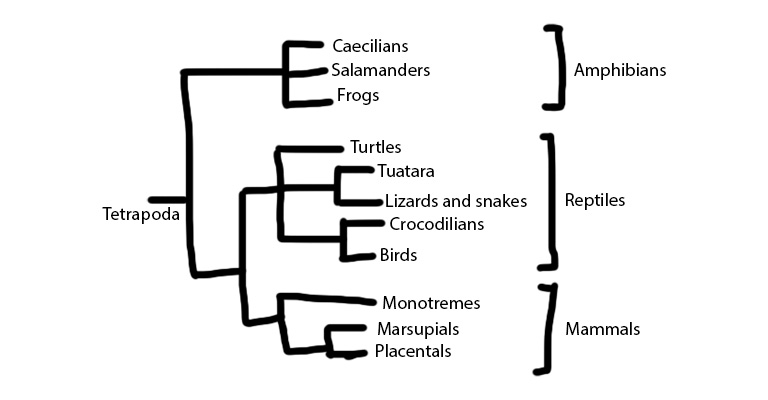
Birds Are Part Of The Group Diapsida
Diapsida is a group of animals that have two openings in their skulls behind their eyes. Diapsida includes all living reptiles (crocodilians, turtles, tuataras, and squamates) and birds.
Birds belong to a subgroup of Diapsida called Archosauria, which also includes crocodilians and extinct dinosaurs.
Birds And Crocodilians Share A Common Ancestor
Birds and crocodilians are the only living members of Archosauria, and they share a common ancestor that lived about 250 million years ago.
This ancestor was a reptile-like animal that gave rise to many diverse groups of animals, such as pterosaurs (flying reptiles), marine reptiles, and dinosaurs. Birds and crocodilians are more closely related to each other than to any other living reptile.
Birds And Reptiles Have Similar DNA
DNA is the molecule that carries the genetic information of living organisms. By comparing the DNA sequences of different organisms, scientists can estimate how closely related they are.
Studies have shown that birds and reptiles have more similar DNA than birds and mammals.
For example, birds and crocodilians share about 80% of their DNA, while birds and humans share about 60%.
Birds And Reptiles Have Similar Embryos
Embryos are the early stages of development of animals before they hatch or are born. By observing the embryos of different animals, scientists can identify similarities and differences that reveal their evolutionary history.
Embryos of birds and reptiles show many similarities, such as having gill slits, a long tail, and claws on their fingers.
These features indicate that birds and reptiles share a common ancestor that had these traits.
Birds And Reptiles Have Similar Anatomy
Anatomy is the study of the structure and function of the body parts of animals. By comparing the anatomy of different animals, scientists can infer how they are adapted to their environment and lifestyle.
The anatomy of birds and reptiles show many similarities, such as having a single ear bone, a four-chambered heart, and a cloaca (a single opening for excretion and reproduction).
These features indicate that birds and reptiles have inherited these traits from their common ancestor.
Birds And Reptiles Have Similar Physiology
Physiology is the study of the processes and activities that occur within the body of animals. By measuring the physiology of different animals, scientists can understand how they function and survive in their environment.
The physiology of birds and reptiles shows some similarities, such as having uric acid as their main waste product, having nucleated red blood cells, and having a high metabolic rate.
These features indicate that birds and reptiles have evolved some similar adaptations to cope with their environment.
Birds And Reptiles Have Similar Behavior
Behavior is the study of the actions and reactions of animals in response to their environment and other animals.
By observing the behavior of different animals, scientists can learn about their social interactions, communication, learning abilities, and intelligence. The behavior of birds and reptiles shows some similarities, such as territorial displays, vocalizations, parental care, and social learning.
These features indicate that birds and reptiles have developed some similar strategies to survive and reproduce in their environment.
Birds And Reptiles Have Similar Ecology
Ecology is the study of the relationships between animals and their environment. By analyzing the ecology of different animals, scientists can discover how they affect and are affected by their habitat, food sources, predators, competitors, parasites, and diseases.
The ecology of birds and reptiles show some similarities, such as occupying diverse habitats (from deserts to oceans), having varied diets (from plants to animals), facing threats from human activities (such as habitat loss, hunting, and pollution), and being important for ecosystem services (such as pollination, seed dispersal, and pest control).
These features indicate that birds and reptiles have adapted to and influenced their environment in similar ways.
What Are Some Common Bird Species That Evolved From Dinosaurs?
Some common bird species that evolved from dinosaurs are:
Chickens
Chickens are domesticated birds that belong to the order Galliformes, which also includes turkeys, quails, and pheasants.
Chickens are descended from a group of theropod dinosaurs called coelurosaurs, which also gave rise to tyrannosaurs, oviraptorosaurs, and dromaeosaurs.
Chickens have many features that are similar to their dinosaur ancestors, such as a wishbone, a three-toed foot, and a cloaca.
Eagles
Eagles are large birds of prey that belong to the order Accipitriformes, which also includes hawks, vultures, and ospreys.
Eagles are descended from a group of theropod dinosaurs called paravians, which also gave rise to Archaeopteryx, the first known bird.
Eagles have many features that are similar to their dinosaur ancestors, such as feathers, a four-chambered heart, and a single-ear bone.
Penguins
Penguins are flightless aquatic birds that belong to the order Sphenisciformes, which includes 18 living species.
Penguins are descended from a group of theropod dinosaurs called maniraptorans, which also gave rise to dromaeosaurs, troodontids, and birds.
Penguins have many features that are similar to their dinosaur ancestors, such as a keeled sternum, a pygostyle (a fused tailbone), and nucleated red blood cells.
These are just some examples of common bird species that evolved from dinosaurs.
There are many more bird species that share a common ancestry with dinosaurs, and they exhibit a remarkable diversity of forms and functions.
FAQ
Yes, birds are considered a type of reptile. They belong to a subgroup of reptiles known as archosaurs, which also include dinosaurs and crocodiles.
Birds share common ancestry with certain dinosaurs, and their evolutionary lineage can be traced back to reptilian ancestors.
The evidence lies in comparative anatomy, genetics, and paleontology. Birds share several characteristics with reptiles, such as scales on their legs, the presence of a single middle-ear bone, and the structure of their eggshells.
Additionally, molecular studies and fossil discoveries support their reptilian lineage.
Birds are believed to have evolved from a group of two-legged, carnivorous dinosaurs known as theropods. Over Time, some theropod dinosaurs develop feathers, which initially served as insulation and later evolved for flight. These adaptations gradually led to the emergence of modern birds.
While birds share certain features with reptiles, they have distinct adaptations that differentiate them.
Feathers, the most distinctive bird trait, are unique to them and are used for flight, insulation, and display. Birds also have a high metabolic rate and a specialized respiratory system to support their energy-demanding activities.
Classification is based on shared evolutionary history and ancestry. While birds have evolved many distinct traits, they still possess key reptilian characteristics that link them to their common ancestors.
The classification highlights the fascinating story of how organisms have adapted and diversified over millions of years.
Conclusion
The journey from scaly reptiles to feathered aviators is a testament to the power of evolution’s creativity.
The classification of birds as descendants of reptiles is not merely a taxonomic label but a profound insight into the interconnectedness of life forms.
Through ages of gradual change and selective pressures, these once reptilian ancestors underwent transformative adaptations, ultimately giving rise to the breathtaking diversity of birds that grace our skies today.
The link between birds and reptiles is a reminder that the story of life is a continuum, each species a chapter in an ever-evolving narrative that spans millions of years.